Wanganui High School
... DNA: this is the chemical which carries genetic information in the nuclei of cells / made up of phosphate units, sugar units and 4 types of bases dominant: this is the allele which will be "expressed" in the phenotype if it is present as either a single gene or as two genes. e.g. B double helix: nam ...
... DNA: this is the chemical which carries genetic information in the nuclei of cells / made up of phosphate units, sugar units and 4 types of bases dominant: this is the allele which will be "expressed" in the phenotype if it is present as either a single gene or as two genes. e.g. B double helix: nam ...
Gene Technologies
... this risk, do you think that this research should continue? If not, why? If so, under what conditions? ...
... this risk, do you think that this research should continue? If not, why? If so, under what conditions? ...
Supplementary Information (doc 63K)
... Human aging is associated with a functional decline in both replicating and nonreplicating tissues. The transgenerational functional decline in replicative capacity of DNA repair mutants that we report here is reminiscent of that observed in germ cells of telomere replication defective C. elegans mu ...
... Human aging is associated with a functional decline in both replicating and nonreplicating tissues. The transgenerational functional decline in replicative capacity of DNA repair mutants that we report here is reminiscent of that observed in germ cells of telomere replication defective C. elegans mu ...
CHAPTER 18 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION I. Student
... lifetime of an individual. True b. In prokaryotes, coordinately controlled genes are united by control elements; in eukaryotes, they are united by location. False c. During embryonic development, a cytoplasmic enzyme may cleave poly-A tails from mRNAs to initiate their translation. False d. Ubiquiti ...
... lifetime of an individual. True b. In prokaryotes, coordinately controlled genes are united by control elements; in eukaryotes, they are united by location. False c. During embryonic development, a cytoplasmic enzyme may cleave poly-A tails from mRNAs to initiate their translation. False d. Ubiquiti ...
lec-4 - ucsf biochemistry website
... GMR = a promoter that drives expression late in eye development hid – a gene whose expression induces an apoptotic program Here GMR is directly driving hid expression and the construct is on 2L, and an FRT is on the base of the same chromosome arm. B) When hid expression is driven by GMR almost all ...
... GMR = a promoter that drives expression late in eye development hid – a gene whose expression induces an apoptotic program Here GMR is directly driving hid expression and the construct is on 2L, and an FRT is on the base of the same chromosome arm. B) When hid expression is driven by GMR almost all ...
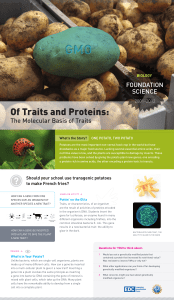
Of Traits and Proteins:
... Unlike bacteria, which are single-cell organisms, plants are made up of many different cells. How can a gene be inserted into a multi-cellular plant to give it a new trait? Inserting a gene into a plant involves the same principle as inserting a gene into bacteria: DNA containing the gene of interes ...
... Unlike bacteria, which are single-cell organisms, plants are made up of many different cells. How can a gene be inserted into a multi-cellular plant to give it a new trait? Inserting a gene into a plant involves the same principle as inserting a gene into bacteria: DNA containing the gene of interes ...
Lecture 1, Part I
... • Chromosomes are made of compressed and entwined DNA. • A (protein-coding) gene is a segment of chromosomal DNA that directs the synthesis of a protein. ...
... • Chromosomes are made of compressed and entwined DNA. • A (protein-coding) gene is a segment of chromosomal DNA that directs the synthesis of a protein. ...
2005 exam
... 6. Discuss the role of Pax6 as a master regulator of eye development and what characterizes a developmental master regulator or selector gene. Explain the structural components needed for recruiting a gene into a novel developmental pathway during the course of evolution. ...
... 6. Discuss the role of Pax6 as a master regulator of eye development and what characterizes a developmental master regulator or selector gene. Explain the structural components needed for recruiting a gene into a novel developmental pathway during the course of evolution. ...
This is to serve as a general overview of important topics. I highly
... Where does DNA replication occur? DNA is copied via a ____________________________ model. Other proposed models include conservative and dispersive models. The two complementary strands are held together ______________________ bonds. Within the DNA there bonds are __________________ ...
... Where does DNA replication occur? DNA is copied via a ____________________________ model. Other proposed models include conservative and dispersive models. The two complementary strands are held together ______________________ bonds. Within the DNA there bonds are __________________ ...
Chapter 6 Review Terms: Somatic Cell, Game - District 196 e
... a. DNA condensing into tightly packaged chromosomes b. homologous chromosomes crossing over c. alleles assorting independently into gametes d. homologous pairs of chromosomes separating into different gametes ...
... a. DNA condensing into tightly packaged chromosomes b. homologous chromosomes crossing over c. alleles assorting independently into gametes d. homologous pairs of chromosomes separating into different gametes ...
PCR - share1
... (such as skin used in burn treatment). - Therapeutic cloning, (the creation of an embryo to supply embryonic stem cells for medical use) is only allowed to the blastocyst stage in most places: uses? pros and cons? - The race is on to reprogram ...
... (such as skin used in burn treatment). - Therapeutic cloning, (the creation of an embryo to supply embryonic stem cells for medical use) is only allowed to the blastocyst stage in most places: uses? pros and cons? - The race is on to reprogram ...
Thomas Hunt Morgan`s Conclusions
... - Large number of offspring to study - Life cycle is only 10 – 15 days so it is possible to study many generations in a short period of time - Small size so many can fit into a small bottle - Males and females are easily identified He discovered that the gene for body colour and the gene for wing si ...
... - Large number of offspring to study - Life cycle is only 10 – 15 days so it is possible to study many generations in a short period of time - Small size so many can fit into a small bottle - Males and females are easily identified He discovered that the gene for body colour and the gene for wing si ...
Gene Finding
... Gene length: 30kb, coding region: 1-2kb Binding site: ~6bp; ~30bp upstream of TSS Average of 6 exons, 150bp long Huge variance: - dystrophin: 2.4Mb long – Blood coagulation factor: 26 exons, 69bp to 3106bp; intron 22 contains another unrelated gene ...
... Gene length: 30kb, coding region: 1-2kb Binding site: ~6bp; ~30bp upstream of TSS Average of 6 exons, 150bp long Huge variance: - dystrophin: 2.4Mb long – Blood coagulation factor: 26 exons, 69bp to 3106bp; intron 22 contains another unrelated gene ...
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 4.) What are the steps in the post-transcriptional regulatory process that miRNAs are involved in? 5.) Why is RNAi also referred to as gene knockdown? 6.) What is a tumor suppressor gene? Why are they associated with cancer? What example of a tumor suppressor did we talk about in lecture? ...
... 4.) What are the steps in the post-transcriptional regulatory process that miRNAs are involved in? 5.) Why is RNAi also referred to as gene knockdown? 6.) What is a tumor suppressor gene? Why are they associated with cancer? What example of a tumor suppressor did we talk about in lecture? ...
Environment and Gene Expression Scientists have learned that
... now clear that not all genes are expressed in every cell, nor are many genes expressed all of the time. Cells have complex systems that regulate whether or not specific genes are expressed. Expression depends on the cell’s need and environment. Through gene regulation, a given sequence can be expres ...
... now clear that not all genes are expressed in every cell, nor are many genes expressed all of the time. Cells have complex systems that regulate whether or not specific genes are expressed. Expression depends on the cell’s need and environment. Through gene regulation, a given sequence can be expres ...
Lesson Plan
... Students view a video describing the process for the lab. Guided Practice: Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab, Students will be given a lab report rubric and the lab report will be due Wednesday/Thursday for a major grade. ...
... Students view a video describing the process for the lab. Guided Practice: Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab, Students will be given a lab report rubric and the lab report will be due Wednesday/Thursday for a major grade. ...
Genetics
... • Some mutations result in genetic disease • If the mutation is recessive then it is possible for a person to be a carrier of the disease • The frequency of mutations are increased by mutagens • Some mutagens are carcinogens ...
... • Some mutations result in genetic disease • If the mutation is recessive then it is possible for a person to be a carrier of the disease • The frequency of mutations are increased by mutagens • Some mutagens are carcinogens ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide
... pattern. DNA stores genetic trait information through the arrangement of the nitrogen bases in the double helix structure. Groups of three nitrogen bases form codons. Dominant. The form (allele) of the gene that appears to dominate or mask another form of the gene when two different forms are presen ...
... pattern. DNA stores genetic trait information through the arrangement of the nitrogen bases in the double helix structure. Groups of three nitrogen bases form codons. Dominant. The form (allele) of the gene that appears to dominate or mask another form of the gene when two different forms are presen ...
DNA in classifying species
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
34 Lambda Appendix - RIT
... This site specific recombination event is reversible. If a lysogen is presented with DNA damage, in the form of ultraviolet light, for example, the int gene together with the xis gene perform the reverse site-specific recombination event and excise the phage from the host genome, restoring it to the ...
... This site specific recombination event is reversible. If a lysogen is presented with DNA damage, in the form of ultraviolet light, for example, the int gene together with the xis gene perform the reverse site-specific recombination event and excise the phage from the host genome, restoring it to the ...
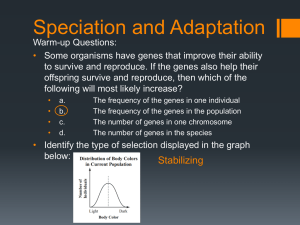
Adaptation and Speciation
... recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. ...
... recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. ...
Genetic Engineering
... chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g. a gene for luminescence from a jellyfish can be added to a frog, making it l ...
... chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g. a gene for luminescence from a jellyfish can be added to a frog, making it l ...
Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse