BSC 1010 Exam 3 Study Guide
... • Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own genomes • traits controlled by these genes do not follow the chromosomal theory of inheritance • Maternal inheritance: 4. Genetic Mapping • The science of determining the location of a gene on a chromosome • Based on the recombination frequency of genes ...
... • Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own genomes • traits controlled by these genes do not follow the chromosomal theory of inheritance • Maternal inheritance: 4. Genetic Mapping • The science of determining the location of a gene on a chromosome • Based on the recombination frequency of genes ...
Name - WordPress.com
... b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. _____ 4. A heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a short plant. The probability that an F1 plant will be tall is a. 2 ...
... b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. _____ 4. A heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a short plant. The probability that an F1 plant will be tall is a. 2 ...
Genetics Slides
... Mendel’s experiments with pea plants looked at one gene for one trait. – This pattern of inheritance is called Mendelian.. § Some examples: Cheek dimples, face freckles & cleft chins § Tom Bradyà ...
... Mendel’s experiments with pea plants looked at one gene for one trait. – This pattern of inheritance is called Mendelian.. § Some examples: Cheek dimples, face freckles & cleft chins § Tom Bradyà ...
Biology -Chapter 14: Human Heredity
... 1. Determine the genotypes of individuals in a pedigree 2. Recognize and determine the meaning of symbols used in a pedigree 3. Use a pedigree to determine how a trait is inherited 4. Construct a pedigree from information gathered on a ficticious family for Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Text Section 14.2 Hum ...
... 1. Determine the genotypes of individuals in a pedigree 2. Recognize and determine the meaning of symbols used in a pedigree 3. Use a pedigree to determine how a trait is inherited 4. Construct a pedigree from information gathered on a ficticious family for Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Text Section 14.2 Hum ...
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
... states that every individual has two alleles of each gene and when gametes are produced, each gamete receives one of these alleles. Mendel’s ...
... states that every individual has two alleles of each gene and when gametes are produced, each gamete receives one of these alleles. Mendel’s ...
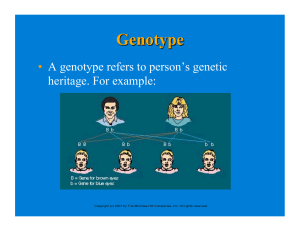
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... • The phenotype is one’s genotype expressed in characteristics that can be observed and measured (e.g, blue eyes). • It includes physical traits (e.g., height, weight) as well as psychological characteristics (intelligence, personality). ...
... • The phenotype is one’s genotype expressed in characteristics that can be observed and measured (e.g, blue eyes). • It includes physical traits (e.g., height, weight) as well as psychological characteristics (intelligence, personality). ...
Module 3 Nature vs. Nurture
... Identical twins – twins that develop from a single fertilized egg and then split in half; are genetically identical Fraternal twins – twins that develop from separate eggs; no more related genetically than ...
... Identical twins – twins that develop from a single fertilized egg and then split in half; are genetically identical Fraternal twins – twins that develop from separate eggs; no more related genetically than ...
EDITORIAL Dissecting Complex Genetic Diseases: Promises and
... detect the specific genetic regions involved in the disease process. However, in complex diseases, due to the large number of loci that may be involved, it has often been difficult both to detect and replicate linkages. The increasing availability of genome-wide markers, combined with multipoint ana ...
... detect the specific genetic regions involved in the disease process. However, in complex diseases, due to the large number of loci that may be involved, it has often been difficult both to detect and replicate linkages. The increasing availability of genome-wide markers, combined with multipoint ana ...
click here and type title
... Trio designs (father, mother and son/daughter) are useful for association and/or linkage between diseases and genetic variants for complex and rare early-onset diseases such as Alzheimer, schizophrenia and autism. Transmission Disequilibrium Test (TDT) is commonly used to test association in trio st ...
... Trio designs (father, mother and son/daughter) are useful for association and/or linkage between diseases and genetic variants for complex and rare early-onset diseases such as Alzheimer, schizophrenia and autism. Transmission Disequilibrium Test (TDT) is commonly used to test association in trio st ...
Genetics - Biology with RuthMarie
... When heredity follows different rules • Mendel’s pattern of inheritance is called simple. But most alleles are not simply dominant or recessive. • What determines dominance? Dominant genes code for polypeptides (enzymes) that work ...
... When heredity follows different rules • Mendel’s pattern of inheritance is called simple. But most alleles are not simply dominant or recessive. • What determines dominance? Dominant genes code for polypeptides (enzymes) that work ...
Applying Mendel`s Principles Learning Objectives
... Making a Punnett Square A cross of ospreys: beak size (B, b) Combine gamete genotypes Possible gametes ...
... Making a Punnett Square A cross of ospreys: beak size (B, b) Combine gamete genotypes Possible gametes ...
Other Patterns of Inheritance PowerPoint Notes
... ______________. Peas happen to have a number of traits that are determined by just two ______________. Also, for the traits he studied, one allele happened to be ______________and the other ______________. Mendel discovered an important pattern of inheritance and his laws are the foundation of _____ ...
... ______________. Peas happen to have a number of traits that are determined by just two ______________. Also, for the traits he studied, one allele happened to be ______________and the other ______________. Mendel discovered an important pattern of inheritance and his laws are the foundation of _____ ...
Mendel, Alleles, Punnentt squares Complex Punnett Squares VOCAB:
... Probability is the fraction of how many boxes contain the genotype of phenotype. Ratio (2:2) will always equal the number of boxes in the Punnett square and you count the boxes for the phenotypes or genotypes. Dihybrid Cross: A cross where you track 2 alleles. Boxes will have 4 letters. KEEP THE LET ...
... Probability is the fraction of how many boxes contain the genotype of phenotype. Ratio (2:2) will always equal the number of boxes in the Punnett square and you count the boxes for the phenotypes or genotypes. Dihybrid Cross: A cross where you track 2 alleles. Boxes will have 4 letters. KEEP THE LET ...
monohybrid cross
... meaning single); that is, a cross between organisms that are heterozygous at a single genetic locus, for example, eye colour in blowflies and flower colour in snapdragons. ...
... meaning single); that is, a cross between organisms that are heterozygous at a single genetic locus, for example, eye colour in blowflies and flower colour in snapdragons. ...
Name - Wsfcs
... The two alleles for a trait must separate when gametes are formed A parent randomly passes only one allele for each trait to each offspring Law of Segregation explained During Meiosis – homologous chromosomes and their alleles separate. 4) Law of Independent Assortment The genes for different tr ...
... The two alleles for a trait must separate when gametes are formed A parent randomly passes only one allele for each trait to each offspring Law of Segregation explained During Meiosis – homologous chromosomes and their alleles separate. 4) Law of Independent Assortment The genes for different tr ...
d. Method Delivery: Lectures, assignments, tutorials and practicals
... The objectives of the course are: At the end of the course, students should be able to: Compare and contrast Pre-Mendelian and Mendelian theories of inheritance and apply Mendel’s first and second laws of inheritance to solve related genetic problems Explain the different factors that can cause ...
... The objectives of the course are: At the end of the course, students should be able to: Compare and contrast Pre-Mendelian and Mendelian theories of inheritance and apply Mendel’s first and second laws of inheritance to solve related genetic problems Explain the different factors that can cause ...
Pedigree
... sex-linked trait Xn X Females do NOT show sexlinked trait Males have to be Xn Y to show sexlinked trait ...
... sex-linked trait Xn X Females do NOT show sexlinked trait Males have to be Xn Y to show sexlinked trait ...
Nonmendelian Genetics
... sex-linked trait Xn X Females do NOT show sexlinked trait Males have to be Xn Y to show sexlinked trait ...
... sex-linked trait Xn X Females do NOT show sexlinked trait Males have to be Xn Y to show sexlinked trait ...
chapter11
... • Traits with a range of small differences • The more factors that influence a trait, the more continuous the distribution of phenotype ...
... • Traits with a range of small differences • The more factors that influence a trait, the more continuous the distribution of phenotype ...
Heredity - TeacherWeb
... of a trait from one generation to the next in a family C. Randomness of traits - inheritance of traits occurs by ________ - when sex cells are made, _________ occur in the ____________ composition from cell to cell probability: how _____ an event is to occur (___) ex.: coins - ___:___ chance of ____ ...
... of a trait from one generation to the next in a family C. Randomness of traits - inheritance of traits occurs by ________ - when sex cells are made, _________ occur in the ____________ composition from cell to cell probability: how _____ an event is to occur (___) ex.: coins - ___:___ chance of ____ ...