Alg 1 - Ch 4.2 Graphing Linear Equations
... equation in which the variables appear in separate terms and neither variable contains an exponent other than 1. The solution to linear equations are ordered pairs which makes the equation true. The graph of an equation in x and y is the set of all points (x, y) that are solutions of the equation. ...
... equation in which the variables appear in separate terms and neither variable contains an exponent other than 1. The solution to linear equations are ordered pairs which makes the equation true. The graph of an equation in x and y is the set of all points (x, y) that are solutions of the equation. ...
a review sheet for the final exam
... Definition: Point-Slope Form of a Line An equation for a nonvertical line with slope m and that contains the point (x1, y1) is: y y1 m x x1 (Point-Slope Form of a Line) Quick Graphing of a line given the y-intercept and the slope: If you are told the y-intercept of a line and the slope of ...
... Definition: Point-Slope Form of a Line An equation for a nonvertical line with slope m and that contains the point (x1, y1) is: y y1 m x x1 (Point-Slope Form of a Line) Quick Graphing of a line given the y-intercept and the slope: If you are told the y-intercept of a line and the slope of ...
Thinking Mathematically - Marquette University High School
... Step 4: Solve for the remaining variable Step 5: Back-substitute this coordinate into Step 2 to find the other coordinate. (Or plug into any equation but step 2 is easiest!) ...
... Step 4: Solve for the remaining variable Step 5: Back-substitute this coordinate into Step 2 to find the other coordinate. (Or plug into any equation but step 2 is easiest!) ...
Big Ideas in Mathematics Chapter Three
... Parts of an algebraic expression are called terms. Like terms are terms that have the same variables raised to the same exponents. Constant terms are also like terms. To identify terms and like terms in an expression, first write the expression as a sum of its terms. ...
... Parts of an algebraic expression are called terms. Like terms are terms that have the same variables raised to the same exponents. Constant terms are also like terms. To identify terms and like terms in an expression, first write the expression as a sum of its terms. ...
3 Solving Equations
... problem, you will need both Algebra and Geometry. Very often, Geometry helps you to see the big picture while Algebra can help you work through nitty gritty details. If you want to understand your Calculus course, you will need to look at each problem through a geometric lens and an algebraic lens. ...
... problem, you will need both Algebra and Geometry. Very often, Geometry helps you to see the big picture while Algebra can help you work through nitty gritty details. If you want to understand your Calculus course, you will need to look at each problem through a geometric lens and an algebraic lens. ...
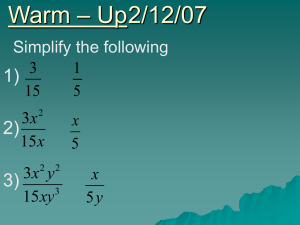
Simplifying Rational Expressions
... Let’s start with what’s a rational number – a number that can be written as the quotient of two integers. HUH? What does that mean? Here are a few examples of Rational Numbers: ½, ⅓, ¼, ¾ You mean they’re just fractions? YEP – that’s it - Rationals are fractions!! ...
... Let’s start with what’s a rational number – a number that can be written as the quotient of two integers. HUH? What does that mean? Here are a few examples of Rational Numbers: ½, ⅓, ¼, ¾ You mean they’re just fractions? YEP – that’s it - Rationals are fractions!! ...
durham public schools 2012-2013
... Properties (6.EE.3-4) Apply the properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. Identify when two expressions are equivalent (i.e. when the two expressions name the same number regardless of which is substituted into them). a. Introduce key vocabulary (word wall, flashcards, graphic org ...
... Properties (6.EE.3-4) Apply the properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. Identify when two expressions are equivalent (i.e. when the two expressions name the same number regardless of which is substituted into them). a. Introduce key vocabulary (word wall, flashcards, graphic org ...