Presentation
... the British colonies, settling primarily in New York and Pennsylvania. Immigration continued in very large numbers during the 19th century, with some eight million arrivals from Germany. • They were pulled by the attractions of land and religious freedom, and pushed out of Europe by shortages of lan ...
... the British colonies, settling primarily in New York and Pennsylvania. Immigration continued in very large numbers during the 19th century, with some eight million arrivals from Germany. • They were pulled by the attractions of land and religious freedom, and pushed out of Europe by shortages of lan ...
U - Humble ISD
... 39. The main objective of the nativists was to do what? 40. Prohibitionists and purity crusaders both worked to do what? 41. The Interstate Commerce Act outlawed the railroads’ practice of what? 42. How were Asians regarded by many white Americans? 43. What contributed to the migration from farms to ...
... 39. The main objective of the nativists was to do what? 40. Prohibitionists and purity crusaders both worked to do what? 41. The Interstate Commerce Act outlawed the railroads’ practice of what? 42. How were Asians regarded by many white Americans? 43. What contributed to the migration from farms to ...
review questions
... Great efforts were made to set up a growing industrial system, which demanded more resources and land. Expanding westwards within the continent was a natural move, and at first supplied the land and resources needed. But the growing production of farming and manufactured goods required more resource ...
... Great efforts were made to set up a growing industrial system, which demanded more resources and land. Expanding westwards within the continent was a natural move, and at first supplied the land and resources needed. But the growing production of farming and manufactured goods required more resource ...
Chapter 9
... investors had made a fortune, but the railroad was almost bankrupt. Congress agreed to give additional grants to the railroad after several members of Congress were given shares in Union Pacific at a price well below market value. An investigation implicated several members of Congress.) ...
... investors had made a fortune, but the railroad was almost bankrupt. Congress agreed to give additional grants to the railroad after several members of Congress were given shares in Union Pacific at a price well below market value. An investigation implicated several members of Congress.) ...
Immigration and US History
... The first, and longest, era stretched from the 17th century through the early 19th century. Immigrants came from a range of places, including the German-speaking area of the Palatinate, France (Protestant Huguenots), and the Netherlands. Other immigrants were Jews, also from the Netherlands and from ...
... The first, and longest, era stretched from the 17th century through the early 19th century. Immigrants came from a range of places, including the German-speaking area of the Palatinate, France (Protestant Huguenots), and the Netherlands. Other immigrants were Jews, also from the Netherlands and from ...
US History - Pearson Access
... The rich valued them as employees because they were willing to work for low wages . . . [and] were dependable. . . . The working class, however, feared that they would take their jobs, thus making discrimination rampant. Chinese immigrants could not become citizens or own property. They were often r ...
... The rich valued them as employees because they were willing to work for low wages . . . [and] were dependable. . . . The working class, however, feared that they would take their jobs, thus making discrimination rampant. Chinese immigrants could not become citizens or own property. They were often r ...
Benchmark__2_Review_of_Modules_5-7
... Farmers faced major debt as they bought new farming machinery. Farmers formed ________________ as social organizations but soon these developed into political and economic meetings. Looking for help, farmers often formed ______________________ to assist each other in storage and transportation costs ...
... Farmers faced major debt as they bought new farming machinery. Farmers formed ________________ as social organizations but soon these developed into political and economic meetings. Looking for help, farmers often formed ______________________ to assist each other in storage and transportation costs ...
Chapter 8
... The Industrial Revolution Period of rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production In the early 1700s, most people in Europe and the United States were farmers First industry to fully mechanize – textiles Richard Arkwright patented the water frame (ran on water power) The ...
... The Industrial Revolution Period of rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production In the early 1700s, most people in Europe and the United States were farmers First industry to fully mechanize – textiles Richard Arkwright patented the water frame (ran on water power) The ...
MAMMON.ECONOMICS.NOTES.2010
... from their regard to their own interest . . . they intend only their own gain, and they are in this, as in many other cases, led by an invisible hand to promote an end which was no part of their intention. Nor is it always the worse for the society that it was no part of it. By pursuing their own in ...
... from their regard to their own interest . . . they intend only their own gain, and they are in this, as in many other cases, led by an invisible hand to promote an end which was no part of their intention. Nor is it always the worse for the society that it was no part of it. By pursuing their own in ...
American Industry/Urbanization PPT
... • Certain inventions helped move the American Industrial Revolution forward. • One of the most important invention in the late 1800s was the telephone. -> Alexander Graham Bell came up with the idea by which he believed it would be possible to “talk by ...
... • Certain inventions helped move the American Industrial Revolution forward. • One of the most important invention in the late 1800s was the telephone. -> Alexander Graham Bell came up with the idea by which he believed it would be possible to “talk by ...
US History WWI Semester 1 Exam Review ANSWERS
... 11. What would a bar graph showing a trend of American’s moving from rural areas into cities from 1860 – 1900 look like? Trend in growth. 13. Who were the industrialists of the Gilded Age known as and why? Captains of Industry & Robber Barrons 14. Industrial growth in the United States led to a conc ...
... 11. What would a bar graph showing a trend of American’s moving from rural areas into cities from 1860 – 1900 look like? Trend in growth. 13. Who were the industrialists of the Gilded Age known as and why? Captains of Industry & Robber Barrons 14. Industrial growth in the United States led to a conc ...
Topic 4d Notes-Uncertainty in the 1920s
... in the 1920s 1. Examine the clash between science and religion that occurred in the 1920s in the United States 2. Analyze how foreign events after World War I and nativism led to the first Red Scare and immigrant quotas 3. Analyze the intended and unintended consequences of Prohibition. ...
... in the 1920s 1. Examine the clash between science and religion that occurred in the 1920s in the United States 2. Analyze how foreign events after World War I and nativism led to the first Red Scare and immigrant quotas 3. Analyze the intended and unintended consequences of Prohibition. ...
Building a Powerful Nation Revision - bshs
... How did John D. Rockefeller gain control over much of the oil industry? What did both Thomas Edison and George Westinghouse work with? How did Andrew Carnegie gain control of the steel industry? Collective Bargaining Social Darwinism Division of Labor Monopoly Business Cycle Chapter 8 What were the ...
... How did John D. Rockefeller gain control over much of the oil industry? What did both Thomas Edison and George Westinghouse work with? How did Andrew Carnegie gain control of the steel industry? Collective Bargaining Social Darwinism Division of Labor Monopoly Business Cycle Chapter 8 What were the ...
USH Ch 11.1 Notes
... • Workers could live farther away from their jobs. • Families used cars for leisure trips and ...
... • Workers could live farther away from their jobs. • Families used cars for leisure trips and ...
Document
... intensified in the late 19th century. – Women had the opportunity for higher education at new women’s colleges and new opportunities in factories and offices. – However, it was the movement west that had the greater impact on gaining the right of women to vote. • The first state to grant women suffr ...
... intensified in the late 19th century. – Women had the opportunity for higher education at new women’s colleges and new opportunities in factories and offices. – However, it was the movement west that had the greater impact on gaining the right of women to vote. • The first state to grant women suffr ...
A FEW THOUGHTS ON ECONOMIC POLICIES AND EMPLOYMENT
... 2) UN Millenium Goal – commitment to reduce extreme poverty level to half its share of the total population as observed in ...
... 2) UN Millenium Goal – commitment to reduce extreme poverty level to half its share of the total population as observed in ...
Chapter 9: Discontent and Reform
... ley, especially its foreign policy. arose called “progressivism,” which Meeting at Philadelphia, the Repub- gave American politics and thought licans expressed jubilation over the its special character from approxisuccessful outcome of the war with mately 1890 until the American Spain, the restorati ...
... ley, especially its foreign policy. arose called “progressivism,” which Meeting at Philadelphia, the Repub- gave American politics and thought licans expressed jubilation over the its special character from approxisuccessful outcome of the war with mately 1890 until the American Spain, the restorati ...
27-30 Review Quiz PDF
... (A) The United States became the most powerful country in the world. (B) The United States began to import much more than it exported. (C) The United States ...
... (A) The United States became the most powerful country in the world. (B) The United States began to import much more than it exported. (C) The United States ...
Flashcards US 9 - White Plains Public Schools
... And Andrew Carnegie, a monopolist, wrote about the need for the wealthy to use their wealth to benefit or improve society [The Gospel of Wealth] The Main Benefit Gained by Labor Unions in the late 19th Century Higher wages Safer working conditions Even sometimes an eight-hour workday Yes, ...
... And Andrew Carnegie, a monopolist, wrote about the need for the wealthy to use their wealth to benefit or improve society [The Gospel of Wealth] The Main Benefit Gained by Labor Unions in the late 19th Century Higher wages Safer working conditions Even sometimes an eight-hour workday Yes, ...
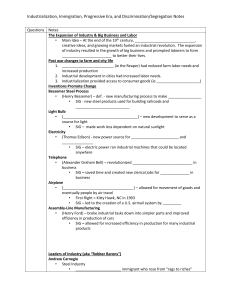
Industrialization, Immigration, Progressive Era, and Discrimination
... • _________________________________ Company – controlled 90% of all U.S. oil production • Controlled other companies by forming a ___________ – def. – several corporations made an agreement to be run by one executive board that ran the trust like one big company Cornelius Vanderbilt • ______________ ...
... • _________________________________ Company – controlled 90% of all U.S. oil production • Controlled other companies by forming a ___________ – def. – several corporations made an agreement to be run by one executive board that ran the trust like one big company Cornelius Vanderbilt • ______________ ...
Chapter 06 sec 1 and 2
... • The party bosses who ran the political machines also controlled the city’s finances. − Many machine politicians grew rich as the result of fraud or graft. − George Plunkitt was one of New York’s most powerful party bosses. ...
... • The party bosses who ran the political machines also controlled the city’s finances. − Many machine politicians grew rich as the result of fraud or graft. − George Plunkitt was one of New York’s most powerful party bosses. ...
A. Gilded Age Politics
... 2. Exams for federal jobs Chester Arthur became president after Garfield’s death and worked with Congress to reform the spoils system. In 1883, Congress passed the Pendleton Act and it created a Civil Service Commission to conduct exams for federal jobs. What is the ‘civil service’? ...
... 2. Exams for federal jobs Chester Arthur became president after Garfield’s death and worked with Congress to reform the spoils system. In 1883, Congress passed the Pendleton Act and it created a Civil Service Commission to conduct exams for federal jobs. What is the ‘civil service’? ...
The United States Industrializes - B.Brown US History Class Website
... In many ways, the United States practiced laissez-faire economics in the late 1800s. State and federal governments kept taxes and spending low. They did not impose costly regulations on industry or try to control wages and prices. In the late 1800s, the United States was also one of the largest free ...
... In many ways, the United States practiced laissez-faire economics in the late 1800s. State and federal governments kept taxes and spending low. They did not impose costly regulations on industry or try to control wages and prices. In the late 1800s, the United States was also one of the largest free ...
CHAPTER SUMMARIES 21-42
... settlement, lured by free homesteads, railroads, and irrigation. The census declared the end of the frontier in 1890, concluding a formative phase of American history. The frontier was less of a “safety valve” than many believed, but the growth of cities actually made the West the most urbanized reg ...
... settlement, lured by free homesteads, railroads, and irrigation. The census declared the end of the frontier in 1890, concluding a formative phase of American history. The frontier was less of a “safety valve” than many believed, but the growth of cities actually made the West the most urbanized reg ...
Gilded Age

The Gilded Age in United States history is the late 19th century, from the 1870s to about 1900. The term was coined by writer Mark Twain in The Gilded Age: A Tale of Today (1873), which satirized an era of serious social problems masked by a thin gold gilding.The Gilded Age was an era of rapid economic growth, especially in the North and West. As American wages were much higher than those in Europe, especially for skilled workers, the period saw an influx of millions of European immigrants. The rapid expansion of industrialization led to real wage growth of 60% between 1860 and 1890, despite the ever-increasing labor force. However, the Gilded Age was also an era of abject poverty and inequality as millions of immigrants—many from impoverished European nations—poured into the United States, and wealth became highly concentrated. Railroads were the major industry, but the factory system, mining, and finance increased in importance. Immigration from Europe, China and the eastern states led to the rapid growth of the West, based on farming, ranching and mining. Labor unions became important in industrial areas. Two major nationwide depressions—the Panic of 1873 and the Panic of 1893—interrupted growth and caused social and political upheavals. The South after the American Civil War remained economically devastated; its economy became increasingly tied to cotton and tobacco production, which suffered from low prices. Black people in the South were stripped of political power, voting rights, and left economically disadvantaged.The political landscape was notable in that despite some corruption, turnout was very high and elections between the evenly matched parties were close. The dominant issues were cultural (especially regarding prohibition, education and ethnic racial groups), and economic (tariffs and money supply). With the rapid growth of cities, political machines increasingly took control of urban politics. Unions crusaded for the 8-hour working day and the abolition of child labor; middle class reformers demanded civil service reform, prohibition, and women's suffrage. Local governments built schools and hospitals, while private schools and hospitals were founded by local philanthropists. Numerous religious denominations were growing in membership and wealth; they expanded their missionary activity to the world arena. Catholics and Lutherans set up parochial schools and the larger denominations set up many colleges and hospitals.