bYTEBoss Doc
... with 1 short plant he found 100% of F1 was tall. When Mendel crossed F1 X F1 he found the F2 to be 75% tall and 25% short (3:1 ratio) ...
... with 1 short plant he found 100% of F1 was tall. When Mendel crossed F1 X F1 he found the F2 to be 75% tall and 25% short (3:1 ratio) ...
Thomas Hunt Morgan, 1933
... Reasoning that the closer genes are on the chromosome the less likely they are to cross over with the homologous chromosome, he worked all night and the next morning presented Morgan with a linear arrangement of the genes on the X chromosome. Sturtevant was 19 at the time. In 1928 he moved with Morg ...
... Reasoning that the closer genes are on the chromosome the less likely they are to cross over with the homologous chromosome, he worked all night and the next morning presented Morgan with a linear arrangement of the genes on the X chromosome. Sturtevant was 19 at the time. In 1928 he moved with Morg ...
Multiple Choice Questions – Answers
... cells. Mitotic division results in daughter cells containing a full number of genes as the parent cell they came from. 5. The type of cell division that occurs in the gamete cells is known as: A Cytosis B Meiosis [True] C Osmosis D Mitosis The correct answer is B. Meiosis is the cell division proces ...
... cells. Mitotic division results in daughter cells containing a full number of genes as the parent cell they came from. 5. The type of cell division that occurs in the gamete cells is known as: A Cytosis B Meiosis [True] C Osmosis D Mitosis The correct answer is B. Meiosis is the cell division proces ...
Chromosomes & Heredity - Fox Valley Lutheran High School
... Each gene occupies a specific place A gene may exist in several forms or alleles Each chromosome has just one allele for each of its genes ...
... Each gene occupies a specific place A gene may exist in several forms or alleles Each chromosome has just one allele for each of its genes ...
1. Describe the contributions that Thomas Hunt Morgan, Walter
... - smaller head, unusual features, cry sounds like a mewing cat • Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) part of chromosome 22 switches places with a small fragment from chromosome 9 (translocations) ...
... - smaller head, unusual features, cry sounds like a mewing cat • Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) part of chromosome 22 switches places with a small fragment from chromosome 9 (translocations) ...
Genetics 3 – Aneuploidies and Other Chromosome
... There are 3 main types of chromosome aberrations: • Structural – translocations, deletions, insertions, inversions, rings • Numerical – aneuploidy, loss or gain • Mosaicism – different cell lines Aberrations cause: - 60% of all early spontaneous miscarriages. - 4.5% of all still births (dead when bo ...
... There are 3 main types of chromosome aberrations: • Structural – translocations, deletions, insertions, inversions, rings • Numerical – aneuploidy, loss or gain • Mosaicism – different cell lines Aberrations cause: - 60% of all early spontaneous miscarriages. - 4.5% of all still births (dead when bo ...
3. Fundamentals of human genetics.methods of research of human
... Male-to-male transmission never occurs Carrier females are usually asymptomatic, but some may express the condition with variable severity because of Lyonization, or X-inactivation. ...
... Male-to-male transmission never occurs Carrier females are usually asymptomatic, but some may express the condition with variable severity because of Lyonization, or X-inactivation. ...
Ch 2: Genetics and Prenatal Development
... 11. _______________________________ is when eggs and sperm are fertilized in a petri dish then placed in the mother’s uterus for further development. 12. During ____________________ the cell copies its own chromosome. 13. During____________________ sperm and egg cells form. 14. The sex cell is calle ...
... 11. _______________________________ is when eggs and sperm are fertilized in a petri dish then placed in the mother’s uterus for further development. 12. During ____________________ the cell copies its own chromosome. 13. During____________________ sperm and egg cells form. 14. The sex cell is calle ...
File
... in gametes. Embryos that develop from these gametes will have missing or extra chromosomes • Duplication, deletion, inversion and translocation are types of damage that can occur to chromosomes during meiosis ...
... in gametes. Embryos that develop from these gametes will have missing or extra chromosomes • Duplication, deletion, inversion and translocation are types of damage that can occur to chromosomes during meiosis ...
Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation
... This is observed cytologically. One of the X-chromosomes in females appears highly condensed. This inactivated chromosome is called a Barr-body. ...
... This is observed cytologically. One of the X-chromosomes in females appears highly condensed. This inactivated chromosome is called a Barr-body. ...
Lecture 14
... The probability of recombination occurring between 2 loci on the same chromosome is a function of the distance between them ...
... The probability of recombination occurring between 2 loci on the same chromosome is a function of the distance between them ...
Chromosomal Inheritance pdf
... In females, most diploid cells have only one fully functional X chromosome Lyon hypothesis (Mary Lyon) each embryonic cell inactivates one X producing densely staining body: Barr body Barr bodies are highly methylated: XIST gene X Inactive Specific Transcript (RNA) Barr bodies are reactivated in gon ...
... In females, most diploid cells have only one fully functional X chromosome Lyon hypothesis (Mary Lyon) each embryonic cell inactivates one X producing densely staining body: Barr body Barr bodies are highly methylated: XIST gene X Inactive Specific Transcript (RNA) Barr bodies are reactivated in gon ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度
... (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or from “is” to “isn’t”). (10%) (i) Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites that always located between genes. (ii ...
... (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or from “is” to “isn’t”). (10%) (i) Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites that always located between genes. (ii ...
Lecture 33: Mitosis and Meiosis
... the same genes in the same location. Humans have 23 pairs. Allele: Indicates a different DNA sequence in a gene. Genes on homologous chromosomes can be different alleles. The different alleles may result in different amino acid sequences with different functional properties. In the diagram above “A” ...
... the same genes in the same location. Humans have 23 pairs. Allele: Indicates a different DNA sequence in a gene. Genes on homologous chromosomes can be different alleles. The different alleles may result in different amino acid sequences with different functional properties. In the diagram above “A” ...
Chromosomal Disorders
... Chromosomal Disorders Chromosomal deletion: when cells go through meiosis, portions of the chromosome are lost. Chromosomal inversion: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosome are flipped. Chromosomal translocation: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosomes stick tog ...
... Chromosomal Disorders Chromosomal deletion: when cells go through meiosis, portions of the chromosome are lost. Chromosomal inversion: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosome are flipped. Chromosomal translocation: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosomes stick tog ...
Chromosomal Disorders
... Chromosomal Disorders Chromosomal deletion: when cells go through meiosis, portions of the chromosome are lost. Chromosomal inversion: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosome are flipped. Chromosomal translocation: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosomes stick tog ...
... Chromosomal Disorders Chromosomal deletion: when cells go through meiosis, portions of the chromosome are lost. Chromosomal inversion: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosome are flipped. Chromosomal translocation: when cells go through meiosis, parts of the chromosomes stick tog ...
TECHNICAL NOTE 4.1
... the offspring that brings our total to 46 chromosomes. If a parent were able to pass on all of its genes, then the offspring would be a clone of the parent. Because some of a parent’s genetic make-up may be detrimental (e.g., one ...
... the offspring that brings our total to 46 chromosomes. If a parent were able to pass on all of its genes, then the offspring would be a clone of the parent. Because some of a parent’s genetic make-up may be detrimental (e.g., one ...
sex in drosophila
... In about 1 in 1000 female births, the infant’s cells possess three X chromosomes, a condition often referred to as triplo-X syndrome. These persons have no distinctive features other than a tendency to be tall and thin. Although a few are sterile, many menstruate regularly and are fertile. The incid ...
... In about 1 in 1000 female births, the infant’s cells possess three X chromosomes, a condition often referred to as triplo-X syndrome. These persons have no distinctive features other than a tendency to be tall and thin. Although a few are sterile, many menstruate regularly and are fertile. The incid ...
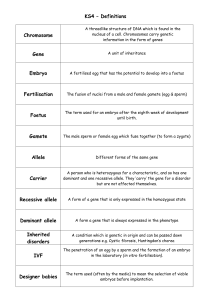
Definitions
... The penetration of an egg by a sperm and the formation of an embryo in the laboratory (in vitro fertilisation). ...
... The penetration of an egg by a sperm and the formation of an embryo in the laboratory (in vitro fertilisation). ...
Honors Biology Final Exam-‐Part 2-‐Semester 2
... 1. The process of cell division which produces cells identical to the original cell is: 2. The purpose of meiosis is to produce ____________ . 3. Body cells are 2n or ________________ . 4. Ga ...
... 1. The process of cell division which produces cells identical to the original cell is: 2. The purpose of meiosis is to produce ____________ . 3. Body cells are 2n or ________________ . 4. Ga ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.