Best Practices
... Source: Stock Plan Dilution, 2002: Overhang from Stock Plans at S&P Super 1,500 Companies—Investor Responsibility Research Corp ...
... Source: Stock Plan Dilution, 2002: Overhang from Stock Plans at S&P Super 1,500 Companies—Investor Responsibility Research Corp ...
Professor Banko`s Presentation
... • Jay’s view: (research) assume(s) that thousands of companies that didn’t go public would have grown as fast as companies such as Google if they had! This assumption, which I would tend to categorize as completely ridiculous … ...
... • Jay’s view: (research) assume(s) that thousands of companies that didn’t go public would have grown as fast as companies such as Google if they had! This assumption, which I would tend to categorize as completely ridiculous … ...
FinancialDisclosure
... When a potential financial conflict of interest is indicated, the financial interest will need to be reviewed by the IRB. Check one of the following. Describe the extent of the involvement in the space provided. [ ]Financial Interest Under $10,000 in aggregate Check all that apply: [ ] Consulting [ ...
... When a potential financial conflict of interest is indicated, the financial interest will need to be reviewed by the IRB. Check one of the following. Describe the extent of the involvement in the space provided. [ ]Financial Interest Under $10,000 in aggregate Check all that apply: [ ] Consulting [ ...
Fall 10 489f10t1.pdf
... 4. (20 points) An insurance company is concerned about health insurance claims. Through an extensive audit, the company has determined that overstatements (claims for more health insurance money than is justified by the medical procedures performed) vary randomly with an exponential distribution X ...
... 4. (20 points) An insurance company is concerned about health insurance claims. Through an extensive audit, the company has determined that overstatements (claims for more health insurance money than is justified by the medical procedures performed) vary randomly with an exponential distribution X ...
Options
... • A move large enough in the direction you want it too, the OTM option can deliver large gains • But if the move is against you, the loss will be less than ATM and ITM • OTM near expiration dates tends to fare well ...
... • A move large enough in the direction you want it too, the OTM option can deliver large gains • But if the move is against you, the loss will be less than ATM and ITM • OTM near expiration dates tends to fare well ...
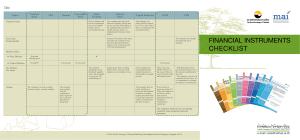
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS CHECKLIST
... voting against to veto. - If offering price is < 90% of market price & new shares offered > 5% of paid up capital, needs 5% voting against to veto. - If the company allocates shares to any one director and/or any one employee > 5% of total issued shares, must ask for approval on individual basis; ne ...
... voting against to veto. - If offering price is < 90% of market price & new shares offered > 5% of paid up capital, needs 5% voting against to veto. - If the company allocates shares to any one director and/or any one employee > 5% of total issued shares, must ask for approval on individual basis; ne ...
Valuing Stock Options: The Black
... • The implied volatility of an option is the volatility for which the Black-Scholes price equals the market price • The is a one-to-one correspondence between prices and implied volatilities • Traders and brokers often quote implied volatilities rather than dollar prices ...
... • The implied volatility of an option is the volatility for which the Black-Scholes price equals the market price • The is a one-to-one correspondence between prices and implied volatilities • Traders and brokers often quote implied volatilities rather than dollar prices ...
Option Price and Portfolio Simulation
... Want to guarantee that t periods from now you will have at least I*z ◦ z is a number generally between 0 and 1that guarantees a minimum value ◦ Want to invest in Stock with price S0 and Put for stock with exercise price X ◦ A package of share + put costs S0 + P(S0,X) ◦ Buy a packages where a =I/(S ...
... Want to guarantee that t periods from now you will have at least I*z ◦ z is a number generally between 0 and 1that guarantees a minimum value ◦ Want to invest in Stock with price S0 and Put for stock with exercise price X ◦ A package of share + put costs S0 + P(S0,X) ◦ Buy a packages where a =I/(S ...
489f10h4_soln.pdf
... 4. A long strangle option pays max(K1 − S, 0, S − K2 ) if it expires when the underlying stock value is S. The parameters K1 and K2 are the lower strike price and the upper strike price, and K1 < K2 . A stock currently has price $100 and goes up or down by 20% in each time period. What is the value ...
... 4. A long strangle option pays max(K1 − S, 0, S − K2 ) if it expires when the underlying stock value is S. The parameters K1 and K2 are the lower strike price and the upper strike price, and K1 < K2 . A stock currently has price $100 and goes up or down by 20% in each time period. What is the value ...
Risk Analysis
... • Compute the cash flows from the option at expiration t years from now. • Discount the cash flow value back to time 0 by multiplying by e-rt to calculate the current value of the option. • Select the current value of the option as the output variable and perform many iterations to quantify the expe ...
... • Compute the cash flows from the option at expiration t years from now. • Discount the cash flow value back to time 0 by multiplying by e-rt to calculate the current value of the option. • Select the current value of the option as the output variable and perform many iterations to quantify the expe ...
TopicsInAnalysis
... Does certainty equivalent depend on mean and variance? What does Barry Schwartz think of all this? 8. Uncertain future payments (uncertainty and time) Expected values of cash flows Higher discount rates as a proxy for uncertainty (Bringing in the lawyers: “We agree that the truth is between 3.2% and ...
... Does certainty equivalent depend on mean and variance? What does Barry Schwartz think of all this? 8. Uncertain future payments (uncertainty and time) Expected values of cash flows Higher discount rates as a proxy for uncertainty (Bringing in the lawyers: “We agree that the truth is between 3.2% and ...
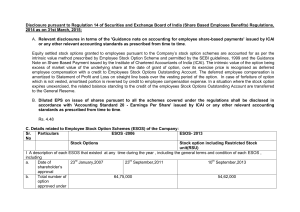
Share Based Employee Benefits
... Equity settled stock options granted to employees pursuant to the Company’s stock option schemes are accounted for as per the intrinsic value method prescribed by Employee Stock Option Scheme and permitted by the SEBI guidelines, 1999 and the Guidance Note on Share Based Payment issued by the Instit ...
... Equity settled stock options granted to employees pursuant to the Company’s stock option schemes are accounted for as per the intrinsic value method prescribed by Employee Stock Option Scheme and permitted by the SEBI guidelines, 1999 and the Guidance Note on Share Based Payment issued by the Instit ...
Valuing Stock Options: The Black
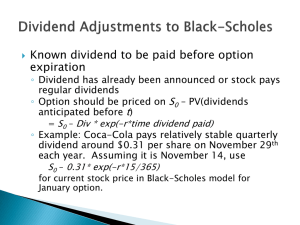
... into the BSM formula (D vs. q) Only dividends with ex-dividend dates during life of option should be included The “dividend” should be the expected reduction in the stock price expected ...
... into the BSM formula (D vs. q) Only dividends with ex-dividend dates during life of option should be included The “dividend” should be the expected reduction in the stock price expected ...
Key Issues and Ideas - BYU Marriott School
... 13. Which security should sell at a greater price? a. A 10-year Treasury bond with a 9% coupon rate or a 10-year T-bond with a 10% coupon. b. A three-month maturity call option with an exercise price of $40 or a three-month call on the same stock with an exercise price of $35. c. A put option of a s ...
... 13. Which security should sell at a greater price? a. A 10-year Treasury bond with a 9% coupon rate or a 10-year T-bond with a 10% coupon. b. A three-month maturity call option with an exercise price of $40 or a three-month call on the same stock with an exercise price of $35. c. A put option of a s ...
Geren. Con.SU.J:t1nlil
... talented people to come to work for them. Frankly, it would be all but impossible to attract those people without being able to offer stock options. Simply put, stock options are a great incentive in attracting talented people. Offering stock options is a way of showing prospective employees that a ...
... talented people to come to work for them. Frankly, it would be all but impossible to attract those people without being able to offer stock options. Simply put, stock options are a great incentive in attracting talented people. Offering stock options is a way of showing prospective employees that a ...