powerpoint file
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
WEEK 8: CSI UCSC: ASTRO EDITION SOLUTIONS This week you
... (1) Compare Types I and II supernovae. What kinds of objects explode and what are their explosion mechanisms? There are two main types. The first one is Type Ia supernova, which comes from a white dwarf in a binary system with another star. A white dwarf may steal material from the companion star, a ...
... (1) Compare Types I and II supernovae. What kinds of objects explode and what are their explosion mechanisms? There are two main types. The first one is Type Ia supernova, which comes from a white dwarf in a binary system with another star. A white dwarf may steal material from the companion star, a ...
Test 3, February 7, 2007 - Brock physics
... by (a) looking at the shape of the “milky band” across the sky. (b) mapping the distribution of stars in the galaxy. (c) mapping the distribution of gas clouds in the spiral arms. (d) mapping the distribution of globular clusters in the galaxy. 46. Disk stars are mostly (a) Population I stars. (b) P ...
... by (a) looking at the shape of the “milky band” across the sky. (b) mapping the distribution of stars in the galaxy. (c) mapping the distribution of gas clouds in the spiral arms. (d) mapping the distribution of globular clusters in the galaxy. 46. Disk stars are mostly (a) Population I stars. (b) P ...
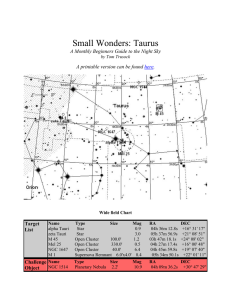
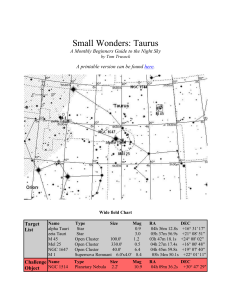
Small Wonders: Taurus
... NGC1514 is the first object this month that you really can't grab in a standard set of binoculars, and thus a fitting challenge object to close out this month's tour. Its a fairly accessible planetary nebula (to a moderate sized scope anyway), but with a small twist. With many PN's, the challenge l ...
... NGC1514 is the first object this month that you really can't grab in a standard set of binoculars, and thus a fitting challenge object to close out this month's tour. Its a fairly accessible planetary nebula (to a moderate sized scope anyway), but with a small twist. With many PN's, the challenge l ...
stars - science1d
... 1. In which constellation is Polaris ( the North Star) located? 2. What planet is shown in the constellation Capricornus? 3. Betelgeuse is a large star located in what constellation? 4. What is the name of the constellation that has three bright stars in a row? 5. What is the name of the star that s ...
... 1. In which constellation is Polaris ( the North Star) located? 2. What planet is shown in the constellation Capricornus? 3. Betelgeuse is a large star located in what constellation? 4. What is the name of the constellation that has three bright stars in a row? 5. What is the name of the star that s ...
neutron star - The University of Chicago
... Multi-dimensional simulations show us that the last few moments before core-collapse the star undergoes quite a turbulent situation. Convective turbulence, triggered by vigorous shell nuclear burning, changes the internal structure and shape of the star and drives it away from spherical symmetry. ...
... Multi-dimensional simulations show us that the last few moments before core-collapse the star undergoes quite a turbulent situation. Convective turbulence, triggered by vigorous shell nuclear burning, changes the internal structure and shape of the star and drives it away from spherical symmetry. ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... When core hydrogen fusion ceases, a main-sequence star becomes a giant • When hydrogen fusion ceases in the core, the star will collapse inward – this causes the layer just outside the core to become so hot and dense that hydrogen fusion will begin in this outer layer. • The energy produced by hydr ...
... When core hydrogen fusion ceases, a main-sequence star becomes a giant • When hydrogen fusion ceases in the core, the star will collapse inward – this causes the layer just outside the core to become so hot and dense that hydrogen fusion will begin in this outer layer. • The energy produced by hydr ...
BAS Visit to the Norman Lockyer Observatory, October 2015
... Omicron Ceti, better known as Mira in the constellation Cetus, is a binary star consisting of a red giant and a companion star. The system is approximately 400 light years distant. See page 13 for star map and location. Mira A, a red giant belonging to the spectral type M7 IIIe, is an oscillating va ...
... Omicron Ceti, better known as Mira in the constellation Cetus, is a binary star consisting of a red giant and a companion star. The system is approximately 400 light years distant. See page 13 for star map and location. Mira A, a red giant belonging to the spectral type M7 IIIe, is an oscillating va ...
Death of Stars notes
... explosions called supernovae, the chemical elements forged in the stars’ interiors-and created in the heat and pressure of the explosion--are released into space as a debris cloud of hot gas and dust. • Scientists had evidence of such dust formation, but couldn’t be sure that the dust wasn’t destroy ...
... explosions called supernovae, the chemical elements forged in the stars’ interiors-and created in the heat and pressure of the explosion--are released into space as a debris cloud of hot gas and dust. • Scientists had evidence of such dust formation, but couldn’t be sure that the dust wasn’t destroy ...
Astronomy Merit Badge Workshop
... place, for four days in a row. Include landmarks on the horizon such as hills, trees, and buildings. Suggested Procedure: First check to see whether it is a morning or evening moon and choose a time to view the moon. Avoid an observation period when there will be a new moon. Choose a time and place ...
... place, for four days in a row. Include landmarks on the horizon such as hills, trees, and buildings. Suggested Procedure: First check to see whether it is a morning or evening moon and choose a time to view the moon. Avoid an observation period when there will be a new moon. Choose a time and place ...
File
... *After a nova fades, astronomers can photograph the spectrum of the remaining faint point of light. ...
... *After a nova fades, astronomers can photograph the spectrum of the remaining faint point of light. ...
observingnebulaeclusters-1
... above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Teles ...
... above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Teles ...
2014 State Test
... parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, choose from the following list: Gamma ray, Infrared, Microwave, Radio, Ultraviolet, Visible, X-ray All questions at this station are worth one (1) point. ...
... parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, choose from the following list: Gamma ray, Infrared, Microwave, Radio, Ultraviolet, Visible, X-ray All questions at this station are worth one (1) point. ...
March
... candidate for either the Broadband or the OIII filter for visual observing in order to accentuate the nebulosity. ...
... candidate for either the Broadband or the OIII filter for visual observing in order to accentuate the nebulosity. ...
Supernovae and supernova remnants
... wavelengths. This is especially true in the Galactic plane. Since most of the stars of the Galaxy are in the Galactic plane, only those supernovae that occur nearby are visible. On the contrary, supernovae appearing in external galaxies lying outside of the Galactic plane can be easily seen. We can ...
... wavelengths. This is especially true in the Galactic plane. Since most of the stars of the Galaxy are in the Galactic plane, only those supernovae that occur nearby are visible. On the contrary, supernovae appearing in external galaxies lying outside of the Galactic plane can be easily seen. We can ...
Star Formation
... • Julio Navarro says No – correct age but wrong space motion • Or maybe HD162826 is a sibling? ...
... • Julio Navarro says No – correct age but wrong space motion • Or maybe HD162826 is a sibling? ...
Open Houses at the Campus Observatory Astronomical Horizons Lecture
... Guest star of 1054 • Records of Sung Dynasty • In the first year of the period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
... Guest star of 1054 • Records of Sung Dynasty • In the first year of the period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
SN 1054

SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 4 July 1054 A.D. (hence its name), and that lasted for a period of around two years. The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a document from the Arab world. Furthermore, there are a number of proposed, but doubtful, references from European sources recorded in the 15th century, and perhaps a pictograph associated with the Ancestral Puebloan culture found near the Peñasco Blanco site in New Mexico.The remnant of SN 1054, which consists of debris ejected during the explosion, is known as the Crab Nebula. It is located in the sky near the star Zeta Tauri (ζ Tauri). The core of the exploding star formed a pulsar, called the Crab Pulsar (or PSR B0531+21). The nebula and the pulsar it contains are the most studied astronomical objects outside the Solar System. It is one of the few Galactic supernovae where the date of the explosion is well known. The two objects are the most luminous in their respective categories. For these reasons, and because of the important role it has repeatedly played in the modern era, SN 1054 is the best known supernova in the history of astronomy.The Crab Nebula is easily observed by amateur astronomers thanks to its brightness, and was also catalogued early on by professional astronomers, long before its true nature was understood and identified. When the French astronomer Charles Messier watched for the return of Halley's Comet in 1758, he confused the nebula for the comet, as he was unaware of the former's existence. Due to this error, he created his catalogue of non-cometary nebulous objects, the Messier Catalogue, to avoid such mistakes in the future. The nebula is catalogued as the first Messier object, or M1.








![HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010665051_1-e4f26b4aee29f3f3aaab891d368963d6-300x300.png)