Download PDF
... separates from the edge of the flow restriction is more predictable and consistent. This separation of the fluid creates the low pressure zone on the downstream side of the restriction, thus allowing that restriction to function as the primary element of a DP meter. Depending on the type of restrict ...
... separates from the edge of the flow restriction is more predictable and consistent. This separation of the fluid creates the low pressure zone on the downstream side of the restriction, thus allowing that restriction to function as the primary element of a DP meter. Depending on the type of restrict ...
Chapter 6 - Equations of Motion and Energy in Cartesian... Equations of motion of a Newtonian fluid The Reynolds number
... parts. The left side or inertial and potential terms, which dominates for large NRe and the right side or viscous terms, which dominates for small NRe. The potential gradient term could have been on the right side if the dimensionless pressure was defined differently, i.e., normalized with respect t ...
... parts. The left side or inertial and potential terms, which dominates for large NRe and the right side or viscous terms, which dominates for small NRe. The potential gradient term could have been on the right side if the dimensionless pressure was defined differently, i.e., normalized with respect t ...
Coriolis Flowmeter
... by pushing down on the tube. On the opposite side, the liquid flowing out of the meter resists having its vertical motion decreased by pushing up on the tube. This action causes the tube to twist. When the tube is moving downward during the second half of the vibration cycle, it twists in the opposi ...
... by pushing down on the tube. On the opposite side, the liquid flowing out of the meter resists having its vertical motion decreased by pushing up on the tube. This action causes the tube to twist. When the tube is moving downward during the second half of the vibration cycle, it twists in the opposi ...
Velocity Profiles for Circular Sections and Flow in
... number is 708 when glycerine at 25°C flows with an average flow velocity of 3.6 m/s in a pipe having a 150mm inside diameter. Thus the flow is laminar. Compute points on the velocity profile from the pipe wall to the centerline of the pipe in increments of 15 mm. Plot the data for the local velocity ...
... number is 708 when glycerine at 25°C flows with an average flow velocity of 3.6 m/s in a pipe having a 150mm inside diameter. Thus the flow is laminar. Compute points on the velocity profile from the pipe wall to the centerline of the pipe in increments of 15 mm. Plot the data for the local velocity ...
Chapter 5 Pressure Variation in Flowing Fluids
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
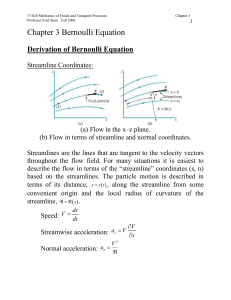
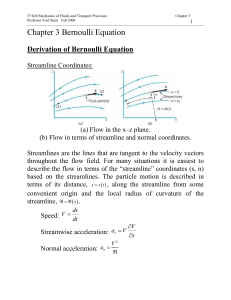
Chapter 3 Bernoulli Equation
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
Chapter 2: Pressure Distribution in a Fluid
... Since, by definition, a fluid cannot withstand a shear stress without moving, (deformation) a stationary fluid must necessarily be completely free of shear stress (σij=0, i ≠ j). The only stress is the normal stress, which is referred to as the pressure. σii = -p σn = -p, which is compressive, as it ...
... Since, by definition, a fluid cannot withstand a shear stress without moving, (deformation) a stationary fluid must necessarily be completely free of shear stress (σij=0, i ≠ j). The only stress is the normal stress, which is referred to as the pressure. σii = -p σn = -p, which is compressive, as it ...
Physical Principles - Thayer School of Engineering
... Because fluid motions occur under the action of pressure and other forces, a necessary budget is that for momentum. The momentum of a piece of matter in movement is equal to the product of its mass by its velocity. In general, the velocity is a three-dimensional vector, ~u, and on a per-volume basis ...
... Because fluid motions occur under the action of pressure and other forces, a necessary budget is that for momentum. The momentum of a piece of matter in movement is equal to the product of its mass by its velocity. In general, the velocity is a three-dimensional vector, ~u, and on a per-volume basis ...
Chapter 3 Basic of Fluid Flow
... vary in the direction of flow and not across the cross-section. The flow may be unsteady, in this case the parameter vary in time but still not across the cross-section. An example of one-dimensional flow is the flow in a pipe. Note that since flow must be zero at the pipe wall - yet nonzero in th ...
... vary in the direction of flow and not across the cross-section. The flow may be unsteady, in this case the parameter vary in time but still not across the cross-section. An example of one-dimensional flow is the flow in a pipe. Note that since flow must be zero at the pipe wall - yet nonzero in th ...
bioslurping – horizontal radial flow – theory and experimental
... forces between the fluids and the soil, and that the liquid and air can move at significantly different veloci ties with negligible interacting forces. Thus the two fluids can flow independently, except that the interface pressures and the elevations must be the same. It is expected that at the int ...
... forces between the fluids and the soil, and that the liquid and air can move at significantly different veloci ties with negligible interacting forces. Thus the two fluids can flow independently, except that the interface pressures and the elevations must be the same. It is expected that at the int ...
2 Mechanics of fluids at rest
... E2: The lift force of an airplane In order to make an airplane lift, the pressure under the wing need be higher than that on the wing. A good idea is to make the wing have different curve surfaces ...
... E2: The lift force of an airplane In order to make an airplane lift, the pressure under the wing need be higher than that on the wing. A good idea is to make the wing have different curve surfaces ...
Lecture Packet#6
... • If PGF was the only force acting upon air, we would always find winds blowing directly from higher pressure to lower pressure. • However, the moment air starts to move from higher pressure to lower pressure it is deflected (to the right in the N. Hemisphere and to the left in the S. Hemisphere) by ...
... • If PGF was the only force acting upon air, we would always find winds blowing directly from higher pressure to lower pressure. • However, the moment air starts to move from higher pressure to lower pressure it is deflected (to the right in the N. Hemisphere and to the left in the S. Hemisphere) by ...
Drag and Drag Coefficients
... Form drag can be minimized by forcing seperation toward the rear of the object. This is accomplished by streamlining. The usual method of streamlining is to so proportion the rear of the object that the increase in pressure in the boundary layer, which is the basic cause of seperation, is sufficien ...
... Form drag can be minimized by forcing seperation toward the rear of the object. This is accomplished by streamlining. The usual method of streamlining is to so proportion the rear of the object that the increase in pressure in the boundary layer, which is the basic cause of seperation, is sufficien ...
Design specifications
... unpowered state or submerging the device in water in an unpowered state and visually inspecting for bubble production. No leaks can be present other than what is accepted through the outlet of the device by the leak rate, above. ...
... unpowered state or submerging the device in water in an unpowered state and visually inspecting for bubble production. No leaks can be present other than what is accepted through the outlet of the device by the leak rate, above. ...
Lift (force)

A fluid flowing past the surface of a body exerts a force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the surface force parallel to the flow direction. If the fluid is air, the force is called an aerodynamic force. In water, it is called a hydrodynamic force.