Lecture 5
... length/time! Examples of hydraulic conductivity (found experimentally) for various materials are given in our text on page 26 – Table 2.1. Notice that the hydraulic conductivity of gravel and sand is higher than that for silt or clay – does this make sense with which materials allow water to flow mo ...
... length/time! Examples of hydraulic conductivity (found experimentally) for various materials are given in our text on page 26 – Table 2.1. Notice that the hydraulic conductivity of gravel and sand is higher than that for silt or clay – does this make sense with which materials allow water to flow mo ...
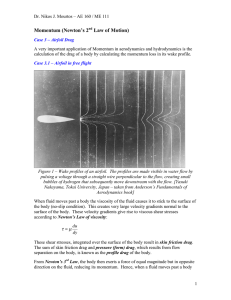
Momentum (Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion)
... cancel each other out. As a result, none of these forces would appear in Momentum. Streamsurfaces are used for the upper and lower bounds of the control volume, so there is no flow crossing the top and bottom control surface. The control surface is taken far enough from the body in all direction ...
... cancel each other out. As a result, none of these forces would appear in Momentum. Streamsurfaces are used for the upper and lower bounds of the control volume, so there is no flow crossing the top and bottom control surface. The control surface is taken far enough from the body in all direction ...
Physics, Chapter 9: Hydrodynamics (Fluids in Motion)
... The fundamental theorem regarding the motion of fluids is due to Daniel Bernoulli (1700-1782), a Swiss physicist and mathematician. Bernoulli's theorem is essentially a formulation of the mechanical concept that the work done on a body is equal to the change in its mechanical energy, in the case tha ...
... The fundamental theorem regarding the motion of fluids is due to Daniel Bernoulli (1700-1782), a Swiss physicist and mathematician. Bernoulli's theorem is essentially a formulation of the mechanical concept that the work done on a body is equal to the change in its mechanical energy, in the case tha ...
Wilson-Ch
... An object’s density will tell you whether it will sink or float in a particular fluid. ...
... An object’s density will tell you whether it will sink or float in a particular fluid. ...
True or False? In the absence of air friction, the vertical component
... –Less area covered results in more pressure ...
... –Less area covered results in more pressure ...
09_Solids and Fluids
... Nonviscous flow means that viscosity is negligible. Viscosity produces drag, and retards fluid flow. Incompressible flow means that the fluid’s density is constant. This is generally true for liquids, but not ...
... Nonviscous flow means that viscosity is negligible. Viscosity produces drag, and retards fluid flow. Incompressible flow means that the fluid’s density is constant. This is generally true for liquids, but not ...
Chapter1_08-24-2015
... V* = limiting volume below which molecular variations may be important and above which macroscopic variations may be important V* 10-9 mm3 (or length scale of l* 10-6 m) for all liquids and for gases at atmospheric pressure 10-9 mm3 air (at standard conditions, 20C and 1 atm) contains 3x107 m ...
... V* = limiting volume below which molecular variations may be important and above which macroscopic variations may be important V* 10-9 mm3 (or length scale of l* 10-6 m) for all liquids and for gases at atmospheric pressure 10-9 mm3 air (at standard conditions, 20C and 1 atm) contains 3x107 m ...
chapter 1: introduction and basic concepts
... V* 10-9 mm3 for all liquids and for gases at atmospheric pressure 10-9 mm3 air (at standard conditions, 20C and 1 atm) contains 3x107 molecules such that M/V = constant = Note that typical “smallest” measurement volumes are about 10-3 – 100 mm3 >> V* and that the “scale” of macroscopic vari ...
... V* 10-9 mm3 for all liquids and for gases at atmospheric pressure 10-9 mm3 air (at standard conditions, 20C and 1 atm) contains 3x107 molecules such that M/V = constant = Note that typical “smallest” measurement volumes are about 10-3 – 100 mm3 >> V* and that the “scale” of macroscopic vari ...