Chapter 9
... Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
... Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
fluid transport mechanisms in microfluidic devices
... Electroosmosis refers to the bulk movement of an aqueous solution past a stationary solid surface, due to an externally applied electric field. Electroosmosis requires the existence of a charged double-layer at the solid-liquid interface. This charged double layer results from an attraction between ...
... Electroosmosis refers to the bulk movement of an aqueous solution past a stationary solid surface, due to an externally applied electric field. Electroosmosis requires the existence of a charged double-layer at the solid-liquid interface. This charged double layer results from an attraction between ...
Bin and Hopper Design
... gas pressure and solids stresses subject to changing bulk density and permeability. Fortunately, in many cases the rate will be limited by some type of discharge device such as a rotary valve or screw feeder. ...
... gas pressure and solids stresses subject to changing bulk density and permeability. Fortunately, in many cases the rate will be limited by some type of discharge device such as a rotary valve or screw feeder. ...
Lecture 14
... together by weak cohesive forces & by forces exerted by the walls of a container. Both liquids & gases are fluids ...
... together by weak cohesive forces & by forces exerted by the walls of a container. Both liquids & gases are fluids ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Conservation of Energy for Ideal Fluid Recall the standard work-energy relation W = K = Kf - Ki Apply the principle to a section of flowing fluid with volume V and mass m = V (here W is work done on fluid) ...
... Conservation of Energy for Ideal Fluid Recall the standard work-energy relation W = K = Kf - Ki Apply the principle to a section of flowing fluid with volume V and mass m = V (here W is work done on fluid) ...
School of Physics - The University of Sydney
... flow changes from laminar to turbulent will depend to some extent on the shape of the object. As a rough guide, however, we can also say in this case that the transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs around a value of 2000. With increasing Reynolds number, before the flow becomes fully turbu ...
... flow changes from laminar to turbulent will depend to some extent on the shape of the object. As a rough guide, however, we can also say in this case that the transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs around a value of 2000. With increasing Reynolds number, before the flow becomes fully turbu ...
final1-mc-298220-publishable-summary
... A microfluidic extensional flow device based on the principle of mutually bisecting channels (known as crossslots) was fabricated according to a computer-generated optimized design, see Fig. 1(a).1,2 A comprehensive set of experiments was carried out in order to characterize the device and confirm t ...
... A microfluidic extensional flow device based on the principle of mutually bisecting channels (known as crossslots) was fabricated according to a computer-generated optimized design, see Fig. 1(a).1,2 A comprehensive set of experiments was carried out in order to characterize the device and confirm t ...
Characterization of flow contributions to drag and lift of a circular
... A 2D numerical simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder is investigated during the onset of unsteadiness within the range of Reynolds numbers between 50 and 400. Using the recent formulation of Wu, Lu and Zhuang [J. Fluid Mech. 576, (2007)], the fluid force is successfully approximated by a ...
... A 2D numerical simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder is investigated during the onset of unsteadiness within the range of Reynolds numbers between 50 and 400. Using the recent formulation of Wu, Lu and Zhuang [J. Fluid Mech. 576, (2007)], the fluid force is successfully approximated by a ...
Viscous flow in pipe
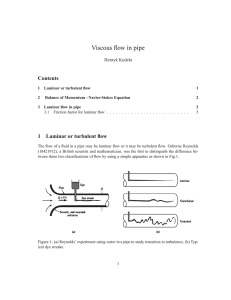
... ranges for which laminar, transitional, or turbulent pipe flows are obtained cannot be precisely given. The actual transition from laminar to turbulent flow may take place at various Reynolds numbers, depending on how much the flow is disturbed by vibrations of the pipe, roughness of the entrance re ...
... ranges for which laminar, transitional, or turbulent pipe flows are obtained cannot be precisely given. The actual transition from laminar to turbulent flow may take place at various Reynolds numbers, depending on how much the flow is disturbed by vibrations of the pipe, roughness of the entrance re ...
buoyant force
... • Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow • Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids Section 9.7 ...
... • Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow • Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids Section 9.7 ...
zero. Ans. (b) P4.8 When a valve is opened, fluid flows in the
... P4.23 A tank volume V contains gas at conditions ( o, po, To). At time t 0 it is punctured by a small hole of area A. According to the theory of Chap. 9, the mass flow out of such a hole is approximately proportional to A and to the tank pressure. If the tank temperature is assumed constant and the ...
... P4.23 A tank volume V contains gas at conditions ( o, po, To). At time t 0 it is punctured by a small hole of area A. According to the theory of Chap. 9, the mass flow out of such a hole is approximately proportional to A and to the tank pressure. If the tank temperature is assumed constant and the ...
Lift (force)

A fluid flowing past the surface of a body exerts a force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the surface force parallel to the flow direction. If the fluid is air, the force is called an aerodynamic force. In water, it is called a hydrodynamic force.