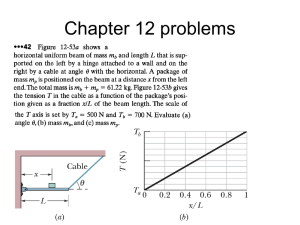
Chapter 4 Study Guide. Section 1 Matter A. Matter—anything that
... 1. Thermal energy—total energy of all the particles in a sample of matter A warmer substance has more thermal energy than a cooler one. 2. The average kinetic energy of particles in a substance is its temperature. 3. Heat—movement of thermal energy from a substance with a higher temperature to one ...
... 1. Thermal energy—total energy of all the particles in a sample of matter A warmer substance has more thermal energy than a cooler one. 2. The average kinetic energy of particles in a substance is its temperature. 3. Heat—movement of thermal energy from a substance with a higher temperature to one ...
Pressure station
... Atmospheric Pressure: (remember to takes notes and observations in your ISN) High vs. Low Pressure System Explained An important characteristic of the Earth's atmosphere is its air pressure as it often determines wind and weather patterns across the globe. By definition, atmospheric or air pressure ...
... Atmospheric Pressure: (remember to takes notes and observations in your ISN) High vs. Low Pressure System Explained An important characteristic of the Earth's atmosphere is its air pressure as it often determines wind and weather patterns across the globe. By definition, atmospheric or air pressure ...
Pressure field and buoyancy. Elementary fluid dynamics. Bernoulli
... On any body in a flowing fluid there is a stagnation point. Some of the fluid flows "over" and some "under" the body. The dividing line (the stagnation streamline) terminates at the stagnation point on the body. As indicated by the dye filaments in the water flowing past a streamlined object, the v ...
... On any body in a flowing fluid there is a stagnation point. Some of the fluid flows "over" and some "under" the body. The dividing line (the stagnation streamline) terminates at the stagnation point on the body. As indicated by the dye filaments in the water flowing past a streamlined object, the v ...
File
... any surface - the bottom or sides of its container, or even the surface of an object submerged in the liquid to that depth. • Pressure a liquid exerts depends only on its density and depth. • Total pressure (or absolute pressure) Pabsolute on a submerged surface equals the pressure the liquid exerts ...
... any surface - the bottom or sides of its container, or even the surface of an object submerged in the liquid to that depth. • Pressure a liquid exerts depends only on its density and depth. • Total pressure (or absolute pressure) Pabsolute on a submerged surface equals the pressure the liquid exerts ...
fluid and air pressure
... • Others appeal to a model based on Newton's laws and assert that the main lift comes as a result of the angle of attack. Part of the Newton's law model of part of the lift force involves attachment of the boundary layer of air on the top of the wing with a resulting downwash of air behind the win ...
... • Others appeal to a model based on Newton's laws and assert that the main lift comes as a result of the angle of attack. Part of the Newton's law model of part of the lift force involves attachment of the boundary layer of air on the top of the wing with a resulting downwash of air behind the win ...
Chapter 14
... Fluids at rest • The hydrostatic pressure at a point in a fluid depends on the depth of that point but not on any horizontal dimension of the fluid or its container • Difference between an absolute pressure and an atmospheric pressure is called the gauge pressure ...
... Fluids at rest • The hydrostatic pressure at a point in a fluid depends on the depth of that point but not on any horizontal dimension of the fluid or its container • Difference between an absolute pressure and an atmospheric pressure is called the gauge pressure ...
Pressure and mass conservation
... Composition of the atmosphere • Air is a mixture of various gases • Particularly, nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide • We can assume air behaves like an ideal gas ...
... Composition of the atmosphere • Air is a mixture of various gases • Particularly, nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide • We can assume air behaves like an ideal gas ...
Chap2-Che312
... - A very common pressure measuring device. - A coiled hollow tube in the gage tends to straighten out when subjected to internal pressure, and the degree of straightening depends on the pressure difference between the inside and outside pressures. - The tube is connected to a pointer on a calibrated ...
... - A very common pressure measuring device. - A coiled hollow tube in the gage tends to straighten out when subjected to internal pressure, and the degree of straightening depends on the pressure difference between the inside and outside pressures. - The tube is connected to a pointer on a calibrated ...