Chapter 8 Constant Current Sources
... Magnitude and direction of resultant source Add currents in one direction Subtract currents in opposite direction ...
... Magnitude and direction of resultant source Add currents in one direction Subtract currents in opposite direction ...
Test Procedure for the LV5693PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors TEST Procedure
... through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimum voltage. Load regulation Load regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as t ...
... through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimum voltage. Load regulation Load regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as t ...
ac-circuits-test-16
... 6. An inductor in a high frequency ac circuit nearly amounts to an open circuit. A capacitor in a high frequency ac circuit nearly amounts to a ‘short circuit’. Explain. (2) ...
... 6. An inductor in a high frequency ac circuit nearly amounts to an open circuit. A capacitor in a high frequency ac circuit nearly amounts to a ‘short circuit’. Explain. (2) ...
Datasheet - CREATIVE CHIPS GmbH
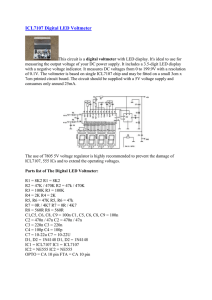
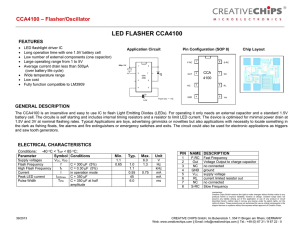
... The CCA4100 is an insensitive and easy to use IC to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). For operating it only needs an external capacitor and a standard 1.5V battery cell. The circuite is self starting and includes internal timing resistors and a resistor to limit LED current. The device is optimise ...
... The CCA4100 is an insensitive and easy to use IC to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). For operating it only needs an external capacitor and a standard 1.5V battery cell. The circuite is self starting and includes internal timing resistors and a resistor to limit LED current. The device is optimise ...
Things you should know about LED`s and
... its capacitance is decreased and therefore it can respond 1M faster. The speed of the transimpedance amplifier to the right will be faster than the one above. Note: In this case the output will be positive since the polarity of the diode is Vout the opposite of the above circuit. The diode capacitan ...
... its capacitance is decreased and therefore it can respond 1M faster. The speed of the transimpedance amplifier to the right will be faster than the one above. Note: In this case the output will be positive since the polarity of the diode is Vout the opposite of the above circuit. The diode capacitan ...
LED Current Regulators - Integrated Silicon Solution
... follows. When LED VSupply is applied Q2 will turn on because it gets its base current through R1. As Q2 turns on, the ILED will begin to flow through the LED, through Q2, and through RLED. As this current flows through RLED, the voltage across RLED (VR) will increase due to ohm’s law, where VR = ILE ...
... follows. When LED VSupply is applied Q2 will turn on because it gets its base current through R1. As Q2 turns on, the ILED will begin to flow through the LED, through Q2, and through RLED. As this current flows through RLED, the voltage across RLED (VR) will increase due to ohm’s law, where VR = ILE ...
Name Symbol Units
... Current, Voltage and Resistance This is how an alkaline cell (AA battery) works. TOP ...
... Current, Voltage and Resistance This is how an alkaline cell (AA battery) works. TOP ...
Electricity Ohms, Power 2013
... I=V/R And, to find Resistance, we need to DIVIDE voltage by current. R= V I To find voltage we multiple current and resistance. V = IR ...
... I=V/R And, to find Resistance, we need to DIVIDE voltage by current. R= V I To find voltage we multiple current and resistance. V = IR ...
Voltage in Electrical Systems
... Define electric potential, or voltage. Differentiate between AC and DC. Identify the most common source of DC voltage. Describe how to connect DC voltage sources so that ...
... Define electric potential, or voltage. Differentiate between AC and DC. Identify the most common source of DC voltage. Describe how to connect DC voltage sources so that ...
Series wiring means that the devices are connected in such a way
... in series, I is constant, the V is divided between the resistors (V1 +V2 = V), and the equivalent resistance RS is the sum of the individual resistances (RS = R1 + R2, etc.). ...
... in series, I is constant, the V is divided between the resistors (V1 +V2 = V), and the equivalent resistance RS is the sum of the individual resistances (RS = R1 + R2, etc.). ...
Circuits Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... When you purchase a light bulb, the wattage is usually listed. Watts are the units of energy used per second known as the power. Power is equal to the voltage multiplied by the current. ...
... When you purchase a light bulb, the wattage is usually listed. Watts are the units of energy used per second known as the power. Power is equal to the voltage multiplied by the current. ...
NOTES 9.1: Series and Parallel Circuits Series: One Pathway
... Voltage is the __________________________ difference in __________________________ between two points. If electrons________ 12 V from the battery, they will ________all 12 V as they travel from the – ve to the +ve terminal of the battery through the circuit Staircase analogy –12 steps up-gain potent ...
... Voltage is the __________________________ difference in __________________________ between two points. If electrons________ 12 V from the battery, they will ________all 12 V as they travel from the – ve to the +ve terminal of the battery through the circuit Staircase analogy –12 steps up-gain potent ...
EEG 443
... 1. Compute the apparent power S, the reactive power Q and load Power Factor (PF) from the measured voltage, current and real Power for each of the 7 cases a) through g). Indicate for each case whether the power factor is lagging or leading. 2. Use the measured value of the source voltage and the giv ...
... 1. Compute the apparent power S, the reactive power Q and load Power Factor (PF) from the measured voltage, current and real Power for each of the 7 cases a) through g). Indicate for each case whether the power factor is lagging or leading. 2. Use the measured value of the source voltage and the giv ...
POTI-MODUL MIRO 12.4, 24VDC/ outp. 0...10VDC Transmitter
... Murrelektronik B.V. | Takkebijsters 3,4817 BL Breda | Fon 085-22 20 282,Fax 085-22 20 283 | shop@murrelektronik.nl | shop.murrelektronik.nl ...
... Murrelektronik B.V. | Takkebijsters 3,4817 BL Breda | Fon 085-22 20 282,Fax 085-22 20 283 | shop@murrelektronik.nl | shop.murrelektronik.nl ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.