Organic Chemistry
... Nomenclature for Alkenes 1. Root hydrocarbon name ends in -ene C2H4 is ethene 2. With more than 3 carbons, double bond is indicated by the lowest numbered carbon atom in the bond. C=CCC is 1-butene ...
... Nomenclature for Alkenes 1. Root hydrocarbon name ends in -ene C2H4 is ethene 2. With more than 3 carbons, double bond is indicated by the lowest numbered carbon atom in the bond. C=CCC is 1-butene ...
Chemistry and the Environment - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 1. What does it mean to say that the Earth is a “closed system”? Nothing can leave the ecosystem once it is created. There is no “away”. We can't just throw something “away” when we no longer want it. 2. List three examples of how nature recycles. Production and recycling of oxygen, nitrogen, and ca ...
... 1. What does it mean to say that the Earth is a “closed system”? Nothing can leave the ecosystem once it is created. There is no “away”. We can't just throw something “away” when we no longer want it. 2. List three examples of how nature recycles. Production and recycling of oxygen, nitrogen, and ca ...
Episode 25 0 Chemistry and the Environment
... 1. What does it mean to say that the Earth is a “closed system”? Nothing can leave the ecosystem once it is created. There is no “away”. We can't just throw something “away” when we no longer want it. 2. List three examples of how nature recycles. Production and recycling of oxygen, nitrogen, and ca ...
... 1. What does it mean to say that the Earth is a “closed system”? Nothing can leave the ecosystem once it is created. There is no “away”. We can't just throw something “away” when we no longer want it. 2. List three examples of how nature recycles. Production and recycling of oxygen, nitrogen, and ca ...
Notes 6.4 - St. Ignace Area Schools
... Alkanes are hydrocarbons that form only single covalent bonds. (See figure 3 on page 199) Alkanes are bonded in a single line because it is their only possible arrangement. Alkenes have double carbon-carbon bonds. They are hydrocarbons with at least one double carbon bond. Alcohols are organic compo ...
... Alkanes are hydrocarbons that form only single covalent bonds. (See figure 3 on page 199) Alkanes are bonded in a single line because it is their only possible arrangement. Alkenes have double carbon-carbon bonds. They are hydrocarbons with at least one double carbon bond. Alcohols are organic compo ...
Origin of Life - Hicksville Public Schools
... Experiments show that membranes can form around organic polymers in a solution if certain kinds of lipids are present. ...
... Experiments show that membranes can form around organic polymers in a solution if certain kinds of lipids are present. ...
Chapter 3
... made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorous Functions: contain instructions that cells need to carry out all the functions of life 2 types of nucleic acids: o DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)– carries ...
... made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorous Functions: contain instructions that cells need to carry out all the functions of life 2 types of nucleic acids: o DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)– carries ...
Wednesday, October 22
... Alkenes • Hydrocarbons with at least one double covalent bond between carbon atoms – C=C ...
... Alkenes • Hydrocarbons with at least one double covalent bond between carbon atoms – C=C ...
Carbon Compounds Power Point
... Carbon can bond to form a number of different shapes! Straight chain, branched and ring!! ...
... Carbon can bond to form a number of different shapes! Straight chain, branched and ring!! ...
Carbon Compounds - Southgate Schools
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry – study of all compounds that contain carbon Carbon has 4 valence electrons ...
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry – study of all compounds that contain carbon Carbon has 4 valence electrons ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Substance formed from positive ion of a base and the negative ion of an acid – When an acid and a base are combined, they produce a salt and water • HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O Acid ...
... • Substance formed from positive ion of a base and the negative ion of an acid – When an acid and a base are combined, they produce a salt and water • HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O Acid ...
Acid Basics
... Carbon: the Element of Life Carbon is the basis of organic chemistry. Organic compounds (with some exceptions) are those compounds that have carbon as a constituent atom of the compound. And organic compounds are the key components of biochemistry, the chemistry of life as we know it. What makes ca ...
... Carbon: the Element of Life Carbon is the basis of organic chemistry. Organic compounds (with some exceptions) are those compounds that have carbon as a constituent atom of the compound. And organic compounds are the key components of biochemistry, the chemistry of life as we know it. What makes ca ...
Topic 3 The chemistry of life
... Topic 2 Molecular Biology Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts ...
... Topic 2 Molecular Biology Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts ...
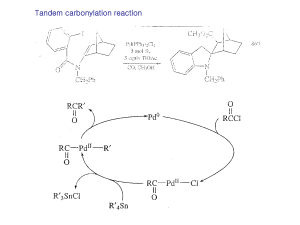
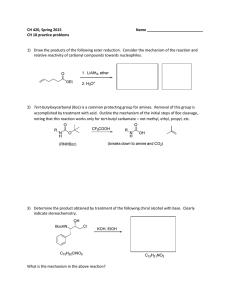
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... accomplished by treatment with acid. Outline the mechanism of the initial steps of Boc cleavage, noting that this reaction works only for tert-butyl carbamate – not methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc. ...
... accomplished by treatment with acid. Outline the mechanism of the initial steps of Boc cleavage, noting that this reaction works only for tert-butyl carbamate – not methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc. ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
Organic compounds
... • Carbon compounds – Organic compounds- primarily made of carbon • Carbon can from four covalent bonds • As a result, carbon can bon in a number of ways ...
... • Carbon compounds – Organic compounds- primarily made of carbon • Carbon can from four covalent bonds • As a result, carbon can bon in a number of ways ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... The general formula of the alkyne series is: a) CnH2n c) CnH2n–2 b) CnH2n–4 ...
... The general formula of the alkyne series is: a) CnH2n c) CnH2n–2 b) CnH2n–4 ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.