No Slide Title
... for 1 cup of peanut butter and all you have is ½ a cup, even though you have all the other ingredients, you can at most make ½ a batch of cookies. ...
... for 1 cup of peanut butter and all you have is ½ a cup, even though you have all the other ingredients, you can at most make ½ a batch of cookies. ...
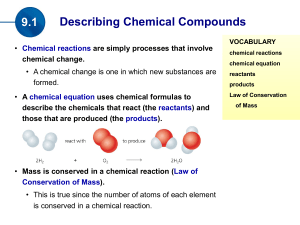
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... • Coefficients in a chemical equation describe the number of molecules of each compound or element, whereas subscripts describe the number of atoms of each element. • Balancing an equation involves changing the coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts ...
... • Coefficients in a chemical equation describe the number of molecules of each compound or element, whereas subscripts describe the number of atoms of each element. • Balancing an equation involves changing the coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OBJECTIVES 1. To study reactions
... Reaction 1: In a small test tube, mix one piece of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with 2- 5 ml of water. (Be sure to feel the test tube.) Reaction 2: Place approximately 1/2 teaspoon of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) into a small test tube. (Use the end of your scoopit.) Add about 5 ml of water. ...
... Reaction 1: In a small test tube, mix one piece of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with 2- 5 ml of water. (Be sure to feel the test tube.) Reaction 2: Place approximately 1/2 teaspoon of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) into a small test tube. (Use the end of your scoopit.) Add about 5 ml of water. ...
Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
... • Every chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms into different combinations. However, during these reactions, the total number of atoms of each type of element is the same after the reaction as it was before the reaction. • Chemical reactions have to be properly balanced in order to cl ...
... • Every chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms into different combinations. However, during these reactions, the total number of atoms of each type of element is the same after the reaction as it was before the reaction. • Chemical reactions have to be properly balanced in order to cl ...
chemical reaction
... Chemical vs Physical Change • Physical change – a change in substance that does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tar ...
... Chemical vs Physical Change • Physical change – a change in substance that does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tar ...
Homework Assignment #4
... b) How much water is needed to make a 100 mM (milli-molar) solution given 0.3g of sucrose (C12H22O11)? ...
... b) How much water is needed to make a 100 mM (milli-molar) solution given 0.3g of sucrose (C12H22O11)? ...
Chemistry Standards Review
... 37. In the reaction, 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO, if 100.0 g of magnesium reacts with 50.0 g of oxygen, what mass of product is produced? Gases and Their Properties 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 39. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 40. Explain diffusion, use KMT to sup ...
... 37. In the reaction, 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO, if 100.0 g of magnesium reacts with 50.0 g of oxygen, what mass of product is produced? Gases and Their Properties 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 39. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 40. Explain diffusion, use KMT to sup ...
Review for Exam 1
... other that you think are bonded together. Place H and halogens on the periphery, since they can only form one bond. ...
... other that you think are bonded together. Place H and halogens on the periphery, since they can only form one bond. ...
Synthesis of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds1i2 A simple new
... Preparation of %nitrooctane from b-iodo~ctane.~2-Iodooctane (71.2 g., 0.30 mole) was poured into a stirred solution of 225 ml. dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 36 g. of sodium nitrite (0.52 mole) contained in a 500 ml. flask immersed in a water bath held a t room temperature. Stirring was continued for ...
... Preparation of %nitrooctane from b-iodo~ctane.~2-Iodooctane (71.2 g., 0.30 mole) was poured into a stirred solution of 225 ml. dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 36 g. of sodium nitrite (0.52 mole) contained in a 500 ml. flask immersed in a water bath held a t room temperature. Stirring was continued for ...
111 Exam I F 04 use
... Tear off this top page (pg. 1)-It is your scratch paper The following are molar masses you may or may not need: H2O = 18.02 ...
... Tear off this top page (pg. 1)-It is your scratch paper The following are molar masses you may or may not need: H2O = 18.02 ...
File
... Produced by condensation polymerization reactions. These reactions involve the formation of a small molecule (such as H2O, NH3, or HCl) The small molecule is said to be “condensed out” of the reaction. The monomer molecules bond at the site where atoms are removed from their functional groups. To fo ...
... Produced by condensation polymerization reactions. These reactions involve the formation of a small molecule (such as H2O, NH3, or HCl) The small molecule is said to be “condensed out” of the reaction. The monomer molecules bond at the site where atoms are removed from their functional groups. To fo ...
Sample % Sulfate Absolute Deviation A 44.02 B 44.11 C 43.98 D
... 8. Calculate the percent error that resulted if the theoretically accepted value (according to the handbook of Chemistry & Physics) for the sample measured is known to be 0.703 g/cm3. ...
... 8. Calculate the percent error that resulted if the theoretically accepted value (according to the handbook of Chemistry & Physics) for the sample measured is known to be 0.703 g/cm3. ...
Dr. Baxley`s Thermodynamics Worksheet
... 6. Since formation of a bond has − ∆H° and − ∆S°, breaking of bonds has + ∆H° and + ∆S°. Putting this into the equation ∆G° = ∆H° − T∆S°, you get sign of ∆G° = (+) − [T(+)]. When temperatures are low, the product of T∆S° < ∆H°, so ∆G° is + and the breakdown of the compound is nonspontaneous. At high ...
... 6. Since formation of a bond has − ∆H° and − ∆S°, breaking of bonds has + ∆H° and + ∆S°. Putting this into the equation ∆G° = ∆H° − T∆S°, you get sign of ∆G° = (+) − [T(+)]. When temperatures are low, the product of T∆S° < ∆H°, so ∆G° is + and the breakdown of the compound is nonspontaneous. At high ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... of R1 values. Gas chromatography, the use of peak heights and retention times. The widespread application of these methods in industry and medicine should be noted. ...
... of R1 values. Gas chromatography, the use of peak heights and retention times. The widespread application of these methods in industry and medicine should be noted. ...
File
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
powerpoint
... Do single replacement reactions always occur? NO! A metal will only replace a less reactive metal. The activity series is a way to predict whether or not certain reactions will occur. Any specific metal can replace any metal listed below it that is in a compound. It cannot replace any metal ...
... Do single replacement reactions always occur? NO! A metal will only replace a less reactive metal. The activity series is a way to predict whether or not certain reactions will occur. Any specific metal can replace any metal listed below it that is in a compound. It cannot replace any metal ...
Example - cloudfront.net
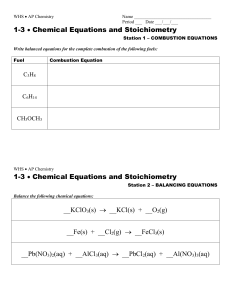
... a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound __________ (NH4)2CO3 NH3 + CO2 + H2O b) Balance __________________ as though they are one item as long as the ion stays together as a group on each side of the arrow. Al + CuSO4 Al2(SO4)3 + Cu c) If you can’t seem to get it balanced, ____ ...
... a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound __________ (NH4)2CO3 NH3 + CO2 + H2O b) Balance __________________ as though they are one item as long as the ion stays together as a group on each side of the arrow. Al + CuSO4 Al2(SO4)3 + Cu c) If you can’t seem to get it balanced, ____ ...