Forms of energy
... 8. The movement of objects and substances from place to place is ______ energy. 9. Electromagnetic energy traveling in transverse waves is ________ energy. 10. Energy stored in bonds of atoms and molecules is ________ energy. 11. The movements of atoms, molecules, waves and electrons is ________ ene ...
... 8. The movement of objects and substances from place to place is ______ energy. 9. Electromagnetic energy traveling in transverse waves is ________ energy. 10. Energy stored in bonds of atoms and molecules is ________ energy. 11. The movements of atoms, molecules, waves and electrons is ________ ene ...
Energy Conversion Quiz Answer Key
... 10. Give an example of energy changing from one form to another. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Energy changes from chemical energy to mechanical energy when you digest food and use the energy it releases to move your body. ...
... 10. Give an example of energy changing from one form to another. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Energy changes from chemical energy to mechanical energy when you digest food and use the energy it releases to move your body. ...
Chemical Energy
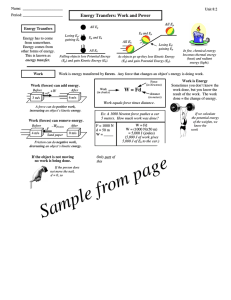
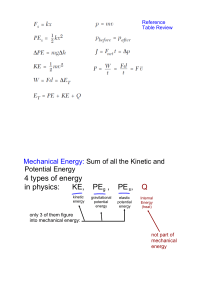
... What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your answer from #3? What is mechanical energy? ...
... What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your answer from #3? What is mechanical energy? ...
Forms of Energy
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
CHAPTER 7: ENERGY RESOURCES
... --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another but it cannot be created or lost Where Does Energy Come From? Pg. 87 --Using technology, we have created methods for converting resources into more useful energy forms 1. Fossil Fuels: created when heat and pressure act on decayin ...
... --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another but it cannot be created or lost Where Does Energy Come From? Pg. 87 --Using technology, we have created methods for converting resources into more useful energy forms 1. Fossil Fuels: created when heat and pressure act on decayin ...
Study Guide Energy
... 7. By increasing the _______________ (kinetic / potential) energy of molecules in a substance the substances temperature will rise. 8. In order for sound to travel it must have a ______________ to travel through. 9. Electromagnetic energy does not require a medium and can travel through the ________ ...
... 7. By increasing the _______________ (kinetic / potential) energy of molecules in a substance the substances temperature will rise. 8. In order for sound to travel it must have a ______________ to travel through. 9. Electromagnetic energy does not require a medium and can travel through the ________ ...
Energy Worksheet
... 6. The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is ________ 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is __________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substances from place to place is ______ energy. 9. Electromagnetic energy traveling in transverse waves is _______ ...
... 6. The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is ________ 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is __________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substances from place to place is ______ energy. 9. Electromagnetic energy traveling in transverse waves is _______ ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
Different forms of energy
... particles in a substance. All matter is made up of atoms ( particles) that move faster when they heat up. The faster the particles move, higher the temperature. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ...
... particles in a substance. All matter is made up of atoms ( particles) that move faster when they heat up. The faster the particles move, higher the temperature. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ...
Glossary of Terms Energy – the ability to do work or the ability to
... Kinetic energy – the energy of a body which results from its motion. Chemical energy – energy stored in a substance and released during a chemical reaction such as burning wood, coal, or oil. Mechanical energy – the energy of motion used to perform work. Nuclear energy – energy that comes from split ...
... Kinetic energy – the energy of a body which results from its motion. Chemical energy – energy stored in a substance and released during a chemical reaction such as burning wood, coal, or oil. Mechanical energy – the energy of motion used to perform work. Nuclear energy – energy that comes from split ...
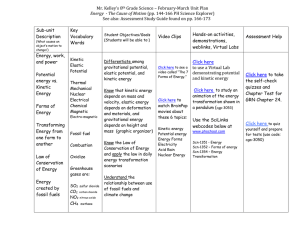
Mr. Kelley`s 8th Grade Science – February
... Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
... Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
Energy storage

Energy storage is accomplished by devices or physical media that store energy to perform useful processes at a later time. A device that stores energy is sometimes called an accumulator.Many forms of energy produce useful work, heating or cooling to meet societal needs. These energy forms include chemical energy, gravitational potential energy, electrical potential, electricity, temperature differences, latent heat, and kinetic energy. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store (electricity, kinetic energy, etc.) to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide only short-term energy storage, and others can be very long-term such as power to gas using hydrogen or methane and the storage of heat or cold between opposing seasons in deep aquifers or bedrock. A wind-up clock stores potential energy (in this case mechanical, in the spring tension), a rechargeable battery stores readily convertible chemical energy to operate a mobile phone, and a hydroelectric dam stores energy in a reservoir as gravitational potential energy. Ice storage tanks store ice (thermal energy in the form of latent heat) at night to meet peak demand for cooling. Fossil fuels such as coal and gasoline store ancient energy derived from sunlight by organisms that later died, became buried and over time were then converted into these fuels. Even food (which is made by the same process as fossil fuels) is a form of energy stored in chemical form.