Circuit Sums with ac
... If we have a series circuit containing more than one of the above, we have to add them up as if they are Vectors (we actually call them "Phasors"). ...
... If we have a series circuit containing more than one of the above, we have to add them up as if they are Vectors (we actually call them "Phasors"). ...
CS 436 HCI Technology Basic Electricity/Electronics Review 1 Basic Quantities and Units
... 2) If Vin > 0.7volts so Vout ...
... 2) If Vin > 0.7volts so Vout ...
CS 436 HCI Technology Basic Electricity/Electronics Review 1 Basic Quantities and Units
... 2) If Vin > 0.7volts so Vout ...
... 2) If Vin > 0.7volts so Vout ...
Linearity and Superposition - No-IP
... (current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone. This helps to analyze a linear circuit with more than one independent source by calculating the ...
... (current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone. This helps to analyze a linear circuit with more than one independent source by calculating the ...
Project Specification - ECE Senior Design
... Higher than 95% for 250 W resistive load with minimal efficiency degradation up to peak power and down to minimum power. Additional scoring points will be awarded for efficiencies higher than ...
... Higher than 95% for 250 W resistive load with minimal efficiency degradation up to peak power and down to minimum power. Additional scoring points will be awarded for efficiencies higher than ...
Exam questions
... 1. Explain the terms power rating and tolerance in relation to resistors. 2. A 10 Ω resistor has a current of 5 amps flowing through it. (a) Calculate the power dissipated in the resistor. (b) State whether the resistor should be of wire-wound or metal film construction. Explain your answer. 3. Draw ...
... 1. Explain the terms power rating and tolerance in relation to resistors. 2. A 10 Ω resistor has a current of 5 amps flowing through it. (a) Calculate the power dissipated in the resistor. (b) State whether the resistor should be of wire-wound or metal film construction. Explain your answer. 3. Draw ...
Electricity Basics
... Voltage is similar to water pressure. It is noted V and measured in Volts Current is similar to flow rate. It is noted I and measured in Amperes For a same wire (/pipe), the higher the voltage (/pressure), the higher the current (/flow rate) ...
... Voltage is similar to water pressure. It is noted V and measured in Volts Current is similar to flow rate. It is noted I and measured in Amperes For a same wire (/pipe), the higher the voltage (/pressure), the higher the current (/flow rate) ...
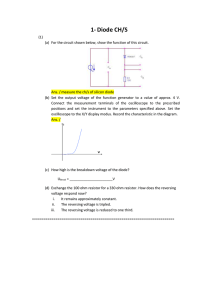
Diode CH/S
... (f) Which of the following statements are correct? The ripple... i. Becomes lower as the load increases. ii. Always remains the same. ...
... (f) Which of the following statements are correct? The ripple... i. Becomes lower as the load increases. ii. Always remains the same. ...
The primary current, , in a conductor through a magnetic core will
... If there is no power lost in the toroid and the compensation winding, then the equivalent insertion impedance, , of the Current Transducer can be estimated by equating the power dissipated in with the power dissipated in the Burden Resistor . This shows that the equivalent insertion impedanc ...
... If there is no power lost in the toroid and the compensation winding, then the equivalent insertion impedance, , of the Current Transducer can be estimated by equating the power dissipated in with the power dissipated in the Burden Resistor . This shows that the equivalent insertion impedanc ...
experiment 2 - Portal UniMAP
... 1. To learn the relationship among R, V and I. 2. To experimentally prove the mathematical relationship among R, V and I. INTRODUCTION Ohm’s law defines that voltage is proportional to the current and vice versa. The circuit current is inversely proportional to the resistance R. Both current and vol ...
... 1. To learn the relationship among R, V and I. 2. To experimentally prove the mathematical relationship among R, V and I. INTRODUCTION Ohm’s law defines that voltage is proportional to the current and vice versa. The circuit current is inversely proportional to the resistance R. Both current and vol ...
Test Procedure for the LV56801PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors
... Line regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as the input voltage is varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimu ...
... Line regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as the input voltage is varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimu ...
Ohms Law Notes
... Current from a battery travels from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. ...
... Current from a battery travels from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. ...
Document
... • Ruggedness and noise immunity are accomplished using an advanced blanking scheme and double-pulse suppression that allows reliable operation in fixed and variable frequency applications. • Supply circuitry is not necessary because the supply comes from the output voltage or from the winding from t ...
... • Ruggedness and noise immunity are accomplished using an advanced blanking scheme and double-pulse suppression that allows reliable operation in fixed and variable frequency applications. • Supply circuitry is not necessary because the supply comes from the output voltage or from the winding from t ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.