Series and Parallel Circuit Worksheet
... resistor connected in series. 2. Calculate the total resistance for ten 120 ohm resistors in series. 3. A string of fifty 15 ohm Christmas tree lights are connected in series. One burns out, they all burn out. Calculate the total resistance. 4. Calculate the total resistance for two 180 ohm resistor ...
... resistor connected in series. 2. Calculate the total resistance for ten 120 ohm resistors in series. 3. A string of fifty 15 ohm Christmas tree lights are connected in series. One burns out, they all burn out. Calculate the total resistance. 4. Calculate the total resistance for two 180 ohm resistor ...
Ohm_Law
... component. Again, set the scale to the maximum and then decrease the scale until you have obtained the highest resolution measurement. Resistance measurements should not be made on resistors that are wired into a circuit as the measurement will also include the effect of the other components in ...
... component. Again, set the scale to the maximum and then decrease the scale until you have obtained the highest resolution measurement. Resistance measurements should not be made on resistors that are wired into a circuit as the measurement will also include the effect of the other components in ...
I battery = I 1 = I 2 = I 3
... Two resistors connected end-to-end are said to be connected in series. The total resistance is simply the sum of the two. In this case, it would be 22000 + 33 = 22033 ohms. If 1 volt is applied to the open end of the 22K resistor, the current through the whole circuit would be I = V/R = 1/22033 or . ...
... Two resistors connected end-to-end are said to be connected in series. The total resistance is simply the sum of the two. In this case, it would be 22000 + 33 = 22033 ohms. If 1 volt is applied to the open end of the 22K resistor, the current through the whole circuit would be I = V/R = 1/22033 or . ...
power transformers
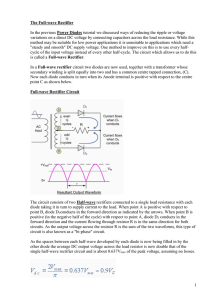
... convection in free air or otherwise) and the power line input voltage and frequency also have an effect on the transformer temperature. These things should all be properly related to the results in any specific application. The “RT-Series” of transformers may also be used in rectifier circuits other ...
... convection in free air or otherwise) and the power line input voltage and frequency also have an effect on the transformer temperature. These things should all be properly related to the results in any specific application. The “RT-Series” of transformers may also be used in rectifier circuits other ...
1 Figure 2. Equivalent circuit of figure 1 if RE= R1+
... Also note that the voltage on each resistance is equal to the product of the value of the resistance (R) expressed in ohms and the value of the current (I) flowing though it expressed in Amperes. For example the value of voltage (V1) on resistance R1 in the above circuit will be V1= R1*I, Similarly ...
... Also note that the voltage on each resistance is equal to the product of the value of the resistance (R) expressed in ohms and the value of the current (I) flowing though it expressed in Amperes. For example the value of voltage (V1) on resistance R1 in the above circuit will be V1= R1*I, Similarly ...
KSE 13003T NPN Silicon Transistor Absolute Maximum Ratings
... NEITHER DOES IT CONVEY ANY LICENSE UNDER ITS PATENT RIGHTS, NOR THE RIGHTS OF OTHERS. ...
... NEITHER DOES IT CONVEY ANY LICENSE UNDER ITS PATENT RIGHTS, NOR THE RIGHTS OF OTHERS. ...
download
... have the same frequency. That is , when the input sources have the same frequency, we can find the phasor response due to each source acting alone and obtain the total response by adding the individual phasors. If the sources have different frequencies, then superposition can still be used but its a ...
... have the same frequency. That is , when the input sources have the same frequency, we can find the phasor response due to each source acting alone and obtain the total response by adding the individual phasors. If the sources have different frequencies, then superposition can still be used but its a ...
16890_chapter-03-voltage
... Figure 3-24. The energy used by the circuit in passing current through the load (resistance) is called a voltage drop. A voltage drop occurs when current flows in the circuit. ...
... Figure 3-24. The energy used by the circuit in passing current through the load (resistance) is called a voltage drop. A voltage drop occurs when current flows in the circuit. ...
Ideal Transformer - Keith E. Holbert
... • Note that the two equations above can be combined to show that the power into the ideal transformer is zero, and it is therefore lossless v1 i1 + v2 i2 = 0 = p1 + p2 • An ideal transformer is very tightly coupled (k1) N2 n ...
... • Note that the two equations above can be combined to show that the power into the ideal transformer is zero, and it is therefore lossless v1 i1 + v2 i2 = 0 = p1 + p2 • An ideal transformer is very tightly coupled (k1) N2 n ...
Unit 4 - Section 13.9 2011 Solving Problems with Ohms Law
... The constant of proportionality is called resistance (R). Ohm’s Law is given by V = I R where V is the potential difference between two points which include a resistance (R). I is the current flowing through the resistance. What Does the Definition and Formula for Ohm’s Law Mean? If V varies (i.e., ...
... The constant of proportionality is called resistance (R). Ohm’s Law is given by V = I R where V is the potential difference between two points which include a resistance (R). I is the current flowing through the resistance. What Does the Definition and Formula for Ohm’s Law Mean? If V varies (i.e., ...
Walker3_ConcepTests_Ch21
... series, their voltages add. Thus the voltage across C2 and C3 each has to be 5 V, which is less than V1. ...
... series, their voltages add. Thus the voltage across C2 and C3 each has to be 5 V, which is less than V1. ...
EUP2571 White LED Step-Up Converter In Tiny SOT-23 Package
... backlight and keypad. Setting the divider-resistors (R1 & R2) is to get a constant output voltage that depends on the forward voltage and the numbers of series-LEDs. It can turn on backlight of main panel and keypad at the same time. Applying different duty cycle of PWM signal above 22kHz to the bac ...
... backlight and keypad. Setting the divider-resistors (R1 & R2) is to get a constant output voltage that depends on the forward voltage and the numbers of series-LEDs. It can turn on backlight of main panel and keypad at the same time. Applying different duty cycle of PWM signal above 22kHz to the bac ...
Electricity
... 4. TYPES OF CIRCUITS 4.2 PARALLEL CIRCUITS In parallel circuits different components are connected on different branches of the wire. If you follow the circuit diagram from one side of the cell to the other, you can only pass through all the different components if you follow all the branches. The ...
... 4. TYPES OF CIRCUITS 4.2 PARALLEL CIRCUITS In parallel circuits different components are connected on different branches of the wire. If you follow the circuit diagram from one side of the cell to the other, you can only pass through all the different components if you follow all the branches. The ...
Circuits II - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Current can branch to multiple paths • Current varies through each resistor (greater resistance = smaller current). • The current flowing into a node equals the current that flows out of that node I = I1 + I2 + I3 . • The voltage drop across each resistor is the same. ...
... Current can branch to multiple paths • Current varies through each resistor (greater resistance = smaller current). • The current flowing into a node equals the current that flows out of that node I = I1 + I2 + I3 . • The voltage drop across each resistor is the same. ...
CoolLED - Acal BFi
... Current sink to BS EN 60929:1992 EN61347-2-13 EN61000-3-2 EN61000-3-3 EN62384 EN60929 EN61547 EN55015 ...
... Current sink to BS EN 60929:1992 EN61347-2-13 EN61000-3-2 EN61000-3-3 EN62384 EN60929 EN61547 EN55015 ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.