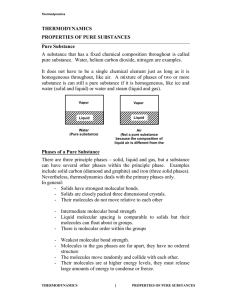
thermodynamics properties of pure substances
... liquid tables, Table A-7. Table A-7 is arranged like Table A-6, except the saturation states are the saturated liquid states. Note that the data in Table A-7 begins at 5 MPa or 50 times atmospheric pressure. At pressures below 5 MPa for water, the data are approximately equal to the saturated liquid ...
... liquid tables, Table A-7. Table A-7 is arranged like Table A-6, except the saturation states are the saturated liquid states. Note that the data in Table A-7 begins at 5 MPa or 50 times atmospheric pressure. At pressures below 5 MPa for water, the data are approximately equal to the saturated liquid ...
CYL110 2012-2013 Classical Thermodynamics Sample Problems
... βP + 1) (iv) ∂V S = γ/β (v) ∂T P = T α . 29. At what pressure can graphite be converted to diamond. Use the data given below. ∆H0298 kJ mol−1 graphite ...
... βP + 1) (iv) ∂V S = γ/β (v) ∂T P = T α . 29. At what pressure can graphite be converted to diamond. Use the data given below. ∆H0298 kJ mol−1 graphite ...
Atmospheric Pressure - Wind - General Circulation
... • Generally, air is either divergent or convergent aloft (in the upper atmosphere) and the opposite in the lower atmosphere. There is a gradual change from divergence to convergence, or vise versa as you go from the surface upward. Somewhere in between the surface and the upper atmosphere is a leve ...
... • Generally, air is either divergent or convergent aloft (in the upper atmosphere) and the opposite in the lower atmosphere. There is a gradual change from divergence to convergence, or vise versa as you go from the surface upward. Somewhere in between the surface and the upper atmosphere is a leve ...
S2213177912000108_mmc1
... was identified. The principle of titration for ASV which has been previously described was used (2). First, the EPAP was manually titrated from 4 cm H2O to the effective pressure, with a maximum of 10 cm H2O, using a similar titration method to that used for CPAP. The minimal IPAP was set at the det ...
... was identified. The principle of titration for ASV which has been previously described was used (2). First, the EPAP was manually titrated from 4 cm H2O to the effective pressure, with a maximum of 10 cm H2O, using a similar titration method to that used for CPAP. The minimal IPAP was set at the det ...
Materials - UCSI A
... Density = Mass / Volume or ρ = m/V ρ is a Greek letter rh. Common units are g cm-3 or kg m-3 1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3 A substance could be (i) denser in large mass and smaller volume (ii) less dense in lower mass and larger volume. Density is not a vector quantity as it does not have direction. Take n ...
... Density = Mass / Volume or ρ = m/V ρ is a Greek letter rh. Common units are g cm-3 or kg m-3 1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3 A substance could be (i) denser in large mass and smaller volume (ii) less dense in lower mass and larger volume. Density is not a vector quantity as it does not have direction. Take n ...
thermodynamics - New Age International
... For defining any system certain parameters are needed. ‘Properties’ are those observable characteristics of the system which can be used for defining it. Thermodynamic properties are the observable characteristics of the thermodynamic system. Pressure, temperature, volume, viscosity, modulus of elas ...
... For defining any system certain parameters are needed. ‘Properties’ are those observable characteristics of the system which can be used for defining it. Thermodynamic properties are the observable characteristics of the thermodynamic system. Pressure, temperature, volume, viscosity, modulus of elas ...
Group–A Thermodynamics - New Age International
... the behaviour of individual molecules. Therefore, it treats the matter as continuous, or the whole of this as a Continuum. For example, when a container contains gas, the gas exerts pressure on the walls of its container. The pressure results from the change in momentum of the gas molecules as they ...
... the behaviour of individual molecules. Therefore, it treats the matter as continuous, or the whole of this as a Continuum. For example, when a container contains gas, the gas exerts pressure on the walls of its container. The pressure results from the change in momentum of the gas molecules as they ...



![documentstyle[12pt]{article}](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010234315_1-392ad57a1bf5b2aaeca94206588a5307-300x300.png)