Chapter 15 Notes, Psych Therapies
... • The most popular form of therapyit is basically a smorgasbord where the therapist combines techniques from different schools of psychology. ...
... • The most popular form of therapyit is basically a smorgasbord where the therapist combines techniques from different schools of psychology. ...
Erikson`s Developmental Stages p. 35
... founded by Anna Freud (Sigmund’s daughter), and later worked in the United States with Henry Murray, who was interested in personality development throughout life. Erikson created his own personality theory based on psychosocial development. In it he described how identity develops in a series of ei ...
... founded by Anna Freud (Sigmund’s daughter), and later worked in the United States with Henry Murray, who was interested in personality development throughout life. Erikson created his own personality theory based on psychosocial development. In it he described how identity develops in a series of ei ...
Psychotherapies and Treatments Crosswalked with David Myers
... Yes; we will look at four major forms of psychotherapies based on different theories of human nature Psychoanalysis The first formal psychotherapy to emerge was psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud. Psychoanalysis: Aims Assumptions: Psychological problems originate from childhood repressed imp ...
... Yes; we will look at four major forms of psychotherapies based on different theories of human nature Psychoanalysis The first formal psychotherapy to emerge was psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud. Psychoanalysis: Aims Assumptions: Psychological problems originate from childhood repressed imp ...
Theories of Personality
... then, is “if it feels good, do it, but only if you can get away with it.” ...
... then, is “if it feels good, do it, but only if you can get away with it.” ...
Chapter 12 - Personality
... • An individual’s unique constellation of consistent behavior traits • Constellation because we have many behavior or personality traits • Consistent across time and situations ...
... • An individual’s unique constellation of consistent behavior traits • Constellation because we have many behavior or personality traits • Consistent across time and situations ...
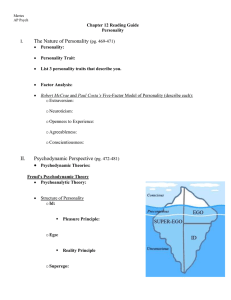
ch 12 personality reading guide
... In the space below, draw Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as a triangle. Label each space with the need and at least one example of that need. It might be helpful to do this in different colors. ...
... In the space below, draw Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as a triangle. Label each space with the need and at least one example of that need. It might be helpful to do this in different colors. ...
Dr. Axel Hoffer
... themselves from waging it. A major way we accomplish this is through continuously working, often with the help of analysis and self-analysis, to increase our capacity to maintain our emotional stability in the face of these intensities. Thus we could learn to find new forms of awareness, beyond word ...
... themselves from waging it. A major way we accomplish this is through continuously working, often with the help of analysis and self-analysis, to increase our capacity to maintain our emotional stability in the face of these intensities. Thus we could learn to find new forms of awareness, beyond word ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Certainly, any attempt to discuss psychodynamic theory in a book like this does a disservice to the many clinicians and theorists who have been instrumental in developing these theories. Nonetheless, for practical purposes, we will briefly review psychodynamic theories, and in doing so will highligh ...
... Certainly, any attempt to discuss psychodynamic theory in a book like this does a disservice to the many clinicians and theorists who have been instrumental in developing these theories. Nonetheless, for practical purposes, we will briefly review psychodynamic theories, and in doing so will highligh ...
Psychological Disorders Treatment Outline
... an approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the client’s problems, uses techniques from various forms of therapy Therapy- Psychoanalysis ...
... an approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the client’s problems, uses techniques from various forms of therapy Therapy- Psychoanalysis ...
Psychoanalysis - Programme Specifications
... learning outcomes of the modules. Option modules are subject to availability. Part time students can take the core modules in any order over two years; the precise balance of modules taken during the year should be discussed with the convenor of the MA. Lectures are knowledge focussed, explaining co ...
... learning outcomes of the modules. Option modules are subject to availability. Part time students can take the core modules in any order over two years; the precise balance of modules taken during the year should be discussed with the convenor of the MA. Lectures are knowledge focussed, explaining co ...
Psychology - Faribault Public Schools
... – Systematic desensitization (behavioral) might be best for someone with OCD ...
... – Systematic desensitization (behavioral) might be best for someone with OCD ...
human behaviour - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (the primitive part of our personality) will take control of the person, leading to eventual punishment (this is thus a form of Moral Anxiety). Moral Anxiety This form of anxiety comes from a fear of violating values and moral codes, and appears as feelings of guilt or shame. Defense Mechanisms Wh ...
... (the primitive part of our personality) will take control of the person, leading to eventual punishment (this is thus a form of Moral Anxiety). Moral Anxiety This form of anxiety comes from a fear of violating values and moral codes, and appears as feelings of guilt or shame. Defense Mechanisms Wh ...
Psychological Diseases
... -- hallucination; his own heart beat sense of guilt; -- the old man's heart, first heard in fact and then imagined to be heard; -- that of deathwatch beetles (see p. 46 par 2) -called so because “it emits a sound resembling the ticking of a watch, supposed to predict the death of some one of the f ...
... -- hallucination; his own heart beat sense of guilt; -- the old man's heart, first heard in fact and then imagined to be heard; -- that of deathwatch beetles (see p. 46 par 2) -called so because “it emits a sound resembling the ticking of a watch, supposed to predict the death of some one of the f ...
Erikson`s Theory of Psychosocial Development
... According to Erikson, our ego identity is constantly changing due to new experience and information we acquire in our daily interactions with others. ...
... According to Erikson, our ego identity is constantly changing due to new experience and information we acquire in our daily interactions with others. ...
Respond Holistically to Client Issues.Session 2
... • The patient talks freely about their life and one idea triggers another, then another. • Because the patient was able to talk freely; free association would occur and inevitably reveal ideas that were suppressed into the unconscious. • This is a helpful concept in allowing clients to freely discus ...
... • The patient talks freely about their life and one idea triggers another, then another. • Because the patient was able to talk freely; free association would occur and inevitably reveal ideas that were suppressed into the unconscious. • This is a helpful concept in allowing clients to freely discus ...
pptx
... Conclusions Freud Drew after Studying Conversion Disorder • There is an unconscious. • There are active processes of defense and repression. • Childhood sexuality is very important. ...
... Conclusions Freud Drew after Studying Conversion Disorder • There is an unconscious. • There are active processes of defense and repression. • Childhood sexuality is very important. ...
Preface
... phenomenological – that implies a constant attention and empathy, on the part of the therapist, to the intentionality with which the patient is revealed to her/him in the here and now of the therapeutic session. It is precisely the therapeutic support of this directionality that permits the authenti ...
... phenomenological – that implies a constant attention and empathy, on the part of the therapist, to the intentionality with which the patient is revealed to her/him in the here and now of the therapeutic session. It is precisely the therapeutic support of this directionality that permits the authenti ...
Personality - Gordon State College
... Charcot, who treated patients using hypnosis. • Freud also sought advice from psychiatrist Joseph Breuer, who used a “talking cure” therapy in which patients reported whatever came to mind. • Freud adapted these two techniques to his own emerging theory of the human mind. ...
... Charcot, who treated patients using hypnosis. • Freud also sought advice from psychiatrist Joseph Breuer, who used a “talking cure” therapy in which patients reported whatever came to mind. • Freud adapted these two techniques to his own emerging theory of the human mind. ...
Psychodynamic Psychotherapy
... through the phenomenon of transference. The term transference refers to the unconscious influence of past learning of traumatic interpersonal relationships on present emotional responses, behaviour and relationships. This maladaptive learning stems from childhood experiences and interferes with norm ...
... through the phenomenon of transference. The term transference refers to the unconscious influence of past learning of traumatic interpersonal relationships on present emotional responses, behaviour and relationships. This maladaptive learning stems from childhood experiences and interferes with norm ...
chapter 15 – therapies
... 4. Most frequently group 5. Emphasis on “whole person” 6. Try to make 7. Many techniques may be used – 8. If want to discuss third person 9. May use dreams D. Large-Group Awareness Training 1. est – Erhard 2. Pre-training session 3. Training over 4. Authoritarian trainer – 5. If express anger – 6. L ...
... 4. Most frequently group 5. Emphasis on “whole person” 6. Try to make 7. Many techniques may be used – 8. If want to discuss third person 9. May use dreams D. Large-Group Awareness Training 1. est – Erhard 2. Pre-training session 3. Training over 4. Authoritarian trainer – 5. If express anger – 6. L ...
Eric Treatment - UEN Instructure Canvas
... I. THERAPY AND TREATMENT A. Introduction Two forms of therapy are administered by people with very different training Biological Treatments: Drugs or direct intervention in brain function. Psychiatrists or other physicians (MDs) administer drugs or direct interventions to patients in hospital ...
... I. THERAPY AND TREATMENT A. Introduction Two forms of therapy are administered by people with very different training Biological Treatments: Drugs or direct intervention in brain function. Psychiatrists or other physicians (MDs) administer drugs or direct interventions to patients in hospital ...
Personality-Theories
... overwhelming stress as may happen with abuse, dissociation is a normal process that can happen to deal with the stress. For example, a child who experiences sexual abuse may ‘space out’ as a way to protect herself from remembering the event. When such stress or trauma happens over and over again, it ...
... overwhelming stress as may happen with abuse, dissociation is a normal process that can happen to deal with the stress. For example, a child who experiences sexual abuse may ‘space out’ as a way to protect herself from remembering the event. When such stress or trauma happens over and over again, it ...