characteristics of passive circuit elements (r,l,c)
... Capacitors are classified according to the dielectric material used in their fabrication. The ranges of values available vary from type to type. Some of the commonly encountered types are: Electrolytic (above 1 F), Polyester (0.001-10 F), Paper (0.001-10 F), Mica (0.001-0.1 F) and Ceramic (less ...
... Capacitors are classified according to the dielectric material used in their fabrication. The ranges of values available vary from type to type. Some of the commonly encountered types are: Electrolytic (above 1 F), Polyester (0.001-10 F), Paper (0.001-10 F), Mica (0.001-0.1 F) and Ceramic (less ...
Lab 4: Bipolar transistors and transistor circuits Lab 4: Bipolar
... series with the load. The blocking capacitor keeps the load from changing the DC biasing scheme while still having a very low impedance at frequencies in the kHz range—for example, a 4.7 μF capacitor has XC=34 Ω at 1 kHz.) 4-5 Transistor switch The following circuit illustrates the use of a transist ...
... series with the load. The blocking capacitor keeps the load from changing the DC biasing scheme while still having a very low impedance at frequencies in the kHz range—for example, a 4.7 μF capacitor has XC=34 Ω at 1 kHz.) 4-5 Transistor switch The following circuit illustrates the use of a transist ...
BD238
... with “Base Island” layout. The resulting transistor shows exceptional high gain performance coupled with very low saturation voltage. The NPN type is BD237. ...
... with “Base Island” layout. The resulting transistor shows exceptional high gain performance coupled with very low saturation voltage. The NPN type is BD237. ...
Lecture27
... 1. The amount of current is the same at every place in a circuit; I=q/t. 2. The power provided by the battery (P=IDV) is exactly equal to the power dissipated in the resistors (P=I2R). 3. Ohm’s Law applies to resistors: DV=IR 4. Series circuit: effective R = R1 + R2 + R3 5. Parallel circuit: effecti ...
... 1. The amount of current is the same at every place in a circuit; I=q/t. 2. The power provided by the battery (P=IDV) is exactly equal to the power dissipated in the resistors (P=I2R). 3. Ohm’s Law applies to resistors: DV=IR 4. Series circuit: effective R = R1 + R2 + R3 5. Parallel circuit: effecti ...
Maxwell`s equation
... point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also i ...
... point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also i ...
Trench Field-Stop IGBT3 Turn-Off
... similar to loading a capacitor by a constant current. This leads to the equivalent circuit of Figure 2, which represents the switching of a Trench-Fieldstop IGBT by the output characteristics to describe the static characteristics, a collector-gate voltage dependent capacitance a con-stant gate emit ...
... similar to loading a capacitor by a constant current. This leads to the equivalent circuit of Figure 2, which represents the switching of a Trench-Fieldstop IGBT by the output characteristics to describe the static characteristics, a collector-gate voltage dependent capacitance a con-stant gate emit ...
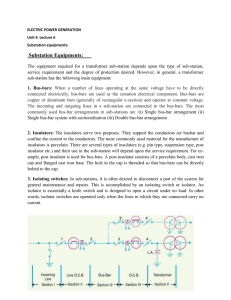
Substation Equipments
... Single bus-bar system with sectionalisation (iii) Double bus-bar arrangement 2. Insulators: The insulators serve two purposes. They support the conductors (or busbar and confine the current to the conductors. The most commonly used material for the manufacture of insulators is porcelain. There are s ...
... Single bus-bar system with sectionalisation (iii) Double bus-bar arrangement 2. Insulators: The insulators serve two purposes. They support the conductors (or busbar and confine the current to the conductors. The most commonly used material for the manufacture of insulators is porcelain. There are s ...
Transient currents and voltages
... Build a RC circuit according to Figure 1, using C = 1.0μF and the Rvar (Potentiometer 5‐25kΩ). Open the Desktop folder: 2nd Yr Lab Files and select Charge and Discharge of a Capacitor (Lab View Application). The Analog Output works as a function generator. Use the Square Wave form and vary the ...
... Build a RC circuit according to Figure 1, using C = 1.0μF and the Rvar (Potentiometer 5‐25kΩ). Open the Desktop folder: 2nd Yr Lab Files and select Charge and Discharge of a Capacitor (Lab View Application). The Analog Output works as a function generator. Use the Square Wave form and vary the ...
NCV885300EVB NCV885300 Evaluation Board User's Manual •
... way to evaluate and integrate a complete high-efficiency non-synchronous buck converter design. No additional components are required, other than dc supplies for the input voltage and enable pin. The board can also be connected to an external clock source to synchronize the switching frequency. The ...
... way to evaluate and integrate a complete high-efficiency non-synchronous buck converter design. No additional components are required, other than dc supplies for the input voltage and enable pin. The board can also be connected to an external clock source to synchronize the switching frequency. The ...
electric field
... 1. Each device in the circuit sees the full battery voltage. 2. Each device in the circuit may be turned off independently without stopping the current flowing to other devices in the circuit. ...
... 1. Each device in the circuit sees the full battery voltage. 2. Each device in the circuit may be turned off independently without stopping the current flowing to other devices in the circuit. ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.






![Series and Parallel Circuits - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001582563_1-10b2646b4b8841784288899ef5e382c0-300x300.png)