PHANTASTICA Regulates Development of the Adaxial Mesophyll in
... is shown in Figure 1 with identical residues shaded. All have a highly conserved MYB DNA binding domain at the N terminus, consisting of two imperfect repeats (55 and 51 residues), both of which are essential for sequence-specific DNA binding based on structural analysis of c-MYB (Jin and Martin, 19 ...
... is shown in Figure 1 with identical residues shaded. All have a highly conserved MYB DNA binding domain at the N terminus, consisting of two imperfect repeats (55 and 51 residues), both of which are essential for sequence-specific DNA binding based on structural analysis of c-MYB (Jin and Martin, 19 ...
Gene Section ID4 (inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein)
... suppression was found in breast cancer cell lines as well as in primary breast cancers. In one study, it was a significant risk factor for nodal metastasis (Umetani et al., 2006). In another study, BRCA1, ER (estrogen receptor), and ID4 were found expressed in breast cancer specimens from patients w ...
... suppression was found in breast cancer cell lines as well as in primary breast cancers. In one study, it was a significant risk factor for nodal metastasis (Umetani et al., 2006). In another study, BRCA1, ER (estrogen receptor), and ID4 were found expressed in breast cancer specimens from patients w ...
Alternative Splicing in Higher Plants
... Phenotypic effects of alternative splicing are most commonly noted in human disease – Cystic fibrosis is commonly associated with SNPs that reduce splicing of exons 9 and 12 – Recent multivariate analysis has supported the intuitive idea that longer genes with higher numbers of introns are more like ...
... Phenotypic effects of alternative splicing are most commonly noted in human disease – Cystic fibrosis is commonly associated with SNPs that reduce splicing of exons 9 and 12 – Recent multivariate analysis has supported the intuitive idea that longer genes with higher numbers of introns are more like ...
Charge Transport in DNA - Insights from
... nucleobase sequences in the design of DNA-based nano-electronic devices. Common to the setup of many DNA conductivity studies [8, 9, 11, 12] is the fact that the aqueous solvent is removed so that the solvent conductivity does not bias the measurement. The amount of residual solvent attached to the ...
... nucleobase sequences in the design of DNA-based nano-electronic devices. Common to the setup of many DNA conductivity studies [8, 9, 11, 12] is the fact that the aqueous solvent is removed so that the solvent conductivity does not bias the measurement. The amount of residual solvent attached to the ...
שקופית 1
... Whether the LHb genes in species other than primates and equids contain an untranslated CTP-like sequence? Yes, a CTP-like sequence is cryptic in the LHb gene of several mammals but not in birds, amphibians and fishes Whether the incorporation of the cryptic CTP sequence in the bovine LHb reading fr ...
... Whether the LHb genes in species other than primates and equids contain an untranslated CTP-like sequence? Yes, a CTP-like sequence is cryptic in the LHb gene of several mammals but not in birds, amphibians and fishes Whether the incorporation of the cryptic CTP sequence in the bovine LHb reading fr ...
Structure and function of the GINS complex, a key component of the
... but two essential proteins, Sld2 and Sld3, have been shown to comprise the minimal set required for replication initiation [21,22]. Phosphorylation of Sld3 by S-CDK on Thr600 and Ser622 is essential for cell viability, substituting these two residues with non-phosphorylatable alanine residues blocks ...
... but two essential proteins, Sld2 and Sld3, have been shown to comprise the minimal set required for replication initiation [21,22]. Phosphorylation of Sld3 by S-CDK on Thr600 and Ser622 is essential for cell viability, substituting these two residues with non-phosphorylatable alanine residues blocks ...
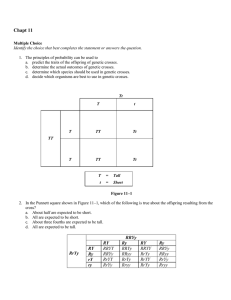
Pedigree Analysis Introduction Developing Conclusions About
... crossed them to one another. He found that their offspring occasionally had white flowers. That's because the white allele was recessive, which means you need two copies of that allele to display a certain trait. The offspring that inherited the white allele from both parents displayed the white phe ...
... crossed them to one another. He found that their offspring occasionally had white flowers. That's because the white allele was recessive, which means you need two copies of that allele to display a certain trait. The offspring that inherited the white allele from both parents displayed the white phe ...
Delivering copper within plant cells Edward Himelblau* and
... be determined. It will be important to determine whether a mutation in CCH or RAN1 can prevent the export of copper from senescing leaves. Studies of leaf senescence have focused on identifying genes that are upregulated during senescence [29]. These ‘senescence-associated genes’ (SAGs) are thought ...
... be determined. It will be important to determine whether a mutation in CCH or RAN1 can prevent the export of copper from senescing leaves. Studies of leaf senescence have focused on identifying genes that are upregulated during senescence [29]. These ‘senescence-associated genes’ (SAGs) are thought ...
C. neoformans
... N2 nematodes were fed on lawns of C. neoformans and then at different time-points transferred to lawns of non-pathogenic cryptococci. All nematodes that survived transfer were rescued, regained normal non-distended anatomy and no C. neoformans yeast cells could be cultured followed “grinding” of the ...
... N2 nematodes were fed on lawns of C. neoformans and then at different time-points transferred to lawns of non-pathogenic cryptococci. All nematodes that survived transfer were rescued, regained normal non-distended anatomy and no C. neoformans yeast cells could be cultured followed “grinding” of the ...
JBS Haldane
... descended from animals created a furor among Europeans (Dronamraju 2009, p. 211), whereas many eastern religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism have long recognized that animals have rights and duties. Indian art and religion depicted divinity in various animal forms. Kindness toward other ...
... descended from animals created a furor among Europeans (Dronamraju 2009, p. 211), whereas many eastern religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism have long recognized that animals have rights and duties. Indian art and religion depicted divinity in various animal forms. Kindness toward other ...
In vitro fertilization (IVF) in mammals: epigenetic and developmental
... between genotype and phenotype. Genetics had discovered the laws of inheritance and had explained how different characters are transmitted from parents to offspring. But, Waddington underlined, that there wasn’t much knowledge about the mechanisms of development. He named this process Epigenetics, w ...
... between genotype and phenotype. Genetics had discovered the laws of inheritance and had explained how different characters are transmitted from parents to offspring. But, Waddington underlined, that there wasn’t much knowledge about the mechanisms of development. He named this process Epigenetics, w ...
Unit 1 Review Answer Key 1. Define the following terms: a
... 20. If you were conducting a testcross with an unknown individual for one allele and you found the offspring to be 50% one phenotype and 50% the other, then what was the genotype of the unknown? A. Homozygous dominant B. Heterozygous C. Homozygous recessive D. Unknown based on this information 21. ...
... 20. If you were conducting a testcross with an unknown individual for one allele and you found the offspring to be 50% one phenotype and 50% the other, then what was the genotype of the unknown? A. Homozygous dominant B. Heterozygous C. Homozygous recessive D. Unknown based on this information 21. ...
Evolutionary relationships between the former species
... sequenced with primers based on the sequences available in the SGD database (Table 2). The GDH1 PCR fragment from strain S288c and the SUC4 PCR fragment from strain CBS 1171NT were used as probes in Southern-hybridisation experiments. 2.2.4. D1/D2 and NTS2 of ribosomal DNA The D1/D2 and NTS2 (Non Tr ...
... sequenced with primers based on the sequences available in the SGD database (Table 2). The GDH1 PCR fragment from strain S288c and the SUC4 PCR fragment from strain CBS 1171NT were used as probes in Southern-hybridisation experiments. 2.2.4. D1/D2 and NTS2 of ribosomal DNA The D1/D2 and NTS2 (Non Tr ...
Disruption and aberrant expression of HMGA2 as a
... that may also encode truncated forms of HMGA2. These mRNAs are structurally similar to those formed by gene fusion, typically consisting of HMGA2 exons 1–3 fused to intronic sequences from the same gene.8,26 These mRNA variants have been found in all the tumor types described above.8,26–29 These fin ...
... that may also encode truncated forms of HMGA2. These mRNAs are structurally similar to those formed by gene fusion, typically consisting of HMGA2 exons 1–3 fused to intronic sequences from the same gene.8,26 These mRNA variants have been found in all the tumor types described above.8,26–29 These fin ...
EXPRESSION OF ADH SYSTEM IN DROSOPHZLA B TZZ
... adaptative significance in the different environments to which larvae and adults are confronted in cactophilic species. In effect, larvae are submerged in an alcoholic environment and its feeding activity is large in order to support the extensive growth to what they are subjected to. Thus the inges ...
... adaptative significance in the different environments to which larvae and adults are confronted in cactophilic species. In effect, larvae are submerged in an alcoholic environment and its feeding activity is large in order to support the extensive growth to what they are subjected to. Thus the inges ...
Genetic analysis of non-syndromic craniosynostosis
... A P250R mutation in FGFR3 was identified in patients with presumably non-syndromic coronal craniosynostosis (34) that were later categorized as having Muenke syndrome (35). Analysis of 26 patients with coronal craniosynostosis found this mutation in 31% of the cases (36). On the basis of statistical ...
... A P250R mutation in FGFR3 was identified in patients with presumably non-syndromic coronal craniosynostosis (34) that were later categorized as having Muenke syndrome (35). Analysis of 26 patients with coronal craniosynostosis found this mutation in 31% of the cases (36). On the basis of statistical ...
An Analytically Tractable Model for Competitive Speciation
... Electronically published November 15, 2007 ...
... Electronically published November 15, 2007 ...
get Assignment File
... 39.Scientists studying a meadow ecosystem collect western white butterflies from a single population in the spring and summer. They notice that all individuals that hatch in the spring have darker wings than those that hatch in the summer. What is the most likely explanation for these different tra ...
... 39.Scientists studying a meadow ecosystem collect western white butterflies from a single population in the spring and summer. They notice that all individuals that hatch in the spring have darker wings than those that hatch in the summer. What is the most likely explanation for these different tra ...
2. Assessing the probative value of DNA evidence
... jurisdictions. It goes without saying that the laws of probability, unlike the laws of the land, are valid irrespective of geography. It would be artificial and sometimes misleading when describing criminal litigation to avoid any reference whatsoever to legal precepts and doctrines, and we have not ...
... jurisdictions. It goes without saying that the laws of probability, unlike the laws of the land, are valid irrespective of geography. It would be artificial and sometimes misleading when describing criminal litigation to avoid any reference whatsoever to legal precepts and doctrines, and we have not ...
Mendel PowerPoint - the Bee
... genetic trait in several generations of a family. Sex-linked gene: A gene found on one of the sex chromosomes, such as the X chromosome or Y chromosome in humans. Polygenic Inheritance: A characteristic of an organism that is determined by many genes. ...
... genetic trait in several generations of a family. Sex-linked gene: A gene found on one of the sex chromosomes, such as the X chromosome or Y chromosome in humans. Polygenic Inheritance: A characteristic of an organism that is determined by many genes. ...
This document has been downloaded from Tampub – The
... where it can be processed by two specific proteases and then release the amino-terminal transcription-activation domain of the SREBF. The active form of SREBF can then travel to the nucleus where it binds to the promoters of target genes [1]. The SREBFs consist of three different SREBF isoforms, SRE ...
... where it can be processed by two specific proteases and then release the amino-terminal transcription-activation domain of the SREBF. The active form of SREBF can then travel to the nucleus where it binds to the promoters of target genes [1]. The SREBFs consist of three different SREBF isoforms, SRE ...
Assessing the Probative Value of DNA Evidence
... jurisdictions. It goes without saying that the laws of probability, unlike the laws of the land, are valid irrespective of geography. It would be artificial and sometimes misleading when describing criminal litigation to avoid any reference whatsoever to legal precepts and doctrines, and we have not ...
... jurisdictions. It goes without saying that the laws of probability, unlike the laws of the land, are valid irrespective of geography. It would be artificial and sometimes misleading when describing criminal litigation to avoid any reference whatsoever to legal precepts and doctrines, and we have not ...
Complete comparative genomic analysis of two field isolates of
... dispersed throughout the genome, specific regions have a significantly higher density of changes (Fig. 2). The most variable region is located between hr1 and orf31 (bro-c) (v90/4, 15?0–27?1 kb; v90/2, 15?0–28?3 kb). In this 12?1 kb region (7?7 % of the genome), there are 261 of the 521 point mutati ...
... dispersed throughout the genome, specific regions have a significantly higher density of changes (Fig. 2). The most variable region is located between hr1 and orf31 (bro-c) (v90/4, 15?0–27?1 kb; v90/2, 15?0–28?3 kb). In this 12?1 kb region (7?7 % of the genome), there are 261 of the 521 point mutati ...
Chromosome Variation
... have three copies of the duplication and much smaller bar-shaped eyes. that one or both chromosomes loop and twist so that these regions are able to line up ( ◗ FIGURE 9.6b). The appearance of this characteristic loop structure during meiosis is one way to detect duplications. Duplications may have ...
... have three copies of the duplication and much smaller bar-shaped eyes. that one or both chromosomes loop and twist so that these regions are able to line up ( ◗ FIGURE 9.6b). The appearance of this characteristic loop structure during meiosis is one way to detect duplications. Duplications may have ...
A PCR approach to determine the distribution of toxin genes in
... interest because of their association with serious infections in injecting drug users (C. novyi type A) and equine and feline dysautonomias (C. botulinum types C/D). The species are defined by the major toxins they produce: the a toxin of C. novyi, and the type C and D neurotoxins of C. botulinum (B ...
... interest because of their association with serious infections in injecting drug users (C. novyi type A) and equine and feline dysautonomias (C. botulinum types C/D). The species are defined by the major toxins they produce: the a toxin of C. novyi, and the type C and D neurotoxins of C. botulinum (B ...