Pedigrees and Autosomal Inheritance - Emery
... Pedigree – a chart that shows the genetic relationships between individuals in a family -using a pedigree chart and Mendelian genetics, you can determine whether the allele for a given trait is dominant, recessive, autosomal or sex-linked female – unaffected ...
... Pedigree – a chart that shows the genetic relationships between individuals in a family -using a pedigree chart and Mendelian genetics, you can determine whether the allele for a given trait is dominant, recessive, autosomal or sex-linked female – unaffected ...
Experimental matings: Df/wt x wt
... reproductive tract (often chambers called storage organs) for various periods of time between the start of sperm transfer and when sperm leave the reproductive tract (Bloch Qazi et al., 2003). This phenomenon is called female sperm storage. Females frequently mate repeatedly over the course of the ...
... reproductive tract (often chambers called storage organs) for various periods of time between the start of sperm transfer and when sperm leave the reproductive tract (Bloch Qazi et al., 2003). This phenomenon is called female sperm storage. Females frequently mate repeatedly over the course of the ...
Unit 7 Heredity PPT
... 1st LAW OF HEREDITY “Law of Segregation” = – The 2 alleles for each trait must separate when gametes (sperm/egg) are formed. -A parent passes on, at random, only one allele for each trait to each offspring A ...
... 1st LAW OF HEREDITY “Law of Segregation” = – The 2 alleles for each trait must separate when gametes (sperm/egg) are formed. -A parent passes on, at random, only one allele for each trait to each offspring A ...
chapter 14 mendel and the gene idea
... The inheritance of characters determined by a single gene deviates from simple Mendelian patterns when alleles are not completely dominant or recessive, when a gene has more than two alleles, or when a gene produces multiple phenotypes. We will consider each of these situations. ...
... The inheritance of characters determined by a single gene deviates from simple Mendelian patterns when alleles are not completely dominant or recessive, when a gene has more than two alleles, or when a gene produces multiple phenotypes. We will consider each of these situations. ...
Genes underlying altruism
... by workers, especially in taxa where the costs of producing ‘excess’ reproductives are relatively low [26]. Another possibility would be essentially the opposite: queen–worker, worker– worker and male–female conflicts over caste determination may maintain variation through ongoing genetically based ...
... by workers, especially in taxa where the costs of producing ‘excess’ reproductives are relatively low [26]. Another possibility would be essentially the opposite: queen–worker, worker– worker and male–female conflicts over caste determination may maintain variation through ongoing genetically based ...
PowerPoint Notes
... A. Mendel needed to answer one more question: When alleles are being segregated during gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determines if a pea plant is tall or dwarf have any ...
... A. Mendel needed to answer one more question: When alleles are being segregated during gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determines if a pea plant is tall or dwarf have any ...
Text (Open Access) - Reading`s CentAUR
... Uyenoyama & Feldman [17] showed that equilibria are possible for a variety of mating systems, [14] showed that stable polymorphisms may occur in the case of full sibs, and [15] showed that stable polymorphisms may occur if benefits are non-additive or there is genetically based discrimination agains ...
... Uyenoyama & Feldman [17] showed that equilibria are possible for a variety of mating systems, [14] showed that stable polymorphisms may occur in the case of full sibs, and [15] showed that stable polymorphisms may occur if benefits are non-additive or there is genetically based discrimination agains ...
Modes of Inheritance
... Genes are particulate and come in different forms known as alleles. Organisms (peas or humans!) have two copies of each gene but transmit only one to each offspring. Which one is transmitted is chosen at random. i.e. if you are heterozygous for two different alleles, the alleles will segregate from ...
... Genes are particulate and come in different forms known as alleles. Organisms (peas or humans!) have two copies of each gene but transmit only one to each offspring. Which one is transmitted is chosen at random. i.e. if you are heterozygous for two different alleles, the alleles will segregate from ...
a laymans walk through basic canine genetics and
... for non-black : brown or dark). Dominant black dogs (Kk or KK) are solid eumelanin (they can have white markings but will show no other colors). They cannot show red (tan) in their coat because this black color is dominant and the gene will just not allow any other color to be expressed (the eumelan ...
... for non-black : brown or dark). Dominant black dogs (Kk or KK) are solid eumelanin (they can have white markings but will show no other colors). They cannot show red (tan) in their coat because this black color is dominant and the gene will just not allow any other color to be expressed (the eumelan ...
Selection against Accumulating Mutations in Niche
... Our current understanding of sympatric speciation is that it occurs primarily through disruptive selection on ecological genes driven by competition, followed by reproductive isolation through reinforcement-like selection against inferior intermediates/heterozygotes. Our evolutionary model of select ...
... Our current understanding of sympatric speciation is that it occurs primarily through disruptive selection on ecological genes driven by competition, followed by reproductive isolation through reinforcement-like selection against inferior intermediates/heterozygotes. Our evolutionary model of select ...
Pedigree - Solon City Schools
... Dominant vs. Recessive • Is it a dominant pedigree or a recessive pedigree? • 1. If two affected people have an unaffected child, it must be a dominant pedigree: D is the dominant mutant allele and d is the recessive wild type allele. Both parents are Dd and the normal child is dd. • 2. If two unaf ...
... Dominant vs. Recessive • Is it a dominant pedigree or a recessive pedigree? • 1. If two affected people have an unaffected child, it must be a dominant pedigree: D is the dominant mutant allele and d is the recessive wild type allele. Both parents are Dd and the normal child is dd. • 2. If two unaf ...
handouts
... 95% of 4 is 4 gene convergence: 4 individuals must have same value for a gene location population convergence: 5 gene locations must be converged Example converged populations: Example 1: Example 2: Example 3: ...
... 95% of 4 is 4 gene convergence: 4 individuals must have same value for a gene location population convergence: 5 gene locations must be converged Example converged populations: Example 1: Example 2: Example 3: ...
Key area 2: Plant and animal breeding by manipulation of heredity
... This is due to the accumulation of homozygous recessive alleles which can be deleterious (harmful). This appears as a decline in vigour, size, fertility and yield of the plant or animal. ...
... This is due to the accumulation of homozygous recessive alleles which can be deleterious (harmful). This appears as a decline in vigour, size, fertility and yield of the plant or animal. ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems Mendelian Genetics and Extensions
... F2 will be ¾ tall (TT and Tt) and ¼ dwarf (tt) c. What will be the phenotypes and fractions if an F1 plant is crossed with its tall parent? This cross is now Tt × TT, so offspring are all tall but ½ TT and ½ Tt d. What will be the phenotypes and fractions if an F1 plant is crossed with its short par ...
... F2 will be ¾ tall (TT and Tt) and ¼ dwarf (tt) c. What will be the phenotypes and fractions if an F1 plant is crossed with its tall parent? This cross is now Tt × TT, so offspring are all tall but ½ TT and ½ Tt d. What will be the phenotypes and fractions if an F1 plant is crossed with its short par ...
1 - SMIC Biology
... (#?) chromosomes in every cell. Of these, pairs are autosomes. An autosome is any chromosome except the sex chromosomes. Each person has one pair of sex chromosomes. Females have 2 X chromosomes while males have ...
... (#?) chromosomes in every cell. Of these, pairs are autosomes. An autosome is any chromosome except the sex chromosomes. Each person has one pair of sex chromosomes. Females have 2 X chromosomes while males have ...
440selection - eweb.furman.edu
... 1. Measuring “fitness” – differential reproductive success a. The mean number of reproducing offspring (or females)/female b. Components of fitness - probability of female surviving to reproductive age - number of offspring the female produces - probability that offspring survive to reproductive age ...
... 1. Measuring “fitness” – differential reproductive success a. The mean number of reproducing offspring (or females)/female b. Components of fitness - probability of female surviving to reproductive age - number of offspring the female produces - probability that offspring survive to reproductive age ...
Genetics: the Breeder`s Blueprint
... In other words, a mating between a brindle dog and a brindle bitch, both of whom are homozygous for the brindle gene can produce nothing but brindle offspring all of whom are genotypically homozygous for brindle and all of whom are phenotypically brindle. A dog which is homozygous for such a trait, ...
... In other words, a mating between a brindle dog and a brindle bitch, both of whom are homozygous for the brindle gene can produce nothing but brindle offspring all of whom are genotypically homozygous for brindle and all of whom are phenotypically brindle. A dog which is homozygous for such a trait, ...
Unit 6 Heredity Chp 14 Mendelian Genetics Notes
... However, Mendel could also move pollen from one plant to another to crosspollinate plants. ...
... However, Mendel could also move pollen from one plant to another to crosspollinate plants. ...
Introduction - GEOCITIES.ws
... only to diverse organisms, but also to patterns of inheritance more complex than Mendel described. In fact, Mendel had the good fortune to choose a system that was relatively simple genetically. Each character (but one) is controlled by a single gene. Each gene has only two alleles, one of whi ...
... only to diverse organisms, but also to patterns of inheritance more complex than Mendel described. In fact, Mendel had the good fortune to choose a system that was relatively simple genetically. Each character (but one) is controlled by a single gene. Each gene has only two alleles, one of whi ...
Name: LAB 3 ANTH 2101 MENDELIAN TRAITS and INHERITANCE
... chromosomes. Each person’s genotype is PpEe and their phenotype is PTC tasting and free earlobes. To complete this Punnet square, you must first find every combination of alleles for each person. This would be what the gametes would carry at the end of meiosis. These combinations are listed at the t ...
... chromosomes. Each person’s genotype is PpEe and their phenotype is PTC tasting and free earlobes. To complete this Punnet square, you must first find every combination of alleles for each person. This would be what the gametes would carry at the end of meiosis. These combinations are listed at the t ...
Student Handout
... genetic material that controls a specific trait. Alleles are the different forms of a gene. For example, a short pea plant displays the "short" allele for stem height, while a tall pea plant displays the "tall" allele for stem height. An organism inherits one allele from each parent, so every gene i ...
... genetic material that controls a specific trait. Alleles are the different forms of a gene. For example, a short pea plant displays the "short" allele for stem height, while a tall pea plant displays the "tall" allele for stem height. An organism inherits one allele from each parent, so every gene i ...
Genotype Phenotype
... Gametes only carry one allele, so if an individual has the genotype Ww what are the possible gametes that this individual can pass on? Answer: either a W or a w but not both Another example: Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Gametes only carry one allele, so if an individual has the genotype Ww what are the possible gametes that this individual can pass on? Answer: either a W or a w but not both Another example: Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Laws of Inheritance
... of all possible random fertilization events and their expected frequencies. [link] shows a Punnett square for a cross between a plant with yellow peas and one with green peas. To prepare a Punnett square, all possible combinations of the parental alleles (the genotypes of the gametes) are listed alo ...
... of all possible random fertilization events and their expected frequencies. [link] shows a Punnett square for a cross between a plant with yellow peas and one with green peas. To prepare a Punnett square, all possible combinations of the parental alleles (the genotypes of the gametes) are listed alo ...
Genetic drift vs. natural selection in a long-term small
... at the dimer interface of αβ-heterodimers on heterozygous individuals. Identical transspecific DQB1 and DRB1 alleles were identified between P. sinus and its closest relative, the Burmeister’s porpoise (Phocoena spinipinnis). Comparison with studies on four island endemic mammals suggests fixation o ...
... at the dimer interface of αβ-heterodimers on heterozygous individuals. Identical transspecific DQB1 and DRB1 alleles were identified between P. sinus and its closest relative, the Burmeister’s porpoise (Phocoena spinipinnis). Comparison with studies on four island endemic mammals suggests fixation o ...
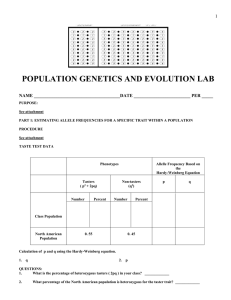
POPULATION GENETICS AND EVOLUTION LAB
... Number of offspring with AA ___ x 2 = ____ A alleles My initial genotype: _______ Number of offspring with Aa ___ x 1 = ____ A alleles F1 genotype: _______ Total = ____ A alleles F2 genotype: _______ p = _______ F3 genotype: _______ Number of a alleles present at the fifth generation F4 genotype: __ ...
... Number of offspring with AA ___ x 2 = ____ A alleles My initial genotype: _______ Number of offspring with Aa ___ x 1 = ____ A alleles F1 genotype: _______ Total = ____ A alleles F2 genotype: _______ p = _______ F3 genotype: _______ Number of a alleles present at the fifth generation F4 genotype: __ ...
Inbreeding avoidance

Inbreeding avoidance, or the inbreeding avoidance hypothesis, is a concept in evolutionary biology that refers to the prevention of the deleterious effects of inbreeding. The inbreeding avoidance hypothesis posits that certain mechanisms develop within a species, or within a given population of a species, as a result of natural and sexual selection in order to prevent breeding among related individuals in that species or population. Although inbreeding may impose certain evolutionary costs, inbreeding avoidance, which limits the number of potential mates for a given individual, can inflict opportunity costs. Therefore, a balance exists between inbreeding and inbreeding avoidance. This balance determines whether inbreeding mechanisms develop and the specific nature of said mechanisms.Inbreeding results in inbreeding depression, which is the reduction of fitness of a given population due to inbreeding. Inbreeding depression occurs via one of two mechanisms. The first mechanism involves the appearance of disadvantageous traits via the pairing of deleterious recessive alleles in a mating pair’s progeny. When two related individuals mate, the probability of deleterious recessive alleles pairing in the resulting offspring is higher as compared to when non-related individuals mate. The second mechanism relates to the increased fitness of heterozygotes. Many studies have demonstrated that homozygous individuals are often disadvantaged with respect to heterozygous individuals. For example, a study conducted on a population of South African cheetahs demonstrated that the lack of genetic variability among individuals in the population has resulted in negative consequences for individuals, such as a greater rate of juvenile mortality and spermatozoal abnormalities. When heterozygotes possess a fitness advantage relative to a homozygote, a population with a large number of homozygotes will have a relatively reduced fitness, thus leading to inbreeding depression. Through these described mechanisms, the effects of inbreeding depression are often severe enough to cause the evolution of inbreeding avoidance mechanisms.