`We are all virtually identical twins`
... imagined. Probably 99 per cent of the discoveries in biology remain to be made. This is very different from what I was told in the 1970s, when I was working on my doctorate at the University of California, San Diego, which was that basically it was going to be very difficult to come up with any new ...
... imagined. Probably 99 per cent of the discoveries in biology remain to be made. This is very different from what I was told in the 1970s, when I was working on my doctorate at the University of California, San Diego, which was that basically it was going to be very difficult to come up with any new ...
A1 / THEME 1 – A3: GENETICS. Série S/ES/L
... […] Genetic variation plays the role of a raw material for natural selection. Some individuals who are favored by natural selection have greater fitness than others because of their alleles (pair of ...
... […] Genetic variation plays the role of a raw material for natural selection. Some individuals who are favored by natural selection have greater fitness than others because of their alleles (pair of ...
Ch. 10 Mendel`s Genetics
... A Pedigree is a family tree that shows the inheritance of a genetic disorder ...
... A Pedigree is a family tree that shows the inheritance of a genetic disorder ...
Unit 8: Inheritance & Human Genetic Patterns
... Early 1900’s Used fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster to identify genetic patterns. Observed that only male fruit flies had white eyes ...
... Early 1900’s Used fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster to identify genetic patterns. Observed that only male fruit flies had white eyes ...
cross-fertilized
... • 2. If you use the letter E for this gene. What is the genotype of the offspring? ...
... • 2. If you use the letter E for this gene. What is the genotype of the offspring? ...
Lecture 13: May 24, 2004
... 1. Alternative versions of genes account for variation in inherited characters 2. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent 3. If two alleles differ, one is dominant, the other recessive 4. The two alleles for each character segregate (separate) during gamete product ...
... 1. Alternative versions of genes account for variation in inherited characters 2. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent 3. If two alleles differ, one is dominant, the other recessive 4. The two alleles for each character segregate (separate) during gamete product ...
MIDDLE SCHOOL GENETICS
... Mendel crossed true breeding plants that had two distinct and contrasting traits, like purple and white flowers. After the first cross, the plants self-fertilized. ...
... Mendel crossed true breeding plants that had two distinct and contrasting traits, like purple and white flowers. After the first cross, the plants self-fertilized. ...
Chap 11 Section 1 - SunsetRidgeMSBiology
... two of the same (2) ____________________ for a particular trait is said to be (3)____________________ for that trait. An organism with two different (4) ____________________ for a particular trait is heterozygous for that trait. When alleles are present in the (5) ____________________ state, the (6) ...
... two of the same (2) ____________________ for a particular trait is said to be (3)____________________ for that trait. An organism with two different (4) ____________________ for a particular trait is heterozygous for that trait. When alleles are present in the (5) ____________________ state, the (6) ...
genetics ppt - Schoolwires.net
... What percentage of the difference among people’s height can be attributed to their genes? ...
... What percentage of the difference among people’s height can be attributed to their genes? ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... What percentage of the difference among people’s height can be attributed to their genes? ...
... What percentage of the difference among people’s height can be attributed to their genes? ...
Biol 258: PP seminar
... Must have read chapter by week before, have paper in mind for assignment Rest of group: come up with paper we'd like for follow up reading 7) Questions--not optional. Submit >=36 h before discussion. 8) Website will list readings. Will post pdf of readings if available. 9) First week reading (ch ...
... Must have read chapter by week before, have paper in mind for assignment Rest of group: come up with paper we'd like for follow up reading 7) Questions--not optional. Submit >=36 h before discussion. 8) Website will list readings. Will post pdf of readings if available. 9) First week reading (ch ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... What percentage of the difference among people’s height can be attributed to their genes? ...
... What percentage of the difference among people’s height can be attributed to their genes? ...
GENETICS Anno accademico 2016/17 CdS BIOLOGICAL
... Problems related to genetics of blood groups. Exclusion of paternity 'by analysis of blood groups. related exercises. Example of sickle cell hemoglobin: complete dominance, co-dominance, incomplete dominance depending on the analyzed phenotype. Interactions between allelic series in single locus, as ...
... Problems related to genetics of blood groups. Exclusion of paternity 'by analysis of blood groups. related exercises. Example of sickle cell hemoglobin: complete dominance, co-dominance, incomplete dominance depending on the analyzed phenotype. Interactions between allelic series in single locus, as ...
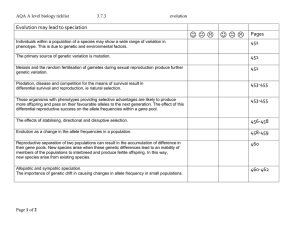
doc 3.7.3 evolution checklist
... Allopatric and sympatric speciation. The importance of genetic drift in causing changes in allele frequency in small populations. ...
... Allopatric and sympatric speciation. The importance of genetic drift in causing changes in allele frequency in small populations. ...
Genetic mapping
... • If we have more than one marker we need to deal with the issue of multiple testing. The solution of this problem depends on the intermarker spacings and the sample size. • One could use permutation tests or other simulation based methods to obtain p-values. • If the sample size is large, one can a ...
... • If we have more than one marker we need to deal with the issue of multiple testing. The solution of this problem depends on the intermarker spacings and the sample size. • One could use permutation tests or other simulation based methods to obtain p-values. • If the sample size is large, one can a ...
- U
... • Y-linked genes are found on the Y chromosome, symbolized by X, YR, Yr • Thomas Morgan experimented with the eye color of fruit flies (Drosophilia) to determine Xlinkage ...
... • Y-linked genes are found on the Y chromosome, symbolized by X, YR, Yr • Thomas Morgan experimented with the eye color of fruit flies (Drosophilia) to determine Xlinkage ...
hedrickbiology
... This results in many different physical traits called __________ Phenotypes can be expressed on a graph as what shape? A ____-________ curve 15. Mutations: natural/unnatural; random/specific; planned/accidental 15. Mutations are ___________, __________, ___________ Natural selection: random/specific ...
... This results in many different physical traits called __________ Phenotypes can be expressed on a graph as what shape? A ____-________ curve 15. Mutations: natural/unnatural; random/specific; planned/accidental 15. Mutations are ___________, __________, ___________ Natural selection: random/specific ...
Chapter 7 (Genetics of Organisms)
... Gregor Mendel's work was done about 140 yrs. ago, but even now much of what we know about genetics is based on Mendel's work and illustrated by it. Gregor Mendel was born in 1822 on a farm in Heinzendorf, Austria. At age 21 entered the Augustinian order of the Roman Catholic Church. As a monk he - s ...
... Gregor Mendel's work was done about 140 yrs. ago, but even now much of what we know about genetics is based on Mendel's work and illustrated by it. Gregor Mendel was born in 1822 on a farm in Heinzendorf, Austria. At age 21 entered the Augustinian order of the Roman Catholic Church. As a monk he - s ...
Document
... Difficult Predictions • Incomplete Dominance is when two different alleles for the same trait combine. R=red, W=white RW= Pink ...
... Difficult Predictions • Incomplete Dominance is when two different alleles for the same trait combine. R=red, W=white RW= Pink ...
Intro. to Genetic Powerpoint
... inheritance of traits. • The “factors” exist in pairs: the female contributes one and the male contributes one. • We now refer to the “factors” that control traits as genes. • The different forms of a gene are called alleles. ...
... inheritance of traits. • The “factors” exist in pairs: the female contributes one and the male contributes one. • We now refer to the “factors” that control traits as genes. • The different forms of a gene are called alleles. ...
Chapter 12
... Extensions to Mendel Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human hei ...
... Extensions to Mendel Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human hei ...