Solutions to Problems
... 52. The lift force would be the difference in pressure between the two wing surfaces, times the area of the wing surface. The difference in pressure can be found from Bernoulli’s equation. We consider the two surfaces of the wing to be at the same height above the ground. Call the bottom surface of ...
... 52. The lift force would be the difference in pressure between the two wing surfaces, times the area of the wing surface. The difference in pressure can be found from Bernoulli’s equation. We consider the two surfaces of the wing to be at the same height above the ground. Call the bottom surface of ...
Fluid Mechanics
... atmospheric pressure p) is filled to a height L with a liquid of density ρ as shown in the diagram. A block of density D (D < ρ) and dimensions x, y, and z is attached to the bottom of the tank by a string so that its top surface is a distance h from the surface of the liquid. a) What is the total f ...
... atmospheric pressure p) is filled to a height L with a liquid of density ρ as shown in the diagram. A block of density D (D < ρ) and dimensions x, y, and z is attached to the bottom of the tank by a string so that its top surface is a distance h from the surface of the liquid. a) What is the total f ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... Consider a pipe of cross sectional area A with a fluid moving through it with velocity v What happens if the pipe narrows? Mass must be conserved so, Avr = constant If the density is constant then, Av= constant = [dV/dt] = volume flow rate Since rate is a constant, if A decreases then v ...
... Consider a pipe of cross sectional area A with a fluid moving through it with velocity v What happens if the pipe narrows? Mass must be conserved so, Avr = constant If the density is constant then, Av= constant = [dV/dt] = volume flow rate Since rate is a constant, if A decreases then v ...
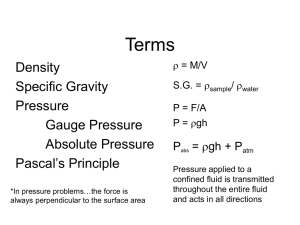
Fluid Terms
... flow rate through a pipe whose cross-sectioanl area, A, gradually decreases: at the exit point, A has decreased to 1/3 its value. If y=60cm and the flow speed of the water at point 1 is 1 m/s, what is the gauge pressure at point 1? ...
... flow rate through a pipe whose cross-sectioanl area, A, gradually decreases: at the exit point, A has decreased to 1/3 its value. If y=60cm and the flow speed of the water at point 1 is 1 m/s, what is the gauge pressure at point 1? ...