Lecture Outline (WORD)
... 1st law: An object at rest will remain at rest (or an object in motion will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed) as long as no net force is exerted on it. o You can think of a force as something that pushes or pulls on an object. Net force is the sum of all individual forces acti ...
... 1st law: An object at rest will remain at rest (or an object in motion will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed) as long as no net force is exerted on it. o You can think of a force as something that pushes or pulls on an object. Net force is the sum of all individual forces acti ...
Advanced Physical Chemistry Problems (VIII)
... three gases, and use this datum with the volume to obtain the final density. 7. N H4 H S(s) dissociates according to the equation: N H4 H S(s)* ) N H3 (g) + H2 S(g) At a certain temperature, the dissociation pressure of the pure solid is 50 mm Hg. This represents the total pressure when N H4 HS(s) i ...
... three gases, and use this datum with the volume to obtain the final density. 7. N H4 H S(s) dissociates according to the equation: N H4 H S(s)* ) N H3 (g) + H2 S(g) At a certain temperature, the dissociation pressure of the pure solid is 50 mm Hg. This represents the total pressure when N H4 HS(s) i ...
Edema, Hyperemia and Congestion
... Higher on arteriolar side Lower on venular side Lowest in interstitium ...
... Higher on arteriolar side Lower on venular side Lowest in interstitium ...
FLUID MECHANICS CE 156 Tutorial Sheet
... These processes are to be carried out in a vertical lift. Calculate the accelerations to be given to the lift to satisfy the above 27. A tube ABCD has the end A opened to the atmosphere and the end D closed. The portion ABC is vertical while the portion CD is a quadrant of radius 250 mm with its cen ...
... These processes are to be carried out in a vertical lift. Calculate the accelerations to be given to the lift to satisfy the above 27. A tube ABCD has the end A opened to the atmosphere and the end D closed. The portion ABC is vertical while the portion CD is a quadrant of radius 250 mm with its cen ...
HOW TO TAKE BLOOD PRESSURES
... 7. Keep squeezing the bulb until the scale on the gauge reads about 160. Or, until the gauge reads at least 10 points higher than when you last hear the heartbeat. 8. Slowly loosen the screw to let air escape from the cuff. Let the gauge fall about 5 points a second. Carefully look at the gauge and ...
... 7. Keep squeezing the bulb until the scale on the gauge reads about 160. Or, until the gauge reads at least 10 points higher than when you last hear the heartbeat. 8. Slowly loosen the screw to let air escape from the cuff. Let the gauge fall about 5 points a second. Carefully look at the gauge and ...
Course 3: Pressure – Volume – Temperature Relationship of Pure
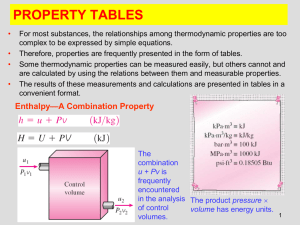
... Ideal gas equation of state is a model equation applicable to all gases to understand their P-V-T behavior and the energy requirements of processes within small margins of error Consider an engine piston full of ideal gas Total energy of the ideal gas can only be changed through transfer of energy ...
... Ideal gas equation of state is a model equation applicable to all gases to understand their P-V-T behavior and the energy requirements of processes within small margins of error Consider an engine piston full of ideal gas Total energy of the ideal gas can only be changed through transfer of energy ...