1. Introduction 2. Fact or Fiction?
... 1. No two cells of the human body contain exactly the same material. 2. Not all individuals are born genetically unique. 3. All the genes a person has show up as observable traits. 4. Alcoholism is inherited. ...
... 1. No two cells of the human body contain exactly the same material. 2. Not all individuals are born genetically unique. 3. All the genes a person has show up as observable traits. 4. Alcoholism is inherited. ...
Document
... Disorder which is produces by a single dominant allele, no symptoms until individual is in their 30’s or 40’s ________________15. Caused by a point mutation (substitution) that changes one amino acid in the polypeptide ________________16. XO is called ________________17. XO is an example of a disord ...
... Disorder which is produces by a single dominant allele, no symptoms until individual is in their 30’s or 40’s ________________15. Caused by a point mutation (substitution) that changes one amino acid in the polypeptide ________________16. XO is called ________________17. XO is an example of a disord ...
Ch.5
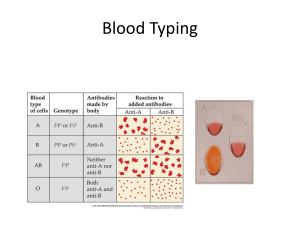
... 2)Multiple alleles-a gene that exists in more than 2 allele forms, although a diploid individual only has 1 or 2 of them. • Although each person has 2 alleles for any autosomal gene (one on each chromosome) a gene can exist in more than 2 allelic forms • Ex: Blood Types ...
... 2)Multiple alleles-a gene that exists in more than 2 allele forms, although a diploid individual only has 1 or 2 of them. • Although each person has 2 alleles for any autosomal gene (one on each chromosome) a gene can exist in more than 2 allelic forms • Ex: Blood Types ...
Heridity: Passing It On
... cell divides twice thus resulting in the formation of sex cells (gametes) that contain exactly half of the chromosomes than the other cells in your body. ...
... cell divides twice thus resulting in the formation of sex cells (gametes) that contain exactly half of the chromosomes than the other cells in your body. ...
Biology 105 - Montgomery College
... While gliding aimlessly in a puddle, a "male" and a "female" water strider encounter each other in the moonlight. Becoming intoxicated in each other’s pheromones (sexual attractant molecules), and being consenting adults, they decide to procreate. The fertilized eggs are laid and the ensuing spring ...
... While gliding aimlessly in a puddle, a "male" and a "female" water strider encounter each other in the moonlight. Becoming intoxicated in each other’s pheromones (sexual attractant molecules), and being consenting adults, they decide to procreate. The fertilized eggs are laid and the ensuing spring ...
11-3- Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... 4. The alleles for different genes usually segregate _____________________ of one another. This is the Law of __________________ _____________________. Beyond Dominant and Recessive Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another are called _______________ ______________. In incomp ...
... 4. The alleles for different genes usually segregate _____________________ of one another. This is the Law of __________________ _____________________. Beyond Dominant and Recessive Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another are called _______________ ______________. In incomp ...
GeneticsJeopardy 1314Purple-Green
... Genotype = the genetic make-up of an organism…its chromosomes ...
... Genotype = the genetic make-up of an organism…its chromosomes ...
Chapter 15~ The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Examples would be skin and eye color. This explains how you can have several different phenotypes for one trait and how parents can have offspring with eye color or skin color different from what they have. ...
... Examples would be skin and eye color. This explains how you can have several different phenotypes for one trait and how parents can have offspring with eye color or skin color different from what they have. ...
Lecture Powerpoint Here
... • When the reciprocal translocation occurred, a gene at the end of chromosome 9 fused with a gene from chromosome 22 • This hybrid gene encodes an abnormal protein that stimulates uncontrolled division of white blood cells ...
... • When the reciprocal translocation occurred, a gene at the end of chromosome 9 fused with a gene from chromosome 22 • This hybrid gene encodes an abnormal protein that stimulates uncontrolled division of white blood cells ...
Chap. 13 Sex Linked Inheiritance_2
... • It would seem that since a female has two X chromosomes, she should create twice as many proteins as a male who has only one causing another set of problems. But this doesn’t happen. Why? • Dosage compensation ...
... • It would seem that since a female has two X chromosomes, she should create twice as many proteins as a male who has only one causing another set of problems. But this doesn’t happen. Why? • Dosage compensation ...
Competency Goal # 3: DNA, Protein Synthesis, Genetics
... 36. __________________________________ - Inserting corrected gene into person who has a defective gene. 37.__________________________________ - also called DNA fingerprinting and is used in crime scene investigation. DNA fragments separate according to __________________. 38. Transgenic Organisms: _ ...
... 36. __________________________________ - Inserting corrected gene into person who has a defective gene. 37.__________________________________ - also called DNA fingerprinting and is used in crime scene investigation. DNA fragments separate according to __________________. 38. Transgenic Organisms: _ ...
Competency Goal # 3: DNA, Protein Synthesis
... 36. __________________________________ - Inserting corrected gene into person who has a defective gene. 37.__________________________________ - also called DNA fingerprinting and is used in crime scene investigation. DNA fragments separate according to __________________. 38. Transgenic Organisms: _ ...
... 36. __________________________________ - Inserting corrected gene into person who has a defective gene. 37.__________________________________ - also called DNA fingerprinting and is used in crime scene investigation. DNA fragments separate according to __________________. 38. Transgenic Organisms: _ ...
Chapter 3: Genetics: From Genotype to Phenotype
... (alleles ) according to Mendelian principles. ...
... (alleles ) according to Mendelian principles. ...
ChromosomesII - life.illinois.edu
... Organisms carrying an inversion tend to undergo little crossing over in the inversion region in both inverted and non-inverted chromosomes. If there is crossing over, half the chromatids involved in crossing over will produce non-viable gametes. ...
... Organisms carrying an inversion tend to undergo little crossing over in the inversion region in both inverted and non-inverted chromosomes. If there is crossing over, half the chromatids involved in crossing over will produce non-viable gametes. ...
Chromosome mutations
... Retrotransposons (retroposons) transpose via RNA intermediate LTR = long terminal repeat Reverse transcriptase gene ...
... Retrotransposons (retroposons) transpose via RNA intermediate LTR = long terminal repeat Reverse transcriptase gene ...
12.4 Mutations
... • Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Can change locations of genes on chromosomes or number of copies of some genes ...
... • Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Can change locations of genes on chromosomes or number of copies of some genes ...
Document
... the inactivated X chromosome. It encodes an RNA that coats the X chromosome, which subsequently attracts proteins that are responsible for the condensation. C20. Erasure and reestablishment of the imprint occurs during gametogenesis. It is necessary to erase the imprint because each sex will either ...
... the inactivated X chromosome. It encodes an RNA that coats the X chromosome, which subsequently attracts proteins that are responsible for the condensation. C20. Erasure and reestablishment of the imprint occurs during gametogenesis. It is necessary to erase the imprint because each sex will either ...
C1. Epigenetic refers to the idea that a genetic phenomenon seems
... the inactivated X chromosome. It encodes an RNA that coats the X chromosome, which subsequently attracts proteins that are responsible for the condensation. C20. Erasure and reestablishment of the imprint occurs during gametogenesis. It is necessary to erase the imprint because each sex will either ...
... the inactivated X chromosome. It encodes an RNA that coats the X chromosome, which subsequently attracts proteins that are responsible for the condensation. C20. Erasure and reestablishment of the imprint occurs during gametogenesis. It is necessary to erase the imprint because each sex will either ...
Exercise week 10 File
... ubiquitously expressed Rosa26 locus. The R26RLSL reporter has been engineered for genetic lineage tracing, e.g. to trace the fate of MyoDexpressing myoblasts. If you cross R26RLSL reporter into Sox2+/Cre mice which express Cre recombinase from the Sox2 locus, which cells and tissues will switch on t ...
... ubiquitously expressed Rosa26 locus. The R26RLSL reporter has been engineered for genetic lineage tracing, e.g. to trace the fate of MyoDexpressing myoblasts. If you cross R26RLSL reporter into Sox2+/Cre mice which express Cre recombinase from the Sox2 locus, which cells and tissues will switch on t ...
Meiosis - Learning on the Loop
... Homologous chromosomes have nearly identical structure, banding patterns, and nucleotide sequences Locus: Physical site on chromosomes where given gene is located ...
... Homologous chromosomes have nearly identical structure, banding patterns, and nucleotide sequences Locus: Physical site on chromosomes where given gene is located ...
Genetics revision for learners
... Meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. This means that pairs of alleles are separated at meiosis. During meiosis matching chromosomes cross over (swap sections of the chromosome) which adds variation. Independent assortment also increases variation as the chromosome pairs rand ...
... Meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. This means that pairs of alleles are separated at meiosis. During meiosis matching chromosomes cross over (swap sections of the chromosome) which adds variation. Independent assortment also increases variation as the chromosome pairs rand ...
09ans - Evergreen Archives
... Mitosis proceeds normally in triploid cells because replicated chromosomes do not pair with homologues. They align independently, and then the sister chromatids separatereplicate-separate over and over. It does not matter how many copies of each type of chromosome are present. However, in meiosis, h ...
... Mitosis proceeds normally in triploid cells because replicated chromosomes do not pair with homologues. They align independently, and then the sister chromatids separatereplicate-separate over and over. It does not matter how many copies of each type of chromosome are present. However, in meiosis, h ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.