Freud and the Political - Unbound – Harvard Journal of the Legal Left
... the treatment of the individual psyche, its symptoms and vicissitudes, and if politics is about constructing a collectivity, then this boundary has always already been crossed. On the first page of Group Psychology and the Analysis of the Ego (1921), Freud starts off by claiming that, ultimately, no ...
... the treatment of the individual psyche, its symptoms and vicissitudes, and if politics is about constructing a collectivity, then this boundary has always already been crossed. On the first page of Group Psychology and the Analysis of the Ego (1921), Freud starts off by claiming that, ultimately, no ...
sample syllabus
... special attention to problems of interpretation in the humanities and related social sciences in both historical and theoretical contexts. Suspicion and Interpretation The philosopher Paul Ricoeur famously labeled Marx, Nietzsche, and Freud the “masters of suspicion.” Though they practiced theory an ...
... special attention to problems of interpretation in the humanities and related social sciences in both historical and theoretical contexts. Suspicion and Interpretation The philosopher Paul Ricoeur famously labeled Marx, Nietzsche, and Freud the “masters of suspicion.” Though they practiced theory an ...
Remaining Notes for Chapter 14
... Became popular in the mid-1950’s with the discovery of antipsychotic medications Led to a huge reduction in the number of hospitalizations The major classes of psychotropic medications ...
... Became popular in the mid-1950’s with the discovery of antipsychotic medications Led to a huge reduction in the number of hospitalizations The major classes of psychotropic medications ...
Module 24 - WLWV Staff Blogs
... • therapist and client talk about the client’s symptoms and problems with the goal of reaching or identifying the cause of the problem – Cognitive-behavior therapy • involves the application of principles of learning • therapist focuses on the client’s problem, identifies specific thoughts and behav ...
... • therapist and client talk about the client’s symptoms and problems with the goal of reaching or identifying the cause of the problem – Cognitive-behavior therapy • involves the application of principles of learning • therapist focuses on the client’s problem, identifies specific thoughts and behav ...
influenced his thinking about personality?
... Charcot demonstrated that hysteria had psychological origins (e.g., demonstrated that the symptoms could be created or removed under hypnosis). Breuer discovered that the symptoms could be removed by talking about their origins. Breuer referred to this remedy as the “talking cure.” Freud adop ...
... Charcot demonstrated that hysteria had psychological origins (e.g., demonstrated that the symptoms could be created or removed under hypnosis). Breuer discovered that the symptoms could be removed by talking about their origins. Breuer referred to this remedy as the “talking cure.” Freud adop ...
History and Approaches
... • Identify key contributors to personality theory (e.g. Paul Costa and Robert McCrae). ...
... • Identify key contributors to personality theory (e.g. Paul Costa and Robert McCrae). ...
some theoretical perspectives on human sexuality
... For example, the skeletons of humans, mice, and bats are strikingly similar, despite the different ways of life of these animals and the diversity of environments in which ...
... For example, the skeletons of humans, mice, and bats are strikingly similar, despite the different ways of life of these animals and the diversity of environments in which ...
File - mrbspsychsite
... Psychodynamic theory focuses on the role of the unconscious mind and on biological causes of personality differences. Behavioral and social cognitive focuses on how learning and environment affect personality. Humanistic focuses on the role of each person’s life experiences in personality developmen ...
... Psychodynamic theory focuses on the role of the unconscious mind and on biological causes of personality differences. Behavioral and social cognitive focuses on how learning and environment affect personality. Humanistic focuses on the role of each person’s life experiences in personality developmen ...
Chapter 1
... -Client variables (i.e., disorders, age, gender, race, intelligence, education, personalities, economic conditions) -Environmental conditions (i.e., physical settings such as hospital or universities, highly differentiated social and cultural systems). 7. Does psychotherapy work? -Eysenck (1952): Re ...
... -Client variables (i.e., disorders, age, gender, race, intelligence, education, personalities, economic conditions) -Environmental conditions (i.e., physical settings such as hospital or universities, highly differentiated social and cultural systems). 7. Does psychotherapy work? -Eysenck (1952): Re ...
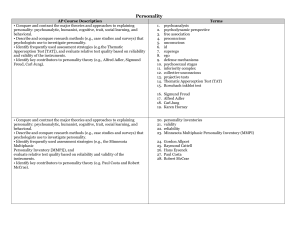
Personality Theory
... are underdeveloped in waking life. However, later research by Hall discovered that the traits people exhibit while they awake are also expressed in dreams. ...
... are underdeveloped in waking life. However, later research by Hall discovered that the traits people exhibit while they awake are also expressed in dreams. ...
Warm-Up for Monday, Nov. 29th
... be met; own satisfaction; no sense of reality • Ego = “the balancer;” based on reality principle; meets needs of id but takes into consideration reality of the situation; in a healthy person, ego is the strongest • Superego = moral part of us and develops due to the moral and ethical restraints plac ...
... be met; own satisfaction; no sense of reality • Ego = “the balancer;” based on reality principle; meets needs of id but takes into consideration reality of the situation; in a healthy person, ego is the strongest • Superego = moral part of us and develops due to the moral and ethical restraints plac ...
Challenge 9 – Critical Theory AIC
... ‘token of their self-respect’, and refers to women who for him as ‘girls’ believing that thy would not have the resolve to keep their strike. • Gerald and Eric both express a mixture of disdain and attraction to the prostitutes who work in the bar, and objectify them in their descriptions of the old ...
... ‘token of their self-respect’, and refers to women who for him as ‘girls’ believing that thy would not have the resolve to keep their strike. • Gerald and Eric both express a mixture of disdain and attraction to the prostitutes who work in the bar, and objectify them in their descriptions of the old ...
Quiz Chapter 2: Theories of Development (10 points)
... to pursue bodily pleasures to compromise between the id and superego to guide our unconscious thoughts ...
... to pursue bodily pleasures to compromise between the id and superego to guide our unconscious thoughts ...
Psychology: The Evolution of a Science
... one to see which parts of the brain are active during a given task ...
... one to see which parts of the brain are active during a given task ...
Chapter 17 Therapy - Germantown School District
... moving away from home and starting college two months ago. He’s heard a lot about Sigmund (1) Freud’s therapy, called (2) psychoanalysis, in which patients use (3) free association to express whatever comes to mind in order to uncover their (4) repressed unconscious conflicts. In this therapy, analy ...
... moving away from home and starting college two months ago. He’s heard a lot about Sigmund (1) Freud’s therapy, called (2) psychoanalysis, in which patients use (3) free association to express whatever comes to mind in order to uncover their (4) repressed unconscious conflicts. In this therapy, analy ...
Meaning or Medicine: The Future of Psychoanalysis
... in the United States, which grew from a fifty-year history of non-clinical, experimental methodologies under the dominance of behaviorist theories before the rise of clinical psychology after World War II. The Psychoanalytic tradition, as is well known, emerged outside of academia: in the clinics, m ...
... in the United States, which grew from a fifty-year history of non-clinical, experimental methodologies under the dominance of behaviorist theories before the rise of clinical psychology after World War II. The Psychoanalytic tradition, as is well known, emerged outside of academia: in the clinics, m ...
Chapter 2 Figures
... and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his ...
... and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his ...
Oedipus…The Myth. The Man. The Legend…
... Id: It’s all about me: Food, sex, aggression. The pleasure principle… Ego: Reality principle. Reason and caution…as well as independence. The Gatekeeper between Id, Superego and Reality. Superego: Conscience…moral…right v. wrong ...
... Id: It’s all about me: Food, sex, aggression. The pleasure principle… Ego: Reality principle. Reason and caution…as well as independence. The Gatekeeper between Id, Superego and Reality. Superego: Conscience…moral…right v. wrong ...
Chapter 17 Notes
... a. Religious ceremonies or physical punishment iii. Mental illness not a good term because it leaves the person feeling passive and helpless b. Functions of Psychotherapy i. Help people realize that they are responsible for their own problems ii. Only they can solve those problems iii. Major task of ...
... a. Religious ceremonies or physical punishment iii. Mental illness not a good term because it leaves the person feeling passive and helpless b. Functions of Psychotherapy i. Help people realize that they are responsible for their own problems ii. Only they can solve those problems iii. Major task of ...
psychopathology in historical context
... The Ego battles with Id and Superego to resolve conflicts, at times the resulting anxiety is so overwhelming that the Ego has to adopt unconscious protective processes called Ego Defense Mechanisms or Coping Styles. They have following characteristics in common 1. Operate at unconscious level. 2. Di ...
... The Ego battles with Id and Superego to resolve conflicts, at times the resulting anxiety is so overwhelming that the Ego has to adopt unconscious protective processes called Ego Defense Mechanisms or Coping Styles. They have following characteristics in common 1. Operate at unconscious level. 2. Di ...
Therapies - Rowena T
... free association, dream analysis, and transference. *free association *dream analysis *transference (countertransference) ...
... free association, dream analysis, and transference. *free association *dream analysis *transference (countertransference) ...
child development theory File
... Theories of child development More on Gesell Gesell’s classic study involved twin girls, both given training for motor skills but one given training for longer than the other. There was no measurable difference in the age at which either child acquired the skills, suggesting that development had ha ...
... Theories of child development More on Gesell Gesell’s classic study involved twin girls, both given training for motor skills but one given training for longer than the other. There was no measurable difference in the age at which either child acquired the skills, suggesting that development had ha ...