Geography and History Activity 17: Cities Within Cities
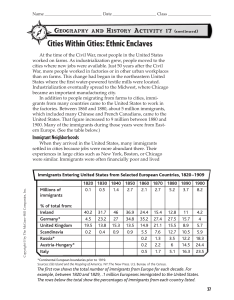
... Cities Within Cities: Ethnic Enclaves At the time of the Civil War, most people in the United States worked on farms. As industrialization grew, people moved to the cities where new jobs were available. Just 50 years after the Civil War, more people worked in factories or in other urban workplaces t ...
... Cities Within Cities: Ethnic Enclaves At the time of the Civil War, most people in the United States worked on farms. As industrialization grew, people moved to the cities where new jobs were available. Just 50 years after the Civil War, more people worked in factories or in other urban workplaces t ...
Chapter 18 Test Study Guide
... What improvements to the railroad affected the economy and transportation in the U.S.? How did steel processing change in the 1850s and how did this affect the United States? What advances in transportation and communication played an important role in the Second Industrial Revolution? How d ...
... What improvements to the railroad affected the economy and transportation in the U.S.? How did steel processing change in the 1850s and how did this affect the United States? What advances in transportation and communication played an important role in the Second Industrial Revolution? How d ...
Statue of Liberty dedicated
... 4. American Expansionism and Economic Revolution American Indians way of life. Before 1800, a million Indians lived north of the Rio Grande, speaking 2,000 languages and subsisting in small villages on maize, game and fish. By the 1820s, the European colonists and American-born settlers of European ...
... 4. American Expansionism and Economic Revolution American Indians way of life. Before 1800, a million Indians lived north of the Rio Grande, speaking 2,000 languages and subsisting in small villages on maize, game and fish. By the 1820s, the European colonists and American-born settlers of European ...
After World War I, many Americans viewed as enemies people
... increased the demand for jobs and unemployment rose. • Many people suspected unions of being Communist. • In 1919 some 4 million workers took part in over 3,000 strikes. • In 1919 Seattle was virtually shut down because of a wide range of labor strikes. • They almost always lost. Job seekers were pl ...
... increased the demand for jobs and unemployment rose. • Many people suspected unions of being Communist. • In 1919 some 4 million workers took part in over 3,000 strikes. • In 1919 Seattle was virtually shut down because of a wide range of labor strikes. • They almost always lost. Job seekers were pl ...
The Growth of Industrial Prosperity The Second Industrial Revolution
... Revolution. Steel, chemicals, electricity, and oil were the new industrial frontiers. B. Between 1870 and 1914 steel replaced iron. New methods for shaping steel made it possible to build lighter, smaller, and faster machines, engines, railroads, and more. By 1913 Great Britain, France, Belgium, and ...
... Revolution. Steel, chemicals, electricity, and oil were the new industrial frontiers. B. Between 1870 and 1914 steel replaced iron. New methods for shaping steel made it possible to build lighter, smaller, and faster machines, engines, railroads, and more. By 1913 Great Britain, France, Belgium, and ...
Ch 9.3 _The Industrial Revolution Spreads PPT File
... share profits not debts Large corporations attempt to control as much business as they can ...
... share profits not debts Large corporations attempt to control as much business as they can ...
5th social studies history (5thsocstud_history)
... 15. During World War I, countries formed alliances with other countries. Which alliance included the countries of Germany and Austria-Hungary? A. the Allied Powers B. the NATO Powers C. the Central Powers D. the Coalition Powers 16. Since World War II, migrant farm workers in America have struggled ...
... 15. During World War I, countries formed alliances with other countries. Which alliance included the countries of Germany and Austria-Hungary? A. the Allied Powers B. the NATO Powers C. the Central Powers D. the Coalition Powers 16. Since World War II, migrant farm workers in America have struggled ...
Chapter 11: The Peculiar Institution
... ordinary Americans, some of which came to pass in the next century, such as direct election of U.S. senators, government control of currency, a graduated income tax, low-cost public financing for farmers, and workers’ right to organize unions. The platform also called for national ownership of railr ...
... ordinary Americans, some of which came to pass in the next century, such as direct election of U.S. senators, government control of currency, a graduated income tax, low-cost public financing for farmers, and workers’ right to organize unions. The platform also called for national ownership of railr ...
The Other America: 19.4
... • National Housing Act of 1949 promises “a decent home and a suitable living environment for every American family.” • Rundown neighborhoods are torn down and low-income housing is built • In a lot of cases, poor people are simply removed to allow building of shopping malls, parking lots, and sports ...
... • National Housing Act of 1949 promises “a decent home and a suitable living environment for every American family.” • Rundown neighborhoods are torn down and low-income housing is built • In a lot of cases, poor people are simply removed to allow building of shopping malls, parking lots, and sports ...
post 1865 grad review part I
... • Slums develop • Tenements • Gradually services such as roads, hospitals develop • Wealth becomes more centered in the cities ...
... • Slums develop • Tenements • Gradually services such as roads, hospitals develop • Wealth becomes more centered in the cities ...
Industrial Revolution: Webquest
... Directions: Complete the 5 sections below. Each section has a website that you need to go to. Be sure to answer every question! 1. Inventions. Go to: http://industrialrevolution.sea.ca/innovations.html o What 2 major agricultural inventions did Jethro Tull create? o What was the “spinning jenny”? o ...
... Directions: Complete the 5 sections below. Each section has a website that you need to go to. Be sure to answer every question! 1. Inventions. Go to: http://industrialrevolution.sea.ca/innovations.html o What 2 major agricultural inventions did Jethro Tull create? o What was the “spinning jenny”? o ...
Reconstruction Test Review
... Who is Lincoln’s Vice President, who eventually becomes president? ...
... Who is Lincoln’s Vice President, who eventually becomes president? ...
Name: 8th Grade Midterm Review Semester 1 2015
... 2. Towns that grew near mines were called _______________________. 3. The _____________________ was a rich vein of gold found in the Sierra Nevada in 1859. 4. Some people __________________ to the United States from other countries to work on the railroads. 5. __________________________ is a ghost t ...
... 2. Towns that grew near mines were called _______________________. 3. The _____________________ was a rich vein of gold found in the Sierra Nevada in 1859. 4. Some people __________________ to the United States from other countries to work on the railroads. 5. __________________________ is a ghost t ...
Chapter 17 Freedom`s Boundaries, at Home and Abroad, 1890-1900
... In 1892 Andrew Carnegie and his partner Henry Clay Frick decided to purge union workers from their steel plant in Homestead, Pennsylvania. The Homestead steelworks was one of the largest factories in the world with nearly 4,000 employees. What followed was one of the worst labor confrontations in Am ...
... In 1892 Andrew Carnegie and his partner Henry Clay Frick decided to purge union workers from their steel plant in Homestead, Pennsylvania. The Homestead steelworks was one of the largest factories in the world with nearly 4,000 employees. What followed was one of the worst labor confrontations in Am ...
Chapter 18 Outline I. Explaining the Industrial Revolution A. At the
... e. little contact between the rich and the poor 5. industrial factories offered a very different work environment a. long hours, low wages, and child labor were typical for the poor b. what was new was the routine and monotony of work, direct supervision, discipline c. industrial work was insecure d ...
... e. little contact between the rich and the poor 5. industrial factories offered a very different work environment a. long hours, low wages, and child labor were typical for the poor b. what was new was the routine and monotony of work, direct supervision, discipline c. industrial work was insecure d ...
THE INDUSTRIAL ERA:
... AMERICA At the end of the Civil War the United States ranked fourth in industrial output, behind Britain, France, and Germany. By the close of the century, in many industries, the United States produced more than the other three combined. So extensive was U.S. industrial growth in the late nineteent ...
... AMERICA At the end of the Civil War the United States ranked fourth in industrial output, behind Britain, France, and Germany. By the close of the century, in many industries, the United States produced more than the other three combined. So extensive was U.S. industrial growth in the late nineteent ...
File
... surplus stood as a continual temptation to distribute it in the form of veterans pension or expensive public-work programs, known as pork barrel projects. Cleveland was convinced that surplus constituted a corrupting influence. Pension GAR: After the Civil War, veterans formed the Grand Army of the ...
... surplus stood as a continual temptation to distribute it in the form of veterans pension or expensive public-work programs, known as pork barrel projects. Cleveland was convinced that surplus constituted a corrupting influence. Pension GAR: After the Civil War, veterans formed the Grand Army of the ...
File
... 1869 at Promontory Point, Utah. As railroads, roads, and canals were developed, the national market for goods expanded. Shipping of raw materials and finished goods became less expensive. With the Industrial Revolution, mass production required this large market to be profitable. This led to the gro ...
... 1869 at Promontory Point, Utah. As railroads, roads, and canals were developed, the national market for goods expanded. Shipping of raw materials and finished goods became less expensive. With the Industrial Revolution, mass production required this large market to be profitable. This led to the gro ...
Chapter 7 Sec 2
... protective tariff that helped Americans to buy products made in the United States by increasing the price on imported goods. Factories appeared in the North because there was greater access to capital, or the money needed to buy equipment and factories. In the South, capital was tied up in land and ...
... protective tariff that helped Americans to buy products made in the United States by increasing the price on imported goods. Factories appeared in the North because there was greater access to capital, or the money needed to buy equipment and factories. In the South, capital was tied up in land and ...
SOL STUDY GUIDE USII.2 -
... Because iron ore could be transported more economically than coal, (the other ingredient needed for steel) iron ore was shipped by rail to Pittsburgh. (coal was in PA already) ...
... Because iron ore could be transported more economically than coal, (the other ingredient needed for steel) iron ore was shipped by rail to Pittsburgh. (coal was in PA already) ...
M / C Review Chapter 20
... They were the products of machine politics, political followers who were typically incompetent leaders E. They were limited in their actions by the overwhelming Populist sentiment of their time. “Waving the bloody shirt” was the name given to the practice of A. Scaring black potential voters into st ...
... They were the products of machine politics, political followers who were typically incompetent leaders E. They were limited in their actions by the overwhelming Populist sentiment of their time. “Waving the bloody shirt” was the name given to the practice of A. Scaring black potential voters into st ...
unit07sg - GEOCITIES.ws
... 13. German immigrants in the early nineteenth century tended to 14. German immigrants to the United States 15. When German immigrants came to the United States, they 16. Those who were frightened by the rapid influx of Irish immigrants organized 17. The sentiment of fear and opposition to open immig ...
... 13. German immigrants in the early nineteenth century tended to 14. German immigrants to the United States 15. When German immigrants came to the United States, they 16. Those who were frightened by the rapid influx of Irish immigrants organized 17. The sentiment of fear and opposition to open immig ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint
... unmarried women from local farms Included a loom that could both spin threat and weave cloth in the same mill Women lived in boarding houses and provided with meals ...
... unmarried women from local farms Included a loom that could both spin threat and weave cloth in the same mill Women lived in boarding houses and provided with meals ...
The Ordeal of Industrialization (from: The National Experience)
... was often ineffective. There were only five commissioners to deal with the entire country. 5. Sherman Anti-Trust Act- (1890)D. Horizontal and Vertical Integration1.Andrew Carnegie became the pioneer of vertical integration. From the mining of iron ore to shipping on the Great Lakes, to the railroad ...
... was often ineffective. There were only five commissioners to deal with the entire country. 5. Sherman Anti-Trust Act- (1890)D. Horizontal and Vertical Integration1.Andrew Carnegie became the pioneer of vertical integration. From the mining of iron ore to shipping on the Great Lakes, to the railroad ...
Gilded Age

The Gilded Age in United States history is the late 19th century, from the 1870s to about 1900. The term was coined by writer Mark Twain in The Gilded Age: A Tale of Today (1873), which satirized an era of serious social problems masked by a thin gold gilding.The Gilded Age was an era of rapid economic growth, especially in the North and West. As American wages were much higher than those in Europe, especially for skilled workers, the period saw an influx of millions of European immigrants. The rapid expansion of industrialization led to real wage growth of 60% between 1860 and 1890, despite the ever-increasing labor force. However, the Gilded Age was also an era of abject poverty and inequality as millions of immigrants—many from impoverished European nations—poured into the United States, and wealth became highly concentrated. Railroads were the major industry, but the factory system, mining, and finance increased in importance. Immigration from Europe, China and the eastern states led to the rapid growth of the West, based on farming, ranching and mining. Labor unions became important in industrial areas. Two major nationwide depressions—the Panic of 1873 and the Panic of 1893—interrupted growth and caused social and political upheavals. The South after the American Civil War remained economically devastated; its economy became increasingly tied to cotton and tobacco production, which suffered from low prices. Black people in the South were stripped of political power, voting rights, and left economically disadvantaged.The political landscape was notable in that despite some corruption, turnout was very high and elections between the evenly matched parties were close. The dominant issues were cultural (especially regarding prohibition, education and ethnic racial groups), and economic (tariffs and money supply). With the rapid growth of cities, political machines increasingly took control of urban politics. Unions crusaded for the 8-hour working day and the abolition of child labor; middle class reformers demanded civil service reform, prohibition, and women's suffrage. Local governments built schools and hospitals, while private schools and hospitals were founded by local philanthropists. Numerous religious denominations were growing in membership and wealth; they expanded their missionary activity to the world arena. Catholics and Lutherans set up parochial schools and the larger denominations set up many colleges and hospitals.























