Weather-seaman
... An aneroid barometer, invented by the French 19th century engineer and inventor Lucien Vidie, uses a small, flexible metal box called an aneroid cell. This aneroid capsule (cell) is made from an alloy of beryllium and copper.[9] The evacuated capsule (or usually more capsules) is prevented from coll ...
... An aneroid barometer, invented by the French 19th century engineer and inventor Lucien Vidie, uses a small, flexible metal box called an aneroid cell. This aneroid capsule (cell) is made from an alloy of beryllium and copper.[9] The evacuated capsule (or usually more capsules) is prevented from coll ...
Chapter 11
... constricted pipe Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
... constricted pipe Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
Fluid Mechanics Concepts
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts Study Guide in PowerPoint
... number of particles, called molecules, make up the substance in question. The macroscopic approach to thermodynamics does not require knowledge of the behavior of individual particles and is called classical thermodynamics. It provides a direct and easy way to obtain the solution of engineering prob ...
... number of particles, called molecules, make up the substance in question. The macroscopic approach to thermodynamics does not require knowledge of the behavior of individual particles and is called classical thermodynamics. It provides a direct and easy way to obtain the solution of engineering prob ...
Chapter 1
... number of particles, called molecules, make up the substance in question. The macroscopic approach to thermodynamics does not require knowledge of the behavior of individual particles and is called classical thermodynamics. It provides a direct and easy way to obtain the solution of engineering prob ...
... number of particles, called molecules, make up the substance in question. The macroscopic approach to thermodynamics does not require knowledge of the behavior of individual particles and is called classical thermodynamics. It provides a direct and easy way to obtain the solution of engineering prob ...
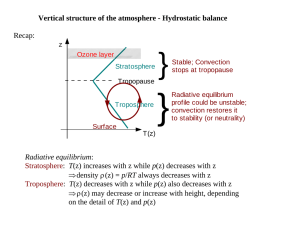
Vertical structure of the atmosphere
... Simple example: Liquid fluid with constant density Pressure = force (or weight) per unit area Weight = mass × gravitational acceleration = (density × volume) × g Pressure at point A = ρ × (depth of fluid above point A) × g = ρ gH ...
... Simple example: Liquid fluid with constant density Pressure = force (or weight) per unit area Weight = mass × gravitational acceleration = (density × volume) × g Pressure at point A = ρ × (depth of fluid above point A) × g = ρ gH ...
Met Wind.pps
... In 24 hours the object at the North Pole will rotate through 360° but will not have any forward speed. 0 mph 360° per 24 hrs The object at the equator will 0 mph also rotate 360° but will travel approximately 24,000 miles in the same 24 hour period, therefore it has a forward speed of 1,000 mph. Any ...
... In 24 hours the object at the North Pole will rotate through 360° but will not have any forward speed. 0 mph 360° per 24 hrs The object at the equator will 0 mph also rotate 360° but will travel approximately 24,000 miles in the same 24 hour period, therefore it has a forward speed of 1,000 mph. Any ...
L16-Pressure-and-Winds
... – The atmospheric molecules are held near surface by gravity – Pressure itself reflects the weight of the mass of overlying atmosphere – Defined as force per unit area at the surface – Units of Pascal (1 N/m2) – In the atmosphere, we measure pressure in millibars (mb) – It is important to remember t ...
... – The atmospheric molecules are held near surface by gravity – Pressure itself reflects the weight of the mass of overlying atmosphere – Defined as force per unit area at the surface – Units of Pascal (1 N/m2) – In the atmosphere, we measure pressure in millibars (mb) – It is important to remember t ...
Charting Air Pressure lesson
... 5. Place your barometer on a table or flat surface. Make sure it’s inside and not near a window, since it might be affected by temperature. 6. Carefully record the height of the straw on the index car. Mark it with a marker and pur the number 1 on it. ...
... 5. Place your barometer on a table or flat surface. Make sure it’s inside and not near a window, since it might be affected by temperature. 6. Carefully record the height of the straw on the index car. Mark it with a marker and pur the number 1 on it. ...
chapter (ii) characteristics of fluids
... Pressure Variation in a Fluid with Rigid-Body Motion: The general equation of motion (Eq. 2.2): ...
... Pressure Variation in a Fluid with Rigid-Body Motion: The general equation of motion (Eq. 2.2): ...
The actual equation that is provided you is where would be some
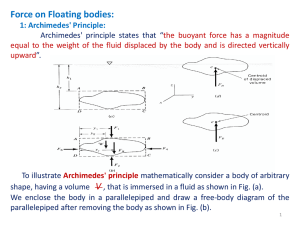
... The mass of the weight is known, suspend the mass from the spring in air, measure the displacement of the spring and calculate k from the equation Fs kx where Fs is the mg, the weight of the thing. (b) The spring-object system is now arranged so that the object (but not the spring) is immersed ...
... The mass of the weight is known, suspend the mass from the spring in air, measure the displacement of the spring and calculate k from the equation Fs kx where Fs is the mg, the weight of the thing. (b) The spring-object system is now arranged so that the object (but not the spring) is immersed ...