Glossary (PDF file)
... reflect To bounce back from a surface. We can see things because light reflects off of them and travels to our eyes. Some objects reflect light better than others. refraction The bending of light when it moves from one material to another. Light travels at different speeds through different materials. ...
... reflect To bounce back from a surface. We can see things because light reflects off of them and travels to our eyes. Some objects reflect light better than others. refraction The bending of light when it moves from one material to another. Light travels at different speeds through different materials. ...
Introduction to Fiber Optics
... The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core (hallway) by constantly bouncing from the cladding (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances. However, some of t ...
... The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core (hallway) by constantly bouncing from the cladding (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances. However, some of t ...
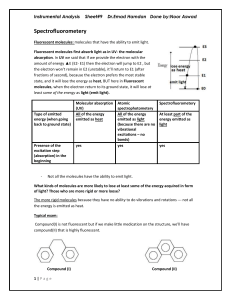
L09 Instru Spectrofluorometery
... light is not reproducible, because the intensity of emitted light may be affected by the ...
... light is not reproducible, because the intensity of emitted light may be affected by the ...
The coherence length of black
... coherence length is slightly less than the mean or effective wavelength. That is why no fringes (modulation of intensity) of order |m| � 1 occur. So, in the case of unfiltered black-body radiation, interference patterns consist only of a central maximum (m = 0) flanked by two weak minima (m = ± 21 , s ...
... coherence length is slightly less than the mean or effective wavelength. That is why no fringes (modulation of intensity) of order |m| � 1 occur. So, in the case of unfiltered black-body radiation, interference patterns consist only of a central maximum (m = 0) flanked by two weak minima (m = ± 21 , s ...
Absorption spectra of plant pigments Objectives Procedure
... (fluorescence) or by stepvise transition to the ground state using the ladder of vibrational levels (nonradiative transition). There may also be a transition from the S1 state into the triplet manifold. ...
... (fluorescence) or by stepvise transition to the ground state using the ladder of vibrational levels (nonradiative transition). There may also be a transition from the S1 state into the triplet manifold. ...
Measurement of Optical Characteristic of Plastic by UH4150
... Plastic is a highly transparent, light, and durable material. For the optical evaluation of an object, such as light transmittance property, color, and transparency, the transmission spectrum and reflectance spectrum are measured by a spectrophotometer. These measurements do not only provide the opt ...
... Plastic is a highly transparent, light, and durable material. For the optical evaluation of an object, such as light transmittance property, color, and transparency, the transmission spectrum and reflectance spectrum are measured by a spectrophotometer. These measurements do not only provide the opt ...
Reflectivity measurements of a quantum well
... - aperture – changes the convergent beam coming out of the halogen lamp into divergent imitating the point source and extracting the center of the light spot which has the biggest intensity being most homogeneous at the same time; its position coincides with the focusing point of the halogen lamp an ...
... - aperture – changes the convergent beam coming out of the halogen lamp into divergent imitating the point source and extracting the center of the light spot which has the biggest intensity being most homogeneous at the same time; its position coincides with the focusing point of the halogen lamp an ...
Determining Ratio - Hinds Instruments
... In any experiment using photoelastic modulators (PEMs) it is necessary to compare the time average intensity of the light at the detector with the amplitude of a single frequency component of the light intensity.1,2 For example, in experiments to measure circular dichroism the effect being measured ...
... In any experiment using photoelastic modulators (PEMs) it is necessary to compare the time average intensity of the light at the detector with the amplitude of a single frequency component of the light intensity.1,2 For example, in experiments to measure circular dichroism the effect being measured ...
Single-Photon Synchronous Detection
... digital mixing operation with a reference signal, shared by the illumination source, and integration over a high number of cycles. Conveniently, these operations are implemented in a SPSD sensor by means of a demultiplexer (or a switch), driven synchronously with the reference signal, that connects ...
... digital mixing operation with a reference signal, shared by the illumination source, and integration over a high number of cycles. Conveniently, these operations are implemented in a SPSD sensor by means of a demultiplexer (or a switch), driven synchronously with the reference signal, that connects ...
14_04_2014 - IB Phys..
... acceptable for a certain signal is 30dB.If the power of the noise is 2.0mW, calculate the least acceptable signal ...
... acceptable for a certain signal is 30dB.If the power of the noise is 2.0mW, calculate the least acceptable signal ...
Magneto Optical Kerr Effect (MOKE)
... In nano-magnets the anisotropy depends not only on the characteristic of the parent bulk material, such as its crystalline structure, but also on the shape, size and thickness of the nano-elements. Therefore the anisotropy of a nano-structure can be controlled using its geometry, or shape. The angul ...
... In nano-magnets the anisotropy depends not only on the characteristic of the parent bulk material, such as its crystalline structure, but also on the shape, size and thickness of the nano-elements. Therefore the anisotropy of a nano-structure can be controlled using its geometry, or shape. The angul ...
EM Waves and Color
... of light waves, called EM waves Electromagnetic Wave: a wave that is partly electrical and partly magnetic and carries energy. A light wave. EM waves are transverse waves EM waves do NOT require a medium to transfer energy Ex: gamma rays, UV, infrared, radio waves ...
... of light waves, called EM waves Electromagnetic Wave: a wave that is partly electrical and partly magnetic and carries energy. A light wave. EM waves are transverse waves EM waves do NOT require a medium to transfer energy Ex: gamma rays, UV, infrared, radio waves ...
Homework Set #7 Due: 4-4-14
... fields. The wavelengths of the signal and idler are determined by rotating the BBO crystal until an angle is found so that the desired output wavelengths are phase matched when traveling, in this case, collinearly with the pump. The pump, signal and idler can be separated using dichroic beamsplitter ...
... fields. The wavelengths of the signal and idler are determined by rotating the BBO crystal until an angle is found so that the desired output wavelengths are phase matched when traveling, in this case, collinearly with the pump. The pump, signal and idler can be separated using dichroic beamsplitter ...
Quantitative Analysis Spectroscope #CQ$ 42581
... Today, our current theory of light now embraces both its wave mud pmrticl.~ ~spects. Light is a~ e!ectrom~n.et~e ~.,~ve, that travels in small particle like packets called photons. Each photon travels at the same speed: 3 x 10s m/see, the speed of light. The energy era photon is determined by its fr ...
... Today, our current theory of light now embraces both its wave mud pmrticl.~ ~spects. Light is a~ e!ectrom~n.et~e ~.,~ve, that travels in small particle like packets called photons. Each photon travels at the same speed: 3 x 10s m/see, the speed of light. The energy era photon is determined by its fr ...
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... Radar waves have a wavelength of 3cm. Suppose the plane is made of metal (speed of propagation=0, n is infinite and ...
... Radar waves have a wavelength of 3cm. Suppose the plane is made of metal (speed of propagation=0, n is infinite and ...
Power Point review
... These are tiny, particle –like bundles of energy that make up electromagnetic waves. ...
... These are tiny, particle –like bundles of energy that make up electromagnetic waves. ...
Practical Laboratory #2: Emission Spectra 2
... Do the following steps for the unknown light source after you’ve set it up: 1. Start data collection on the Logger Pro software. An emission spectrum will be graphed. 2. When you achieve a satisfactory graph, stop data collection. If the highest peak in the emission spectrum is > 1, then the sensor ...
... Do the following steps for the unknown light source after you’ve set it up: 1. Start data collection on the Logger Pro software. An emission spectrum will be graphed. 2. When you achieve a satisfactory graph, stop data collection. If the highest peak in the emission spectrum is > 1, then the sensor ...
Microsoft Word Format - McMaster University > ECE
... From connection and guidance point of view: larger NA is better. However, larger NA may excite high order modes, hence introduce mode dispersion and reduce the transmission bandwidth. In SMF, larger NA yields more negative dispersion. This can be utilized to cancel the positive material dispersion. ...
... From connection and guidance point of view: larger NA is better. However, larger NA may excite high order modes, hence introduce mode dispersion and reduce the transmission bandwidth. In SMF, larger NA yields more negative dispersion. This can be utilized to cancel the positive material dispersion. ...
LIGHT
... The molecules in the filters are aligned parallel to each other. If they are held so that the molecules in both filters are vertical, the vertical vibrations of light can get through, but the horizontal Vibrations can not. The resulting light, that vibrates in one dimension only, is called “POLARIZ ...
... The molecules in the filters are aligned parallel to each other. If they are held so that the molecules in both filters are vertical, the vertical vibrations of light can get through, but the horizontal Vibrations can not. The resulting light, that vibrates in one dimension only, is called “POLARIZ ...
Section 9.4: Light: Wave or Particle?
... 3. Sample answer: Double-slit interference patterns provide strong evidence that light is a wave. 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: The frequency and wavelength of light do not change when light is reflected. So, according to the universal wave equation, v = fλ, the speed must stay the same. 5. An ...
... 3. Sample answer: Double-slit interference patterns provide strong evidence that light is a wave. 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: The frequency and wavelength of light do not change when light is reflected. So, according to the universal wave equation, v = fλ, the speed must stay the same. 5. An ...
lecture1
... I and II are stretching while III is bending. I will not lead to IR absorption while II and III will. Bending may involve movement of a group of atoms within a molecule relative to the rest of the molecule. Different types of bending occur: twisting, rocking, wagging, scissoring e.t.c. IR absorption ...
... I and II are stretching while III is bending. I will not lead to IR absorption while II and III will. Bending may involve movement of a group of atoms within a molecule relative to the rest of the molecule. Different types of bending occur: twisting, rocking, wagging, scissoring e.t.c. IR absorption ...
Name:
... Usually “bits” come in chunks of eight… called “bytes.” A byte can encode a number up to 255 (11111111 in binary)… more than enough to cover the whole alphabet if you are trying to encode information letter by letter. Memory capacity on hard drives, flash disks, CD’s and the like is indicated by “Me ...
... Usually “bits” come in chunks of eight… called “bytes.” A byte can encode a number up to 255 (11111111 in binary)… more than enough to cover the whole alphabet if you are trying to encode information letter by letter. Memory capacity on hard drives, flash disks, CD’s and the like is indicated by “Me ...
Lecture 33 : Chiral molecules and Optical Activity
... or left handed helices, carbon atom covalently bonded to 4 different substituients. Most important biological molecules are chiral. Enzymes prefer to bind to specific isomer. Another common terminology that is used to describe the optically active isomers is dextro and levo or D and L respectively. ...
... or left handed helices, carbon atom covalently bonded to 4 different substituients. Most important biological molecules are chiral. Enzymes prefer to bind to specific isomer. Another common terminology that is used to describe the optically active isomers is dextro and levo or D and L respectively. ...
Light, Light Bulbs and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
... incandescent lamps produce a continuous spectrum, which is something like sunlight. Spectral lamps, on the other hand, emit only a few discrete wavelengths. The quality or “whiteness” of their light depends on how we perceive the particular combination of wavelengths emitted. In order to study the s ...
... incandescent lamps produce a continuous spectrum, which is something like sunlight. Spectral lamps, on the other hand, emit only a few discrete wavelengths. The quality or “whiteness” of their light depends on how we perceive the particular combination of wavelengths emitted. In order to study the s ...
EBB 424E Semiconductor Devices and Optoelectronics
... •If Photon Energy, Evis < Egap Photons will transmitted •If Photon Energy is in the range of Egap ; ...
... •If Photon Energy, Evis < Egap Photons will transmitted •If Photon Energy is in the range of Egap ; ...