Absorption of Radiation
... passed through a medium that has a thickness of b cm and a concentration c of absorbing species ...
... passed through a medium that has a thickness of b cm and a concentration c of absorbing species ...
Light 1 Mathematical representation of light (EM waves)
... Every point of a wavefront may be considered a source of small secondary wavelets, which spread out in all directions from their centers with a velocity equal to the velocity of the propagating wave. Tye new wavefront it then found by constructing a surface tangent to the secondary wavelets, thus gi ...
... Every point of a wavefront may be considered a source of small secondary wavelets, which spread out in all directions from their centers with a velocity equal to the velocity of the propagating wave. Tye new wavefront it then found by constructing a surface tangent to the secondary wavelets, thus gi ...
W - Вернуться к содержанию сайта
... range (f=1015 Hz) into X-ray range (f=1018–1019 Hz), at the same time proportionally decreases wavelength λmax of spectral maximum and color temperature Tc rises thousandfold. Thus, we can say that the nature long ago created effective transformers of optical radiation into other frequency ranges. R ...
... range (f=1015 Hz) into X-ray range (f=1018–1019 Hz), at the same time proportionally decreases wavelength λmax of spectral maximum and color temperature Tc rises thousandfold. Thus, we can say that the nature long ago created effective transformers of optical radiation into other frequency ranges. R ...
39 Steps
... embedding medium will determine the severity of the spherical aberration present. Even for viewing aqueous biological specimens using a water objective, the match is unlikely to be perfect or even close. Spherical aberration of this type is the major cause of signal loss with increasing penetration ...
... embedding medium will determine the severity of the spherical aberration present. Even for viewing aqueous biological specimens using a water objective, the match is unlikely to be perfect or even close. Spherical aberration of this type is the major cause of signal loss with increasing penetration ...
dec 2016_nature of light unit test review sheet answer key
... 2. What is the energy transformation occurring in a lightbulb? (Show the direction of the energy transformation). - Electrical energy to electromagnetic (light) energy and thermal (heat) energy 3. What is a luminous object and a non-luminous object? Give an example of each? - Luminous objects produc ...
... 2. What is the energy transformation occurring in a lightbulb? (Show the direction of the energy transformation). - Electrical energy to electromagnetic (light) energy and thermal (heat) energy 3. What is a luminous object and a non-luminous object? Give an example of each? - Luminous objects produc ...
Acousto-Optic Devices - Panasonic Industrial Devices
... A piezoelectric element is bonded to an acousto-optic medium consisting of single crystal such as tellurium dioxide (TeO2) and lead molybdate (PbMoO4) or glass, and when an electrical signal is applied to this piezoelectric element to generate acoustic waves, which are propagated in the medium, a la ...
... A piezoelectric element is bonded to an acousto-optic medium consisting of single crystal such as tellurium dioxide (TeO2) and lead molybdate (PbMoO4) or glass, and when an electrical signal is applied to this piezoelectric element to generate acoustic waves, which are propagated in the medium, a la ...
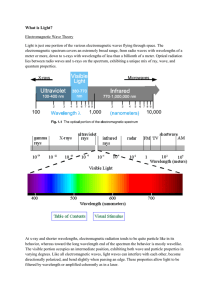
What is Light?
... Quantum type detectors are often used in the near infrared, especially below 1100 nm. Specialized detectors such as InGaAs offer excellent responsivity from 850 to 1700 nm. Typical silicon photodiodes are not sensitive above 1100 nm. These types of detectors are typically employed to measure a known ...
... Quantum type detectors are often used in the near infrared, especially below 1100 nm. Specialized detectors such as InGaAs offer excellent responsivity from 850 to 1700 nm. Typical silicon photodiodes are not sensitive above 1100 nm. These types of detectors are typically employed to measure a known ...
Photoelectric Effect
... The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation falls on an object. It was first theorized by a German physicist named Max Planck and later expanded upon by Albert Einstein. Light consists of discrete bundles of energy called photons. The amount of energy in a ph ...
... The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation falls on an object. It was first theorized by a German physicist named Max Planck and later expanded upon by Albert Einstein. Light consists of discrete bundles of energy called photons. The amount of energy in a ph ...
4) Spectroscopies Involving Energy Exchange
... (2) Glossary for Spectroscopies Involving Energy Exchange i) Optical spectroscopy (Involving Energy Exchange): Methods based on the absorption, emission, luminescence of electromagnetic radiation that is proportional to the amount of analyte in the sample. ii) Absorption spectroscopy: Measuring the ...
... (2) Glossary for Spectroscopies Involving Energy Exchange i) Optical spectroscopy (Involving Energy Exchange): Methods based on the absorption, emission, luminescence of electromagnetic radiation that is proportional to the amount of analyte in the sample. ii) Absorption spectroscopy: Measuring the ...
Electromagnetic radiation
... Absorption: A transition from a lower level to a higher level with transfer of energy from the radiation field to an absorber, atom, molecule, or solid. Emission: A transition from a higher level to a lower level with transfer of energy from the emitter to the radiation field. If no radiation is emi ...
... Absorption: A transition from a lower level to a higher level with transfer of energy from the radiation field to an absorber, atom, molecule, or solid. Emission: A transition from a higher level to a lower level with transfer of energy from the emitter to the radiation field. If no radiation is emi ...
Signal propagation
... Signal Propagation Ranges • Transmission range – communication possible – low error rate ...
... Signal Propagation Ranges • Transmission range – communication possible – low error rate ...
Name: ANSWER KEY Period: Date: Nature of Light Unit Test Review
... 2. What is the energy transformation occurring in a lightbulb? (Show the direction of the energy transformation). - Electrical energy to electromagnetic (light) energy and thermal (heat) energy 3. What is a luminous object and a non-luminous object? Give an example of each? - Luminous objects produc ...
... 2. What is the energy transformation occurring in a lightbulb? (Show the direction of the energy transformation). - Electrical energy to electromagnetic (light) energy and thermal (heat) energy 3. What is a luminous object and a non-luminous object? Give an example of each? - Luminous objects produc ...
Daedalon EO-85 Computerized Spectrophotometer
... appears to be a single color. The goal of this part is to measure the spectrum and determine the width of the wavelength band that is emitted in each case. 2. Measure the emission spectrum of the green, red and blue light emitting diodes in that order. The graphs will then be the same color as the L ...
... appears to be a single color. The goal of this part is to measure the spectrum and determine the width of the wavelength band that is emitted in each case. 2. Measure the emission spectrum of the green, red and blue light emitting diodes in that order. The graphs will then be the same color as the L ...
Two Quick Light Experiments
... light that passes through these slits can be thought of as a new source. (We use laser light for this part because we are looking at interference which involves phases and wavelengths; lasers are monochromatic and coherent, meaning what?) The waves from these sources will interfere, sometimes constr ...
... light that passes through these slits can be thought of as a new source. (We use laser light for this part because we are looking at interference which involves phases and wavelengths; lasers are monochromatic and coherent, meaning what?) The waves from these sources will interfere, sometimes constr ...
6. Light Scattering, Reflection, and Refraction
... A plane wave impinging on a molecule or particle scatters into a spherical wave. ...
... A plane wave impinging on a molecule or particle scatters into a spherical wave. ...
4.3 Wave characteristics
... Wave intensity For example, imagine a window with an area of 1m2. If one joule of light energy flows through that window every second we say the light intensity is 1 W.m-2. ...
... Wave intensity For example, imagine a window with an area of 1m2. If one joule of light energy flows through that window every second we say the light intensity is 1 W.m-2. ...
coefficient extinction molar riboflavin
... UV absorbance is about 1000 x easier to detect per mole than NMR Still used in following reactions where the chromophore changes (useful) because timescale is so fast, and sensitivity is very high. Kinetics, esp. in biochemistry, enzymology. ...
... UV absorbance is about 1000 x easier to detect per mole than NMR Still used in following reactions where the chromophore changes (useful) because timescale is so fast, and sensitivity is very high. Kinetics, esp. in biochemistry, enzymology. ...
Chapter 24
... Change of phase due to reflection When light reflects off of a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. See fig. 24.6 and 24.7 In figure 24.7 the two reflected beam interfere with each other. ...
... Change of phase due to reflection When light reflects off of a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. See fig. 24.6 and 24.7 In figure 24.7 the two reflected beam interfere with each other. ...
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II
... an LED flashlight connected to a radio shines on the solar cell? What type of radiant energy transfers information? A modulated (changing) current from the radio transfers information by modulating the amplitude of the beam of visible light from the LED flashlight. The energy from the LED flashlight ...
... an LED flashlight connected to a radio shines on the solar cell? What type of radiant energy transfers information? A modulated (changing) current from the radio transfers information by modulating the amplitude of the beam of visible light from the LED flashlight. The energy from the LED flashlight ...
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... from a region with a lower n ¾There is a half-wavelength phase change when light reflects from a region with a higher n ...
... from a region with a lower n ¾There is a half-wavelength phase change when light reflects from a region with a higher n ...
الشريحة 1
... Location of Sample cell In all photometers and scanning spectrophotpmeters described above, the cell has been positioned after the monochromators. This is important to decrease the possibility of sample photodecomposition due to prolonged exposure to all frequencies coming from the source. However, ...
... Location of Sample cell In all photometers and scanning spectrophotpmeters described above, the cell has been positioned after the monochromators. This is important to decrease the possibility of sample photodecomposition due to prolonged exposure to all frequencies coming from the source. However, ...
Chapter 6. Light Source and Detectors
... a thin black membrane placed over a small, gas-filled chamber. Heat absorbed by the membrane causes the gas to expand, which in turn can be measured, either optically (by a movable mirror) or electrically (by a change in capacitance). used in the infrared. ...
... a thin black membrane placed over a small, gas-filled chamber. Heat absorbed by the membrane causes the gas to expand, which in turn can be measured, either optically (by a movable mirror) or electrically (by a change in capacitance). used in the infrared. ...
Optical properties
... broader than the input one. It is because light rays traveling in different trajectories have a variety of path lengths. It is possible to avoid pulse broadening by using graded-index fiber. This results in a helical path for the light rays, as opposed to zig-zag path in a step-index fiber. Here ...
... broader than the input one. It is because light rays traveling in different trajectories have a variety of path lengths. It is possible to avoid pulse broadening by using graded-index fiber. This results in a helical path for the light rays, as opposed to zig-zag path in a step-index fiber. Here ...