The RET gene and its associated diseases Hofstra, Robert Martinus
... amino acid changes, act as dominant transforming genes in NIH3T3 cells as a result of a constitutive activation of the RET protein (Santoro et al., 1994). This constitutive activation was caused by a ligand-independent dimerization of the protein. Furthermore, Santoro et al. (1994) suggested that th ...
... amino acid changes, act as dominant transforming genes in NIH3T3 cells as a result of a constitutive activation of the RET protein (Santoro et al., 1994). This constitutive activation was caused by a ligand-independent dimerization of the protein. Furthermore, Santoro et al. (1994) suggested that th ...
marker assisted selection in disease resistance breeding
... they are generally independent of environmental growth conditions. The only problem with isozymes in MAS is that most cultivars (commercial breeds of plants) are genetically very similar and isozymes do not produce a great amount of polymorphism and polymorphism in the protein primary structure may ...
... they are generally independent of environmental growth conditions. The only problem with isozymes in MAS is that most cultivars (commercial breeds of plants) are genetically very similar and isozymes do not produce a great amount of polymorphism and polymorphism in the protein primary structure may ...
Sex-specific Trans-regulatory Variation on the Drosophila melanogaster X Chromosome
... even reversed. In species where neither the X chromosome nor the autosomes recombine in males (e.g. Drosophila), the rate of recombination could be lower on the autosomes. Lower autosomal rates of recombination would, because of Hill-Robertson interference, result in a larger reduction in the effect ...
... even reversed. In species where neither the X chromosome nor the autosomes recombine in males (e.g. Drosophila), the rate of recombination could be lower on the autosomes. Lower autosomal rates of recombination would, because of Hill-Robertson interference, result in a larger reduction in the effect ...
A Fine Physical Map of Arabidopsis thaliana Chromosome 5
... of the YAC contigs were closed by assigquences of positive clones were determined by amplification with cassette-ligated PCR21 followed by sequencing ment of PI, TAC and BAC clones. Finally, the physical with dye terminator cycle sequencing kit FS or dRho- map consisted of two contigs covering 11.6 ...
... of the YAC contigs were closed by assigquences of positive clones were determined by amplification with cassette-ligated PCR21 followed by sequencing ment of PI, TAC and BAC clones. Finally, the physical with dye terminator cycle sequencing kit FS or dRho- map consisted of two contigs covering 11.6 ...
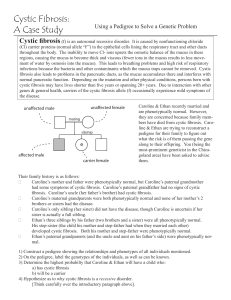
Cystic Fibrosis: A Case Study
... It is caused by nonfunctioning chloride (Cl) carrier proteins (normal allele “F”) in the epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract and other ducts throughout the body. The inability to move Cl- ions upsets the osmotic balance of the mucus in these regions, causing the mucus to become thick and v ...
... It is caused by nonfunctioning chloride (Cl) carrier proteins (normal allele “F”) in the epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract and other ducts throughout the body. The inability to move Cl- ions upsets the osmotic balance of the mucus in these regions, causing the mucus to become thick and v ...
Chapter 25 RNA Metabolism
... Such single-stranded DNA loops was widely observed when examining such RNA-DNA hybrids. Intron sequences were proposed to be present on the template DNA sequences, which are removed during RNA processing, with exons linked together precisely. ...
... Such single-stranded DNA loops was widely observed when examining such RNA-DNA hybrids. Intron sequences were proposed to be present on the template DNA sequences, which are removed during RNA processing, with exons linked together precisely. ...
PLEIOTROPIC MULTI-TRAIT GENOME
... The fatty acid (FA) composition (FAC) of meat products has received considerable attention for its significance to human health. The FAC of meat is influenced by various environmental effects such as diet (e.g. Suzuki et al. 2007), the level of fatness, and genetic factors. Changing FAC through sele ...
... The fatty acid (FA) composition (FAC) of meat products has received considerable attention for its significance to human health. The FAC of meat is influenced by various environmental effects such as diet (e.g. Suzuki et al. 2007), the level of fatness, and genetic factors. Changing FAC through sele ...
Exploring the Mode-of-Action of Bioactive Compounds by Chemical
... (MIPS annotations), whereas our PSMF analysis altogether avoids the need for gene function annotations. In this analysis, we identified 30 factors and represented each signature as a weighted sum of up to three factors. By detecting a factor, the algorithm is identifying compounds that have a simila ...
... (MIPS annotations), whereas our PSMF analysis altogether avoids the need for gene function annotations. In this analysis, we identified 30 factors and represented each signature as a weighted sum of up to three factors. By detecting a factor, the algorithm is identifying compounds that have a simila ...
Generic Representation of Solid-Object Geometry for Genetic Search
... a coding of the phenotype. Obviously for every different design task, a good solution will be a different phenotype. However, today it is also normally the case that for every different design task, the phenotype representation is different. Representations can vary from a few hand-picked dimensions ...
... a coding of the phenotype. Obviously for every different design task, a good solution will be a different phenotype. However, today it is also normally the case that for every different design task, the phenotype representation is different. Representations can vary from a few hand-picked dimensions ...
DNA Testing - Who Murdered Robert Wone
... significant problem. The ability of small amounts of DNA to produce false and misleading results is well-known and well-documented within the research community, where the technology originated. Anyone who has caught a cold from an unknown source, or who has a pollen allergy should have some sense o ...
... significant problem. The ability of small amounts of DNA to produce false and misleading results is well-known and well-documented within the research community, where the technology originated. Anyone who has caught a cold from an unknown source, or who has a pollen allergy should have some sense o ...
A Functional Polymorphism in the HMGCR Promoter
... on prenylation is well established (Naidu et al., 2002), suggesting reduced flux through the mevalonate pathway may have multiple effects on APOE secretion. A very recent study reported that total brain APOE levels are influenced by the APOE genotype, with APOE4 associated with lowest levels (Ridde ...
... on prenylation is well established (Naidu et al., 2002), suggesting reduced flux through the mevalonate pathway may have multiple effects on APOE secretion. A very recent study reported that total brain APOE levels are influenced by the APOE genotype, with APOE4 associated with lowest levels (Ridde ...
Deciphering the developmental program in the ascidian
... the overall GRN (Fig. 1). Living organisms tend to exclude wastefulness from their genomes. Consequently, a paradoxical phenomenon might emerge: genes that are more critical for development might show fewer abnormalities than less important genes when they are knocked out because of functional redun ...
... the overall GRN (Fig. 1). Living organisms tend to exclude wastefulness from their genomes. Consequently, a paradoxical phenomenon might emerge: genes that are more critical for development might show fewer abnormalities than less important genes when they are knocked out because of functional redun ...
movement of flocked subpopulations in distributed genetic
... improvement of deterioration of the search characteristics. Besides the number of subpopulations, the main additional parameters of DGP are: 1. migration frequency - how many generations are run between two subsequent migrations; 2. migration rate - how many individuals migrate each time; 3. migrati ...
... improvement of deterioration of the search characteristics. Besides the number of subpopulations, the main additional parameters of DGP are: 1. migration frequency - how many generations are run between two subsequent migrations; 2. migration rate - how many individuals migrate each time; 3. migrati ...
6 Gene Interaction
... binding site of such a protein product would be different, and it would not be able to bind to a functional gene product of the gene m. Only when both genes ‘m’ and ‘s’ are mutant, wild type could occur at the phenotypic level. ...
... binding site of such a protein product would be different, and it would not be able to bind to a functional gene product of the gene m. Only when both genes ‘m’ and ‘s’ are mutant, wild type could occur at the phenotypic level. ...
proposal
... produced that expressed non-mutated human LMNA or C what would it have meant for there to been no discernable phenotype? After screening for the transgene itself it may have been located in a region that suppressed its transcription. Perhaps the protein was not being incorporated into the nuclear la ...
... produced that expressed non-mutated human LMNA or C what would it have meant for there to been no discernable phenotype? After screening for the transgene itself it may have been located in a region that suppressed its transcription. Perhaps the protein was not being incorporated into the nuclear la ...
Inbreeding and Inbreeding Depression
... The magnitude of the effect depends on how many harmful recessive alleles are found in the population, and how harmful they are. This is called the genetic load. Genetic load will tend to be lower in species (populations) in which inbreeding has been common in the past (e.g. species with small popu ...
... The magnitude of the effect depends on how many harmful recessive alleles are found in the population, and how harmful they are. This is called the genetic load. Genetic load will tend to be lower in species (populations) in which inbreeding has been common in the past (e.g. species with small popu ...
Streptococcus pyogenes - Mike Dyall
... “This is the first time that a human polypeptide has been directly expressed in E.coli in a non-precursor form.” •Made a gene hybrid (cDNA and synthetic DNA) that coded for the processed form of HGH. •Able to express HGH protein in E.coli at high levels (could purify it easily) ...
... “This is the first time that a human polypeptide has been directly expressed in E.coli in a non-precursor form.” •Made a gene hybrid (cDNA and synthetic DNA) that coded for the processed form of HGH. •Able to express HGH protein in E.coli at high levels (could purify it easily) ...
Splice Site Prediction Using Artificial Neural Networks
... The remaining data set, after exclusion of some genes, consists of 21985 genes. This set is divided into a training data set and a benchmarking data set. The training set and the benchmark set have 16965 and 5000 genes, respectively. The remaining 20 genes, four from each chromosome, was kept for a ...
... The remaining data set, after exclusion of some genes, consists of 21985 genes. This set is divided into a training data set and a benchmarking data set. The training set and the benchmark set have 16965 and 5000 genes, respectively. The remaining 20 genes, four from each chromosome, was kept for a ...
A Haploid System of Sex Determination in the Brown Alga - Hal-CEA
... it from the XY and ZW systems described above [10], exhibits specific evolutionary and genetic properties that have no exact equivalent in diploid systems. In UV systems, the female and male SDR haplotypes function in independent, haploid, male and female, individuals and consequently there is no he ...
... it from the XY and ZW systems described above [10], exhibits specific evolutionary and genetic properties that have no exact equivalent in diploid systems. In UV systems, the female and male SDR haplotypes function in independent, haploid, male and female, individuals and consequently there is no he ...
Sex Determination in Flowering Plants
... environmental factors. The highest outcrossing rates are found among dioecious plants, in which outcrossing is obligatory. Lower rates are found among monoecious plants, in which the spatial separation of sexes within the Same individual may favor cross-pollination but does not guarantee it. In dioe ...
... environmental factors. The highest outcrossing rates are found among dioecious plants, in which outcrossing is obligatory. Lower rates are found among monoecious plants, in which the spatial separation of sexes within the Same individual may favor cross-pollination but does not guarantee it. In dioe ...
Pathogen Response Genes Mediate Caenorhabditis elegans Innate
... Host-pathogen interactions involve multiple molecular recognition events that are required both for effective infection by a pathogen and for resistance against infection by a host (Medzhitov 2007). Understanding this complex conversation between host and pathogen has become a major research focus i ...
... Host-pathogen interactions involve multiple molecular recognition events that are required both for effective infection by a pathogen and for resistance against infection by a host (Medzhitov 2007). Understanding this complex conversation between host and pathogen has become a major research focus i ...
Lab 4: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance
... carry two alleles of sex‐linked genes, one on each X chromosome. Males, however, only have one X chromosome and therefore only carry one allele of a sex‐linked gene. This means that whatever allele is passed on to males on the X chromosome will be expressed regardless of whether it is dominant o ...
... carry two alleles of sex‐linked genes, one on each X chromosome. Males, however, only have one X chromosome and therefore only carry one allele of a sex‐linked gene. This means that whatever allele is passed on to males on the X chromosome will be expressed regardless of whether it is dominant o ...
Paper - John Innes Centre
... a susceptible genotype; some leaf sections from such a plant might have little or no disease because they were not successfully infected. On the other hand, leaf sections from an individual with a resistant genotype should never be highly diseased. The wheat– M. graminicola interaction is a difficul ...
... a susceptible genotype; some leaf sections from such a plant might have little or no disease because they were not successfully infected. On the other hand, leaf sections from an individual with a resistant genotype should never be highly diseased. The wheat– M. graminicola interaction is a difficul ...
Supercoils in plant DNA: nucleoid
... higher order organization of nuclear DNA in plants have been conducted. Plants share many common features with the other eukaryotes, but there are also many peculiarities distinguishing them. For example, they possess unusually large genomes, highly variable in size and organization from species to ...
... higher order organization of nuclear DNA in plants have been conducted. Plants share many common features with the other eukaryotes, but there are also many peculiarities distinguishing them. For example, they possess unusually large genomes, highly variable in size and organization from species to ...
A-level Biology Question paper Unit 04 - Populations and
... In cats, males are XY and females are XX. A gene on the X chromosome controls fur colour in cats. The allele G codes for ginger fur and the allele B codes for black fur. These alleles are codominant. Heterozygous females have ginger and black patches of fur and their phenotype is described as tortoi ...
... In cats, males are XY and females are XX. A gene on the X chromosome controls fur colour in cats. The allele G codes for ginger fur and the allele B codes for black fur. These alleles are codominant. Heterozygous females have ginger and black patches of fur and their phenotype is described as tortoi ...