Electrical Resistance
... 4.2 Calculate the effective resistance of the combination from your current and voltage measurements using the relation Reff =VAB/IA . Compare it with what is expected from the formula for combining resistors in series using the values RA and RB. Find the percentage error. 5. Resistors in parallel Y ...
... 4.2 Calculate the effective resistance of the combination from your current and voltage measurements using the relation Reff =VAB/IA . Compare it with what is expected from the formula for combining resistors in series using the values RA and RB. Find the percentage error. 5. Resistors in parallel Y ...
DC Voltmeters and Ammeters Ammeters Voltmeters Homework
... Measures ________________ Inserted into ________________ so ________________ passes ________________ it Connected in ________________ Coil usually measures only ________________ current Has ________________ ________________ connected in ________________ to galvanometer so excess current can ________ ...
... Measures ________________ Inserted into ________________ so ________________ passes ________________ it Connected in ________________ Coil usually measures only ________________ current Has ________________ ________________ connected in ________________ to galvanometer so excess current can ________ ...
Course Outline
... Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Understand, analyze, and safely use basic electrical and electronic circuits/systems and electromechanical devices 2. Troubleshoot and fix problems in electrical circuits/systems and electromechanical devices 3. Use the tools ...
... Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Understand, analyze, and safely use basic electrical and electronic circuits/systems and electromechanical devices 2. Troubleshoot and fix problems in electrical circuits/systems and electromechanical devices 3. Use the tools ...
Chapter 5: Diodes
... 2. Construct the full-wave rectifier with a voltage signal at 1 kHz, 4 diodes, an audio transformer, and a load resistor of 100 kΩ. Use a signal generator with 2 V peak to peak output and connect it to transformer in step up fashion. Measure the amplitude of the signal after transformer and characte ...
... 2. Construct the full-wave rectifier with a voltage signal at 1 kHz, 4 diodes, an audio transformer, and a load resistor of 100 kΩ. Use a signal generator with 2 V peak to peak output and connect it to transformer in step up fashion. Measure the amplitude of the signal after transformer and characte ...
Voltage-Divider Bias
... for all practical purposes we say that IE approximately equals IC. I E ≌ IC ...
... for all practical purposes we say that IE approximately equals IC. I E ≌ IC ...
Current and Resistance
... Consideration of the expression P = I2R might initially lead one to think that the reverse would be true. However, one must realize that the currents will not be the same in the two wires. ...
... Consideration of the expression P = I2R might initially lead one to think that the reverse would be true. However, one must realize that the currents will not be the same in the two wires. ...
5 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... • A series circuit is formed when any number of resistors are connected end-to-end so that there is only one path for current to flow. • Resister here means a device that has resistance. Example a light bulb. ...
... • A series circuit is formed when any number of resistors are connected end-to-end so that there is only one path for current to flow. • Resister here means a device that has resistance. Example a light bulb. ...
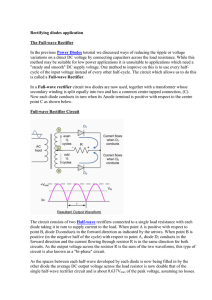
Rectifying diodes application
... given load and a smaller reservoir or smoothing capacitor than an equivalent half-wave rectifier. Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice that of the AC supply frequency (100Hz) where for the half-wave rectifier it is exactly equal to the supply frequency (50Hz). The amou ...
... given load and a smaller reservoir or smoothing capacitor than an equivalent half-wave rectifier. Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice that of the AC supply frequency (100Hz) where for the half-wave rectifier it is exactly equal to the supply frequency (50Hz). The amou ...
Document
... • directly proportional to the voltage across it (over a limited range of V) (more voltage more current) • inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor (the greater the resistance the less the current) ...
... • directly proportional to the voltage across it (over a limited range of V) (more voltage more current) • inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor (the greater the resistance the less the current) ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.