P Cross
... Mendel’s Peas were ideal for learning about inheritance, but they do not represent the norm… • Traits in pea plants are determined by just two alleles • In peas, one allele is clearly dominant & the other is clearly recessive • However, things aren’t always this clearcut and simple in the world of ...
... Mendel’s Peas were ideal for learning about inheritance, but they do not represent the norm… • Traits in pea plants are determined by just two alleles • In peas, one allele is clearly dominant & the other is clearly recessive • However, things aren’t always this clearcut and simple in the world of ...
Name - Animo Venice Biology
... – The allele for widow’s peak (W) is dominant over the allele for no widow’s peak (w). ...
... – The allele for widow’s peak (W) is dominant over the allele for no widow’s peak (w). ...
About Genetic Diseases
... Genetic diseases are defined as diseases caused by aberrations of genetic material. Therefore, these diseases can potentially be passed from generation to generation. However, not every patient has a family history of a similar problem. This is because new mutations can occur when an individual inhe ...
... Genetic diseases are defined as diseases caused by aberrations of genetic material. Therefore, these diseases can potentially be passed from generation to generation. However, not every patient has a family history of a similar problem. This is because new mutations can occur when an individual inhe ...
Notes - MyWeb
... An individual with brown and blue alleles of the bey2 gene on chromosome 15. There are two copies of chromosome 15. Each copy has the bey2 gene. On one copy the bey2 gene is in the brown allele, in the other the bey2 gene is in the blue allele. The difference between the brown and blue alleles is du ...
... An individual with brown and blue alleles of the bey2 gene on chromosome 15. There are two copies of chromosome 15. Each copy has the bey2 gene. On one copy the bey2 gene is in the brown allele, in the other the bey2 gene is in the blue allele. The difference between the brown and blue alleles is du ...
BIO 420 – Mammalian Physiology
... A. Dihybrid crosses involving at least one non-classical ratio will result in F2 progeny with altered ratios as well. B. Example – Inheritance of albinism and blood type in the same individual VI. Gene Interaction A. Definition – phenotype may be affected by more than one gene B. Epistasis – masking ...
... A. Dihybrid crosses involving at least one non-classical ratio will result in F2 progeny with altered ratios as well. B. Example – Inheritance of albinism and blood type in the same individual VI. Gene Interaction A. Definition – phenotype may be affected by more than one gene B. Epistasis – masking ...
Natural Selection - Northwest ISD Moodle
... When natural selection favors one extreme of a trait. Over time, the favored extreme will become more common and the other extreme will be less common or ...
... When natural selection favors one extreme of a trait. Over time, the favored extreme will become more common and the other extreme will be less common or ...
Natural Selection on the Olfactory Receptor Gene Family in
... with at intergenic region (a stretch of DNA sequences located between clusters of genes that contain few or no genes) ...
... with at intergenic region (a stretch of DNA sequences located between clusters of genes that contain few or no genes) ...
Selection and Biotechnology: the best of both worlds
... phenotype, without knowledge of the number of genes that affect the trait or the effects of each gene. In this quantitative genetic approach to genetic improvement, the genetic architecture of traits of interest has essentially been treated as a ‘black box’. Despite this, the substantial rates of ge ...
... phenotype, without knowledge of the number of genes that affect the trait or the effects of each gene. In this quantitative genetic approach to genetic improvement, the genetic architecture of traits of interest has essentially been treated as a ‘black box’. Despite this, the substantial rates of ge ...
Nature VS Nurture
... NATURE • When biology determines behavior • Tower of London • Explains why people who are related to each other- resemble each other ...
... NATURE • When biology determines behavior • Tower of London • Explains why people who are related to each other- resemble each other ...
Day 12: Genetics Part 2 Powerpoint
... A pedigree chart, or just pedigree, shows family history for a particular ...
... A pedigree chart, or just pedigree, shows family history for a particular ...
Genetic Inheritance Type Review
... Some traits have more than two alleles and thus have unique inheritance patterns. For example, human blood type is controlled by three alleles (A, B, O). O is recessive and A and B are co-dominant. A person must receive two O alleles for them to have type O blood. If a person receives an A allele an ...
... Some traits have more than two alleles and thus have unique inheritance patterns. For example, human blood type is controlled by three alleles (A, B, O). O is recessive and A and B are co-dominant. A person must receive two O alleles for them to have type O blood. If a person receives an A allele an ...
bio 11 genetics sep 15
... Single Gene and Polygenic traits The number of genes that control a trait determine the # of phenotypes Single gene trait-one gene controls a trait Widow’s peak/attached vs unattached earlobes Phenotypic ratios are determined by frequency of alleles and whether alleles are dominant or recessive ...
... Single Gene and Polygenic traits The number of genes that control a trait determine the # of phenotypes Single gene trait-one gene controls a trait Widow’s peak/attached vs unattached earlobes Phenotypic ratios are determined by frequency of alleles and whether alleles are dominant or recessive ...
16.1 Genes and Variations
... • Random change in allele frequency (number of times you see a certain letter for a gene) that occur in small populations • Individuals carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. ...
... • Random change in allele frequency (number of times you see a certain letter for a gene) that occur in small populations • Individuals carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. ...
Slide 1
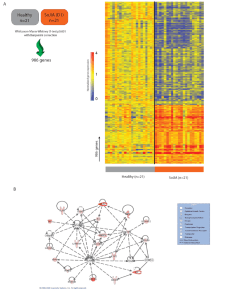
... imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s measurement in the healthy controls. To identify transcripts differentially expressed between study groups that might serve as classifiers, class comparison an ...
... imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s measurement in the healthy controls. To identify transcripts differentially expressed between study groups that might serve as classifiers, class comparison an ...
BIOLOGY CLASS NOTES UNIT 8 Human Heredity PART 2
... ABO blood type is inherited by multiple alleles Rh blood type (+ or -) is inherited independently of ABO blood type Coded by TWO genes: RHD and RHCE Rh+ is DOMINANT Rh is also an antigen on the surface of the red blood cell ...
... ABO blood type is inherited by multiple alleles Rh blood type (+ or -) is inherited independently of ABO blood type Coded by TWO genes: RHD and RHCE Rh+ is DOMINANT Rh is also an antigen on the surface of the red blood cell ...
BIOLOGY: Genotypes and Phenotypes
... draw a picture of their kid based on their coin flip phenotypes. Student Objective(s): Students will learn the difference between a genotype and a phenotype. They will demonstrate that recombination of gametes (demonstrated by flipping coins) will result in the formation of unique individuals. Integ ...
... draw a picture of their kid based on their coin flip phenotypes. Student Objective(s): Students will learn the difference between a genotype and a phenotype. They will demonstrate that recombination of gametes (demonstrated by flipping coins) will result in the formation of unique individuals. Integ ...
Unit 6: Mendelian Genetics
... Gene Mapping based on recombination frequencies Given the following table, construct a simple recombination map for the location of genes on a particular chromosome: P and L – 30% L and X – 5% X and P – 35% M and P – 10% ...
... Gene Mapping based on recombination frequencies Given the following table, construct a simple recombination map for the location of genes on a particular chromosome: P and L – 30% L and X – 5% X and P – 35% M and P – 10% ...
Mendel & Heredity
... Multiple alleles – A trait controlled by three or more alleles. Ex. Blood type Incomplete dominance – When a heterozygous individaul has a phenotype that is intermediate (blending) between the phenotypes of its two homozygous parents. Ex. Red flower crossed with white flower and all the offspring ar ...
... Multiple alleles – A trait controlled by three or more alleles. Ex. Blood type Incomplete dominance – When a heterozygous individaul has a phenotype that is intermediate (blending) between the phenotypes of its two homozygous parents. Ex. Red flower crossed with white flower and all the offspring ar ...
genetic maps
... This illustrates the Hardy-Weinberg Law, which says that, if you assume mating happens at random, the proportions of the different combinations in the blood samples should be as above. The researchers can check, using some simple statistical tests, to see whether the relative frequencies of the comb ...
... This illustrates the Hardy-Weinberg Law, which says that, if you assume mating happens at random, the proportions of the different combinations in the blood samples should be as above. The researchers can check, using some simple statistical tests, to see whether the relative frequencies of the comb ...
Introduction to Genetics
... • Austrian monk who studied mathematics and science • As a boy he could predict the possible types of flowers and fruits that would result from crossbreeding two plants in his father’s garden ...
... • Austrian monk who studied mathematics and science • As a boy he could predict the possible types of flowers and fruits that would result from crossbreeding two plants in his father’s garden ...
File
... Population in the colonial history of Martha's Vineyard An unusually high occurrence of deafness among it's inhabitants Result of genetic drift The population was so small that differing traits from outside populations could not enter in ...
... Population in the colonial history of Martha's Vineyard An unusually high occurrence of deafness among it's inhabitants Result of genetic drift The population was so small that differing traits from outside populations could not enter in ...
Polygenic Inheritance and Epistasis
... 1. Ear length in corn is the result of polygenic inheritance. Ear length is determined by two pairs of genes. When both genes are homozygous dominant then the ear of corn is long and when they are both recessive then the corn is short. The presence of a heterozygous gene results in plants that have ...
... 1. Ear length in corn is the result of polygenic inheritance. Ear length is determined by two pairs of genes. When both genes are homozygous dominant then the ear of corn is long and when they are both recessive then the corn is short. The presence of a heterozygous gene results in plants that have ...
GTEx_Intro_062513
... Generate public resource with tissuespecific eQTLs and gene and isoform expression data across multiple human tissues. Contribute to understanding of effects of genetic variation on gene expression and regulation Assist in interpretation of disease/trait GWAS signals Collect on average 30 tissues pe ...
... Generate public resource with tissuespecific eQTLs and gene and isoform expression data across multiple human tissues. Contribute to understanding of effects of genetic variation on gene expression and regulation Assist in interpretation of disease/trait GWAS signals Collect on average 30 tissues pe ...
Heredity Study Guide
... 19. What is the difference between genetic engineering and selective breeding? Genetic engineering: the actual DNA is altered in some way by inserting a needed gene directly into a persons cells Selective breeding: specific traits are selected in the parents in order to ensure they are passed to the ...
... 19. What is the difference between genetic engineering and selective breeding? Genetic engineering: the actual DNA is altered in some way by inserting a needed gene directly into a persons cells Selective breeding: specific traits are selected in the parents in order to ensure they are passed to the ...