Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false
... 31. To produce a fruit that has some characteristics of an orange and some of a grapefruit, you would use the selective breeding technique of _________________________. 32. Genetic defects caused by excessive inbreeding can be eliminated through the process of _________________________. 33. Scientis ...
... 31. To produce a fruit that has some characteristics of an orange and some of a grapefruit, you would use the selective breeding technique of _________________________. 32. Genetic defects caused by excessive inbreeding can be eliminated through the process of _________________________. 33. Scientis ...
Unit 4 – Genetics Heredity Test Study Guide Chapter 13
... 17. What is the probability that a phenotypically normal child produced by a mating of two heterozygotes will be a carrier? Campbell Chapter 15 - The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance 1. What is meant by the term linked genes? 2. Looking at progeny (offspring), how might one guess that two genes are ...
... 17. What is the probability that a phenotypically normal child produced by a mating of two heterozygotes will be a carrier? Campbell Chapter 15 - The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance 1. What is meant by the term linked genes? 2. Looking at progeny (offspring), how might one guess that two genes are ...
File - Ms. Pennington Pre
... 5. In what two ways is gene regulation in eukaryotes different from gene regulation in ...
... 5. In what two ways is gene regulation in eukaryotes different from gene regulation in ...
Section 14–1 Human Heredity (pages 341–348)
... 19. A progressive loss of muscle control and mental function caused by an autosomal dominant allele ...
... 19. A progressive loss of muscle control and mental function caused by an autosomal dominant allele ...
Slide 1
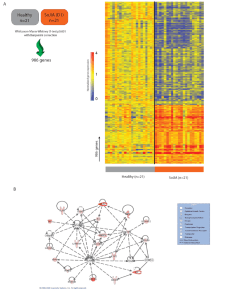
... Differential gene expression in whole blood from SJIA patients and healthy controls. A. Data were normalized in Beadstudio using the "average" method and imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s meas ...
... Differential gene expression in whole blood from SJIA patients and healthy controls. A. Data were normalized in Beadstudio using the "average" method and imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s meas ...
Genetics - Aurora City Schools
... and females because the X and Y chromosomes do not carry the same genes. Genetic disorders that have genes on the X chromosome show up more frequently in males than females. While Y-linked disorders only show up in males. Males get their X chromosome from their ...
... and females because the X and Y chromosomes do not carry the same genes. Genetic disorders that have genes on the X chromosome show up more frequently in males than females. While Y-linked disorders only show up in males. Males get their X chromosome from their ...
Airgas template
... One gene could mask the effect of another: epistasis/hypostasis One gene might depend on another: complementary Two genes together might create a new phenotype: collaborative A form of gene interaction whereby one gene masks or interferes with the phenotypic expression of one or more genes at other ...
... One gene could mask the effect of another: epistasis/hypostasis One gene might depend on another: complementary Two genes together might create a new phenotype: collaborative A form of gene interaction whereby one gene masks or interferes with the phenotypic expression of one or more genes at other ...
Pedigrees and Karyotypes
... ● To label a karyotype correctly, first list the number of chromosomes found in the karyotype. Ex. 46 ● Secondly, list the type of sex chromosomes found in the karyotype. Ex. XX ● Lastly, list the any abnormalities at the appropriate chromosome number. ...
... ● To label a karyotype correctly, first list the number of chromosomes found in the karyotype. Ex. 46 ● Secondly, list the type of sex chromosomes found in the karyotype. Ex. XX ● Lastly, list the any abnormalities at the appropriate chromosome number. ...
Genetics Vocabulary Spring 2011
... • Characteristics inherited from two parents ; A genetically determined characteristic or condition ...
... • Characteristics inherited from two parents ; A genetically determined characteristic or condition ...
S-8-2-2_Vocabulary Matching Worksheet and KEY Vocabulary
... alternate forms of a gene that control the same characteristics traits that an organism is born with that are carried on their genes type of allele that is always expressed when it is present in an individual a molecule in the genes that passes characteristics from one generation to the next traits ...
... alternate forms of a gene that control the same characteristics traits that an organism is born with that are carried on their genes type of allele that is always expressed when it is present in an individual a molecule in the genes that passes characteristics from one generation to the next traits ...
ChromosomeMutations
... (the sex chromosomes). • These genetic diseases occur only in males. • Since males have an XY sex chromosome any problems with the X chromosome causes a genetic disease • In females, which have XX chromosome any issue with an X chromosome is hidden by the other X. • Females can be carriers for the g ...
... (the sex chromosomes). • These genetic diseases occur only in males. • Since males have an XY sex chromosome any problems with the X chromosome causes a genetic disease • In females, which have XX chromosome any issue with an X chromosome is hidden by the other X. • Females can be carriers for the g ...
Ch 12-15 Unit Overvi..
... Meiosis – purpose; location; compare/contrast meiosis I and meiosis II, which is most similar to mitosis? Does meiosis I or II reduce the chromosome number by half? How is anaphase I different from anaphase II? Metaphase I from II? When does cross over take place? Independent assortment? Segregation ...
... Meiosis – purpose; location; compare/contrast meiosis I and meiosis II, which is most similar to mitosis? Does meiosis I or II reduce the chromosome number by half? How is anaphase I different from anaphase II? Metaphase I from II? When does cross over take place? Independent assortment? Segregation ...
Lecture Notes
... chromosome); monosomies of the autosomes are rare. B) Nondisjunction is the most common mechanism leading to aneuploidy. 1) Nondisjunction in mitosis at an early cleavage division may lead to a clinically significant mosaicism. ...
... chromosome); monosomies of the autosomes are rare. B) Nondisjunction is the most common mechanism leading to aneuploidy. 1) Nondisjunction in mitosis at an early cleavage division may lead to a clinically significant mosaicism. ...
Standard Chromosome Analysis - Emory University Department of
... material (other tests are available that are better able to do this), and will NOT be able to detect single gene conditions, such as sickle cell disease. Hundreds of different types of chromosome abnormalities causing well described syndromes have been reported in humans. They fall into 2 categories ...
... material (other tests are available that are better able to do this), and will NOT be able to detect single gene conditions, such as sickle cell disease. Hundreds of different types of chromosome abnormalities causing well described syndromes have been reported in humans. They fall into 2 categories ...
File
... Human Chromosome Disorders Some have high frequency in humans most embryos are spontaneously aborted developmental problems result from ...
... Human Chromosome Disorders Some have high frequency in humans most embryos are spontaneously aborted developmental problems result from ...
chapter10
... Dihybrid cross involves individuals who have different alleles in two different loci. Principle of independent assortment: the alleles of different loci on nonhomologous chromosomes are distributed into gametes. Independent assortment occurs because of the mechanics of meiosis. This can result in co ...
... Dihybrid cross involves individuals who have different alleles in two different loci. Principle of independent assortment: the alleles of different loci on nonhomologous chromosomes are distributed into gametes. Independent assortment occurs because of the mechanics of meiosis. This can result in co ...
Assorted Multiple Choice - mvhs
... 6. One trait in ivy plants is the presence of spots. The purple spotted allele (h) is recessive while the gold spotted allele (H) is dominant. The ability to show spots is controlled by another gene—M. Only ivy plants with an M allele will be able to show their spots. Otherwise, they will show no sp ...
... 6. One trait in ivy plants is the presence of spots. The purple spotted allele (h) is recessive while the gold spotted allele (H) is dominant. The ability to show spots is controlled by another gene—M. Only ivy plants with an M allele will be able to show their spots. Otherwise, they will show no sp ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch.14 Mendel and the Gene Idea
... Monohybrid Cross -two heterozygotes ...
... Monohybrid Cross -two heterozygotes ...
Human karyotype
... • Germ cells (sperm and egg) have 23 chromosomes – 22 autosomes and a Y or an X ...
... • Germ cells (sperm and egg) have 23 chromosomes – 22 autosomes and a Y or an X ...
Genetics – the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring.
... If an organism is either TT or tt (the same case letter), then that individual is homozygous (homo- means “the same”) ...
... If an organism is either TT or tt (the same case letter), then that individual is homozygous (homo- means “the same”) ...
EXAM 2
... 42. (4 points) Other than simply sequencing the human genome, list two goals of the human genome project. Identify effects of radiation Identify the ~30,000 genes in human DNA Determine the sequences of the 3 billion bases of the human genome Develop databases to store and access this information Im ...
... 42. (4 points) Other than simply sequencing the human genome, list two goals of the human genome project. Identify effects of radiation Identify the ~30,000 genes in human DNA Determine the sequences of the 3 billion bases of the human genome Develop databases to store and access this information Im ...
Word Definition 1 non-Mendelian genetics rules
... genetic traits that are controlled by many genes 6 sex-linked gene a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome 7 carrier a person who has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait 8 genetic disorder an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes a genetic disorder that causes ...
... genetic traits that are controlled by many genes 6 sex-linked gene a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome 7 carrier a person who has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait 8 genetic disorder an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes a genetic disorder that causes ...
GENETICS
... Multiple alleles – a human trait controlled by a single gene with more than 2 alleles Sex-linked gene – genes on X and Y chromosomes, alleles are passed from parent to offspring on a sex chromosome Carrier – person who has one recessive allele for a trait and one dominant allele Pedigree – chart or ...
... Multiple alleles – a human trait controlled by a single gene with more than 2 alleles Sex-linked gene – genes on X and Y chromosomes, alleles are passed from parent to offspring on a sex chromosome Carrier – person who has one recessive allele for a trait and one dominant allele Pedigree – chart or ...
Fuggles
... Now look at the decoder symbols for the nose colour gene. Notice that in this case, the heterozygous condition (Nn) codes for a different nose colour variation (pink) than either of the homozygous states (QQ = red, qq = yellow). This is an example of codominance. Many people mistakenly believe that ...
... Now look at the decoder symbols for the nose colour gene. Notice that in this case, the heterozygous condition (Nn) codes for a different nose colour variation (pink) than either of the homozygous states (QQ = red, qq = yellow). This is an example of codominance. Many people mistakenly believe that ...
File
... Some genes on a chromosome are so far apart that a crossover between them is virtually certain. In this case, the frequency of recombination reached is its maximum value of 50% and the genes act as if found on separate chromosomes ...
... Some genes on a chromosome are so far apart that a crossover between them is virtually certain. In this case, the frequency of recombination reached is its maximum value of 50% and the genes act as if found on separate chromosomes ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.