Chapter 7. Solubility
... increased development time) Burden shifted to patient (frequent high-dose administrations) ...
... increased development time) Burden shifted to patient (frequent high-dose administrations) ...
CHAPTER 6 ENERGY RELATIONSHIPS IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... The system is the specific part of the universe that is of interest to us. The surroundings are the rest of the universe outside the system. An open system can exchange mass and energy, usually in the form of heat with its surroundings. A closed system allows the transfer of energy (heat) but not ma ...
... The system is the specific part of the universe that is of interest to us. The surroundings are the rest of the universe outside the system. An open system can exchange mass and energy, usually in the form of heat with its surroundings. A closed system allows the transfer of energy (heat) but not ma ...
Unit X Organic Chem (SmartBoard)
... of the double bonds. Each resonance structure consists of alternating single and double bonds. Benzene is frequently represented as follows. ...
... of the double bonds. Each resonance structure consists of alternating single and double bonds. Benzene is frequently represented as follows. ...
Complete Solution Manual
... When aqueous NaCl is electrolyzed, water, with its less negative reduction potential is preferentially reduced over Na+ ions. Thus, the presence of water doesn’t allow Na+ ions to be reduced to Na. In molten NaCl, water is not present, so Na+ can be reduced to Na. Purification by electrolysis is cal ...
... When aqueous NaCl is electrolyzed, water, with its less negative reduction potential is preferentially reduced over Na+ ions. Thus, the presence of water doesn’t allow Na+ ions to be reduced to Na. In molten NaCl, water is not present, so Na+ can be reduced to Na. Purification by electrolysis is cal ...
Complete Solution Manual
... When aqueous NaCl is electrolyzed, water, with its less negative reduction potential is preferentially reduced over Na+ ions. Thus, the presence of water doesn’t allow Na+ ions to be reduced to Na. In molten NaCl, water is not present, so Na+ can be reduced to Na. Purification by electrolysis is cal ...
... When aqueous NaCl is electrolyzed, water, with its less negative reduction potential is preferentially reduced over Na+ ions. Thus, the presence of water doesn’t allow Na+ ions to be reduced to Na. In molten NaCl, water is not present, so Na+ can be reduced to Na. Purification by electrolysis is cal ...
AS Chemistry 1
... Atoms are the particles whose symbols are found in the periodic table of elements given in all your examination papers and also in Section 12 of this workbook. You can see that there are only about 100 of them. The middle part of the atom, the nucleus, contains one or more protons. It is the number ...
... Atoms are the particles whose symbols are found in the periodic table of elements given in all your examination papers and also in Section 12 of this workbook. You can see that there are only about 100 of them. The middle part of the atom, the nucleus, contains one or more protons. It is the number ...
1.09 MB / 64 pages
... molecule will probably be polar (because of the oxygen bonded to other less electronegative atoms) and, since it is a small molecule is likely to be reasonably soluble in water. However, if the line formula is written as C2H5OH, you can predict that this low molecular mass alcohol should be very sol ...
... molecule will probably be polar (because of the oxygen bonded to other less electronegative atoms) and, since it is a small molecule is likely to be reasonably soluble in water. However, if the line formula is written as C2H5OH, you can predict that this low molecular mass alcohol should be very sol ...
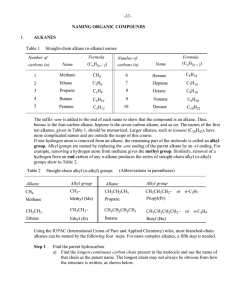
Naming Organic Compounds I
... N.B.: A complex substituent is alphabetized under the first letter of its name. Branched alkyl groups On page 40, it was shown that straight-chain alkyl (n-alkyl) groups are formed by removal of a terminal (end) hydrogen atom from straight-chain alkanes. It is also possible to generate a large numbe ...
... N.B.: A complex substituent is alphabetized under the first letter of its name. Branched alkyl groups On page 40, it was shown that straight-chain alkyl (n-alkyl) groups are formed by removal of a terminal (end) hydrogen atom from straight-chain alkanes. It is also possible to generate a large numbe ...
Ethers - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Ether: is a class of organic compounds in which an oxygen atom connected to two organic groups (alkyl or aryl"benzene ring") by σ bonds. thus Ethers are compounds of general formula R–O–R or Ar–O–Ar or Ar–O–R H ...
... Ether: is a class of organic compounds in which an oxygen atom connected to two organic groups (alkyl or aryl"benzene ring") by σ bonds. thus Ethers are compounds of general formula R–O–R or Ar–O–Ar or Ar–O–R H ...
chapter 5 gases
... The system is the specific part of the universe that is of interest to us. The surroundings are the rest of the universe outside the system. An open system can exchange mass and energy, usually in the form of heat with its surroundings. A closed system allows the transfer of energy (heat) but not ma ...
... The system is the specific part of the universe that is of interest to us. The surroundings are the rest of the universe outside the system. An open system can exchange mass and energy, usually in the form of heat with its surroundings. A closed system allows the transfer of energy (heat) but not ma ...
File
... Waving lotion reduces – S – S – bonds to – SH bonds. Hair can be placed in curlers to form the hair in the desired shape. The neutralizing agent is an oxidizing agent that reforms – S – S – bonds, locking the hair into its curly shape. Similar steps could be used to ...
... Waving lotion reduces – S – S – bonds to – SH bonds. Hair can be placed in curlers to form the hair in the desired shape. The neutralizing agent is an oxidizing agent that reforms – S – S – bonds, locking the hair into its curly shape. Similar steps could be used to ...
Inorganic Chemistry
... of molecules because of the importance of these topics when interpreting properties of substances and their chemical behavior. In view of the importance of the topic, especially in industrial chemistry, this book includes material on rate processes involving inorganic compounds in the solid state (C ...
... of molecules because of the importance of these topics when interpreting properties of substances and their chemical behavior. In view of the importance of the topic, especially in industrial chemistry, this book includes material on rate processes involving inorganic compounds in the solid state (C ...
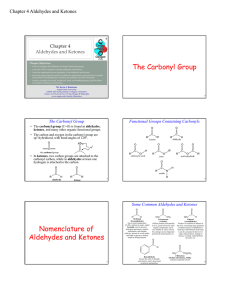
The Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
... triglycerides in meat during cooking; the acrid smell of this compound is obvious during barbeques. It also contributes to the taste of caramel, where it is produced by decomposing sucrose ...
... triglycerides in meat during cooking; the acrid smell of this compound is obvious during barbeques. It also contributes to the taste of caramel, where it is produced by decomposing sucrose ...
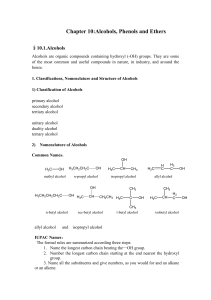
Chapter 10:Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... Note: The alcohols are hydrogen bonded, giving them much higher boiling points. The ethers have boiling points that are closer to those of alkanes with similar molecular weights. compares the dipole moments of dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, and tetrahydrofuran (THF) with those of alkanes and alcohol ...
... Note: The alcohols are hydrogen bonded, giving them much higher boiling points. The ethers have boiling points that are closer to those of alkanes with similar molecular weights. compares the dipole moments of dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, and tetrahydrofuran (THF) with those of alkanes and alcohol ...
Ethers, Epoxides and Sulfides
... Common names – “sulfide” replacing “ether” IUPAC names – “alkylthio” replacing “alkoxy” ...
... Common names – “sulfide” replacing “ether” IUPAC names – “alkylthio” replacing “alkoxy” ...
amine
... Nitrogen atom in alkylamines is sp3-hybridized • Three substituents occupy the three corners of a tetrahedron and the lone pair of electrons occupies the fourth corner • Bond angles are close to 109° ...
... Nitrogen atom in alkylamines is sp3-hybridized • Three substituents occupy the three corners of a tetrahedron and the lone pair of electrons occupies the fourth corner • Bond angles are close to 109° ...
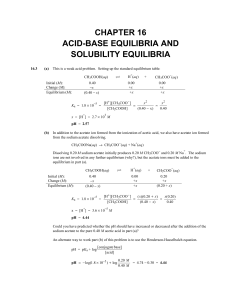
CHAPTER 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA AND SOLUBILITY
... Step 2: Now, the acetic acid equilibrium is reestablished. Since the volume of the solution is 1.00 L, we can convert directly from moles to molar concentration. CH3COOH (aq) Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) ...
... Step 2: Now, the acetic acid equilibrium is reestablished. Since the volume of the solution is 1.00 L, we can convert directly from moles to molar concentration. CH3COOH (aq) Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) ...
研 究 業 績 リ ス ト
... (92) Ruthenium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization of 3-Butyne-1,2-diols into Furans Y. Yada, Y. Miyake, and Y. Nishibayashi Org. Lett., to be submitted. (93) Novel Monophosphido-Bridged Diruthenium Complexes: Efficient Preparative Method and Their Catalytic Activity toward Condensation of Aldehyde ...
... (92) Ruthenium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization of 3-Butyne-1,2-diols into Furans Y. Yada, Y. Miyake, and Y. Nishibayashi Org. Lett., to be submitted. (93) Novel Monophosphido-Bridged Diruthenium Complexes: Efficient Preparative Method and Their Catalytic Activity toward Condensation of Aldehyde ...
Chapter 3: Ionic and Covalent Compounds Chapter 3: Ionic and
... 2. Which is not a covalent compound? A) Br2 B) NO2 C) NH3 D) NaNO2 E) More than one of the compounds above is not a covalent compound. Ans: D Difficulty: Easy 3. In bonding, main group elements _____ to attain the electronic configuration of the noble gas closest to them in the periodic table. A) Ga ...
... 2. Which is not a covalent compound? A) Br2 B) NO2 C) NH3 D) NaNO2 E) More than one of the compounds above is not a covalent compound. Ans: D Difficulty: Easy 3. In bonding, main group elements _____ to attain the electronic configuration of the noble gas closest to them in the periodic table. A) Ga ...
Study materials of Chemistry for class XII
... yellow colour is associated with ZnO. These electrons enhance the electrical conductivity of ZnO. Q10.Noble gases and metals crystallise with closed packed structures, yet the meeting points of noble gas crystals are exceptionally low. Why? 1M Ans. Noble gases crystallise in close packed structures, ...
... yellow colour is associated with ZnO. These electrons enhance the electrical conductivity of ZnO. Q10.Noble gases and metals crystallise with closed packed structures, yet the meeting points of noble gas crystals are exceptionally low. Why? 1M Ans. Noble gases crystallise in close packed structures, ...
Alcohols
... – ethylene oxide is an important building block for the organic chemical industry; it is also used as a fumigant in foodstuffs and textiles, and in hospitals to sterilize ...
... – ethylene oxide is an important building block for the organic chemical industry; it is also used as a fumigant in foodstuffs and textiles, and in hospitals to sterilize ...
Chapter 11 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
... • has two carbon atoms connected by a double bond • has two H atoms bonded to each C atom • is flat, with all the C and H atoms in the same plane • is a plant hormone used to accelerate the ripening of fruits ...
... • has two carbon atoms connected by a double bond • has two H atoms bonded to each C atom • is flat, with all the C and H atoms in the same plane • is a plant hormone used to accelerate the ripening of fruits ...
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
... mechanisms of elimination, E1 and E2, which were discussed in Chapter 8. The E1cB mechanism involves two steps, and proceeds by way of an anionic intermediate. Regular alcohols dehydrate only in the presence of acid but not base, because hydroxide is a poor leaving group. When the hydroxy group is β ...
... mechanisms of elimination, E1 and E2, which were discussed in Chapter 8. The E1cB mechanism involves two steps, and proceeds by way of an anionic intermediate. Regular alcohols dehydrate only in the presence of acid but not base, because hydroxide is a poor leaving group. When the hydroxy group is β ...
SyllAbuS - Cambridge International Examinations
... –– Learning outcomes that have been removed, and contain content that is not covered elsewhere in the syllabus and learning outcomes that have changed level (from AS Level to A Level or from A Level to AS Level) are listed on pages 95 and 96. • Data Booklet: The Data Booklet for use with Papers 1, ...
... –– Learning outcomes that have been removed, and contain content that is not covered elsewhere in the syllabus and learning outcomes that have changed level (from AS Level to A Level or from A Level to AS Level) are listed on pages 95 and 96. • Data Booklet: The Data Booklet for use with Papers 1, ...
Solutions
... the pendulum is all potential energy and is equal to the product mgh (m = mass of pendulum, g = constant acceleration of gravity, and h = height of pendulum). As the pendulum moves downward, its potential energy decreases from mgh to near zero, depending on how close it comes to the earth's surface. ...
... the pendulum is all potential energy and is equal to the product mgh (m = mass of pendulum, g = constant acceleration of gravity, and h = height of pendulum). As the pendulum moves downward, its potential energy decreases from mgh to near zero, depending on how close it comes to the earth's surface. ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.