Notes on Chapter 12 Chemical Equilibrium
... Factors that affect the rate of reaction: a. temperature- increase in temperature increases reaction rates b. concentration- increase in the concentration of reactant(s) increases rates c. catalyst = anything that speeds up the rate of reactions by lowering the energy of activation for the reaction. ...
... Factors that affect the rate of reaction: a. temperature- increase in temperature increases reaction rates b. concentration- increase in the concentration of reactant(s) increases rates c. catalyst = anything that speeds up the rate of reactions by lowering the energy of activation for the reaction. ...
Standard B-2
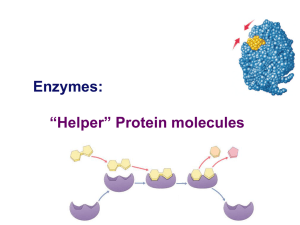
... of a chemical reaction; is not consumed or altered during a chemical reaction, so, it can be used over and over again. o Enzymes: proteins that serve as catalysts in living organisms. o Enzymes are very specific. Each particular enzyme can catalyze only one chemical reaction by working on one partic ...
... of a chemical reaction; is not consumed or altered during a chemical reaction, so, it can be used over and over again. o Enzymes: proteins that serve as catalysts in living organisms. o Enzymes are very specific. Each particular enzyme can catalyze only one chemical reaction by working on one partic ...
Diagnosis Test: EDEXCEL ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Biology
... QWC Suggested marking guidance (Total 6 marks) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Written Communication (QWC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Teachers should apply a ‘best-fit’ approach to the marking. ...
... QWC Suggested marking guidance (Total 6 marks) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Written Communication (QWC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Teachers should apply a ‘best-fit’ approach to the marking. ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - pH scale - _________________ system to indicate the _______________ of ____ ions in ______________, ranges from _______ - Acid – any ______________ that forms _____ ions in ____________ - __________ solutions have __________ concentration of ____ ions than pure _________ & have ____ values _______ ...
... - pH scale - _________________ system to indicate the _______________ of ____ ions in ______________, ranges from _______ - Acid – any ______________ that forms _____ ions in ____________ - __________ solutions have __________ concentration of ____ ions than pure _________ & have ____ values _______ ...
Seminario Tunable electronic properties of self
... between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as well as on morphological and structural aspects. One possible strategy to further steer the structural and electronic properties at interfaces is to use molecular mixtures such as donor-acceptor molecular pairs, since the introduction of th ...
... between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as well as on morphological and structural aspects. One possible strategy to further steer the structural and electronic properties at interfaces is to use molecular mixtures such as donor-acceptor molecular pairs, since the introduction of th ...
do not
... pressure (LOW) 3)Without catalysts reactions would be too slow 4)Needed to sustain life ...
... pressure (LOW) 3)Without catalysts reactions would be too slow 4)Needed to sustain life ...
Syllabus
... Grading Policy: There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encourage ...
... Grading Policy: There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encourage ...
Mass spectrometry-led catalyst discovery
... capable of studying complex mixtures in solution, capabilities that make it, at first glance, the ideal technique for the direct analysis of homogeneous catalytic reactions. However, a variety of challenges have prevented ESI-MS from being more widely applied in this context, including the invisibil ...
... capable of studying complex mixtures in solution, capabilities that make it, at first glance, the ideal technique for the direct analysis of homogeneous catalytic reactions. However, a variety of challenges have prevented ESI-MS from being more widely applied in this context, including the invisibil ...
Equation Intro Worksheet 1213
... 9. Write the skeleton reaction for this situation…(you might also need to remember that peroxide is O2-2 , and that can’t be reduced at all)… An aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen gas when a catalyst of powdered manganese (IV) oxide is used. ...
... 9. Write the skeleton reaction for this situation…(you might also need to remember that peroxide is O2-2 , and that can’t be reduced at all)… An aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen gas when a catalyst of powdered manganese (IV) oxide is used. ...
Supramolecular catalysis

Supramolecular catalysis is not a well-defined field but it generally refers to an application of supramolecular chemistry, especially molecular recognition and guest binding, toward catalysis. This field was originally inspired by enzymatic system which, unlike classical organic chemistry reactions, utilizes non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, cation-pi interaction, and hydrophobic forces to dramatically accelerate rate of reaction and/or allow highly selective reactions to occur. Because enzymes are structurally complex and difficult to modify, supramolecular catalysts offer a simpler model for studying factors involved in catalytic efficiency of the enzyme. Another goal that motivates this field is the development of efficient and practical catalysts that may or may not have an enzyme equivalent in nature.A closely related field of study is asymmetric catalysis which requires molecular recognition to differentiate two chiral starting material or chiral transition states and thus it could be categorized as an area of supramolecular catalysis, but supramolecular catalysis however does not necessarily have to involve asymmetric reaction. As there is another Wikipedia article already written about small molecule asymmetric catalysts, this article focuses primarily on large catalytic host molecules. Non-discrete and structurally poorly defined system such as micelle and dendrimers are not included.