Chemical Dynamics, Thermochemistry, and Quantum Chemistry
... Continue to record the temperature. Readings should be taken approximately every 30 seconds. The temperature should within a minute or so undergo a 1 to 2 degree jump. Continue monitoring the temperature for a 5 to 10 minute period following this jump. Do not stop monitoring temperature until the sl ...
... Continue to record the temperature. Readings should be taken approximately every 30 seconds. The temperature should within a minute or so undergo a 1 to 2 degree jump. Continue monitoring the temperature for a 5 to 10 minute period following this jump. Do not stop monitoring temperature until the sl ...
Thermodynamics Free-Response
... second reactant in reaction X is chlorine gas whereas the second reactant in reaction Y is liquid bromine. Liquids have lower entropies than gases, thus in reaction Y the reactants are more ordered (and have lower entropies) than in reaction X . The products of both reaction X and reaction Y have ab ...
... second reactant in reaction X is chlorine gas whereas the second reactant in reaction Y is liquid bromine. Liquids have lower entropies than gases, thus in reaction Y the reactants are more ordered (and have lower entropies) than in reaction X . The products of both reaction X and reaction Y have ab ...
Effect of microwave preheating on the bonding performance of flip
... A microwave (MW) preheating mechanism of anisotropic conductive adhesive film (ACF) has been introduced in order to reduce the bonding temperature for flip chip technology. Thermal curing of epoxy shows a very sluggish and non-uniform curing kinetics at the beginning of the curing reaction, but the ra ...
... A microwave (MW) preheating mechanism of anisotropic conductive adhesive film (ACF) has been introduced in order to reduce the bonding temperature for flip chip technology. Thermal curing of epoxy shows a very sluggish and non-uniform curing kinetics at the beginning of the curing reaction, but the ra ...
Analysis of PEA photopolymers at zero spatial frequency limit
... these materials are used in holographic applications, where high values of spatial frequencies are recorded. In this range of frequencies many processes are involved in the hologram formation, such as species diffusion, nonlocalpolymerization (due to the finite size of polymer chains), and shrinkage ...
... these materials are used in holographic applications, where high values of spatial frequencies are recorded. In this range of frequencies many processes are involved in the hologram formation, such as species diffusion, nonlocalpolymerization (due to the finite size of polymer chains), and shrinkage ...
Articles relacionats amb el Subcapítol 2.2 109
... original size after exposure to liquid ethanol. Solvent-induced expansion/contraction processes in open-framework metal–organic polymers have been very recently reported24–26, although the large volume changes shown by MOROF-1 (25–35%) have not been seen before. Similar time-dependent experiments fo ...
... original size after exposure to liquid ethanol. Solvent-induced expansion/contraction processes in open-framework metal–organic polymers have been very recently reported24–26, although the large volume changes shown by MOROF-1 (25–35%) have not been seen before. Similar time-dependent experiments fo ...
Chalcogenide glass microphotonics: Stepping into the spotlight
... In our mid-IR sensing demonstraresonators were prepared by thermal be tuned by controlled deformation. For tion, we again elect high-Q-factor glass evaporation of GSS glass film onto example, a focusing-dispersive element optical resonators for spectroscopic CaF2 substrates followed by lithographic ...
... In our mid-IR sensing demonstraresonators were prepared by thermal be tuned by controlled deformation. For tion, we again elect high-Q-factor glass evaporation of GSS glass film onto example, a focusing-dispersive element optical resonators for spectroscopic CaF2 substrates followed by lithographic ...
CHAPTER 1 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Overview The word LASER
... Nowadays most simultaneous generation of multi-wavelength are generated by diode pump solid state lasers. The drawbacks of these operations is that they are continuous or quasi continuous. These operations are difficult to control and in addition they have low peak power (Saiki 2011). ...
... Nowadays most simultaneous generation of multi-wavelength are generated by diode pump solid state lasers. The drawbacks of these operations is that they are continuous or quasi continuous. These operations are difficult to control and in addition they have low peak power (Saiki 2011). ...
Passive House - ISMART Building Group
... Transparent materials like glass let the short-wave radiation from the sun (sunlight) through, but the long wave radiation (heat) is absorbed and then passed on. In double glazed windows, the trapped gas between the layers of glass is the thermal insulator. In this case, the energy can enter the bui ...
... Transparent materials like glass let the short-wave radiation from the sun (sunlight) through, but the long wave radiation (heat) is absorbed and then passed on. In double glazed windows, the trapped gas between the layers of glass is the thermal insulator. In this case, the energy can enter the bui ...
PDF Version - Physics (APS)
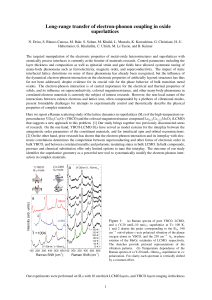
... Materials with extreme properties are not only of great theoretical interest but often also hold the key for unique applications. Solids at the two extremes of heat conductivity are an important example. On one hand, very low thermal conductivity is highly desirable for heatinsulation applications, ...
... Materials with extreme properties are not only of great theoretical interest but often also hold the key for unique applications. Solids at the two extremes of heat conductivity are an important example. On one hand, very low thermal conductivity is highly desirable for heatinsulation applications, ...
Photo cross-linkable poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers III: micro-fabricated temperature responsive hydrogels
... Micro-fabricated temperature responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) hydrogels were produced by photolithographic patterning of photo cross-linkable polymers. These polymers were synthesized by copolymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm) and 2-(dimethyl maleimido)-N-ethyl-acrylamide ...
... Micro-fabricated temperature responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) hydrogels were produced by photolithographic patterning of photo cross-linkable polymers. These polymers were synthesized by copolymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm) and 2-(dimethyl maleimido)-N-ethyl-acrylamide ...
effect of thermal stresses along crack surface on ultrasonic response
... !!!!!Change in temperature induces thermal expansion of the material. If this expansion is hindered, thermal stresses arise. Thermal stresses can arise because of either external or internal constraints. Internal constraints can be caused by nonuniform temperature distribution or nonuniform material ...
... !!!!!Change in temperature induces thermal expansion of the material. If this expansion is hindered, thermal stresses arise. Thermal stresses can arise because of either external or internal constraints. Internal constraints can be caused by nonuniform temperature distribution or nonuniform material ...
- JPS Journals
... terms of Fermi liquid theory and cannot be computed perturbatively in an expansion in the screened Coulomb interactions. Typically the spectra of strongly correlated materials do not remotely resemble the spectra of the corresponding Kohn–Sham system. Instead they contain excitations that resemble t ...
... terms of Fermi liquid theory and cannot be computed perturbatively in an expansion in the screened Coulomb interactions. Typically the spectra of strongly correlated materials do not remotely resemble the spectra of the corresponding Kohn–Sham system. Instead they contain excitations that resemble t ...
energy changes in physical and chemical processes
... QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF ENTHALPY CHANGE IN SOME CHEMICAL PROCESSES In order to compare enthalpy changes for different processes, the temperature and pressure of the reactants and products should be the same before and after the reaction. The standard conditions of temperature and pressure adop ...
... QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF ENTHALPY CHANGE IN SOME CHEMICAL PROCESSES In order to compare enthalpy changes for different processes, the temperature and pressure of the reactants and products should be the same before and after the reaction. The standard conditions of temperature and pressure adop ...
Part V The Third Law and Free Energy
... approaching the absolute zero, it is generally restricted to the temperature range 0 < T<θ/10. Note: For application of the third law, Eq.5-5 is generally integrated from the absolute zero to some convenient low temperature, above which experimental heat capacity data can be used. Integrations at an ...
... approaching the absolute zero, it is generally restricted to the temperature range 0 < T<θ/10. Note: For application of the third law, Eq.5-5 is generally integrated from the absolute zero to some convenient low temperature, above which experimental heat capacity data can be used. Integrations at an ...
High temperature structural and magnetic properties of cobalt
... are respectively 0.67 and 0.46, indicating a higher degree of organisation in the former case, in agreement with the Stoner-Wholfarth model. Several parameters govern the coercivity of an assembly of anisotropic magnetic particles: (i) the distribution of the particle easy axis orientation with res ...
... are respectively 0.67 and 0.46, indicating a higher degree of organisation in the former case, in agreement with the Stoner-Wholfarth model. Several parameters govern the coercivity of an assembly of anisotropic magnetic particles: (i) the distribution of the particle easy axis orientation with res ...
Structure and Sodium Ion Dynamics in Sodium
... for Na+ diffusion in a distribution of local environments such as those found in amorphous compounds like Na2O·2SiO2, confirming the absence of Na doping in SrSiO3 and that Na was present only in the amorphous phase in any significant proportion. Additionally, a decrease in T1 with increasing temperatu ...
... for Na+ diffusion in a distribution of local environments such as those found in amorphous compounds like Na2O·2SiO2, confirming the absence of Na doping in SrSiO3 and that Na was present only in the amorphous phase in any significant proportion. Additionally, a decrease in T1 with increasing temperatu ...
Chymotrypsin is a Serine Protease
... • Correct positioning of two reacting groups (in model reactions or at enzyme active sites): (1) Reduces their degrees of freedom (2) Results in a large loss of entropy (3) The relative enhanced concentration of substrates (“effective molarity”) predicts the rate acceleration expected due to this ef ...
... • Correct positioning of two reacting groups (in model reactions or at enzyme active sites): (1) Reduces their degrees of freedom (2) Results in a large loss of entropy (3) The relative enhanced concentration of substrates (“effective molarity”) predicts the rate acceleration expected due to this ef ...
1 From Chemical Invariance to Genetic Variability - Wiley-VCH
... Next we note that evolutionary variability is not uniform throughout the structure of a metalloenzyme. Variability increases and invariance decreases from the (innermost) transition metal through the (inner) ligators to the (outer) ligand moieties. Hence, in the course of evolution central transitio ...
... Next we note that evolutionary variability is not uniform throughout the structure of a metalloenzyme. Variability increases and invariance decreases from the (innermost) transition metal through the (inner) ligators to the (outer) ligand moieties. Hence, in the course of evolution central transitio ...
Thermodynamics: the Second Law
... the temperature is infinitesimally higher, then heat flows into the system and the substance melts. Because the transition occurs at constant pressure, we can identify the heat transferred per mole of substance with the enthalpy of melting. Trouton’s rule - ΔvapH/Tb is approximately Entropy of fusio ...
... the temperature is infinitesimally higher, then heat flows into the system and the substance melts. Because the transition occurs at constant pressure, we can identify the heat transferred per mole of substance with the enthalpy of melting. Trouton’s rule - ΔvapH/Tb is approximately Entropy of fusio ...
Glass transition
The glass–liquid transition or glass transition for short is the reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle state into a molten or rubber-like state. An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. Supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state is called vitrification, from the Latin vitreum, ""glass"" via French vitrifier.Despite the massive change in the physical properties of a material through its glass transition, the transition is not itself a phase transition of any kind; rather it is a laboratory phenomenon extending over a range of temperature and defined by one of several conventions. Such conventions include a constant cooling rate (20 K/min) and a viscosity threshold of 1012 Pa·s, among others. Upon cooling or heating through this glass-transition range, the material also exhibits a smooth step in the thermal-expansion coefficient and in the specific heat, with the location of these effects again being dependent on the history of the material. However, the question of whether some phase transition underlies the glass transition is a matter of continuing research.The glass-transition temperature Tg is always lower than the melting temperature, Tm, of the crystalline state of the material, if one exists.