letters - 5. Physikalisches Institut
... It is well known that the group velocity yg of a light pulse can exceed c in an anomalously dispersive medium [1–4]. If there is no appreciable loss or gain and the dispersion is linear, an incident pulse described by a sufficiently smooth envelope (an analytic signal) E共t兲 becomes simply E共t 2 L兾yg ...
... It is well known that the group velocity yg of a light pulse can exceed c in an anomalously dispersive medium [1–4]. If there is no appreciable loss or gain and the dispersion is linear, an incident pulse described by a sufficiently smooth envelope (an analytic signal) E共t兲 becomes simply E共t 2 L兾yg ...
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4th ed Donald R
... Thermal emission - Emission of photons from a material due to excitation of the material by heat. ...
... Thermal emission - Emission of photons from a material due to excitation of the material by heat. ...
Controllable optical negative refraction and
... refraction1–3 . The last of these has attracted particular interest, mainly because of its promise for super-resolution imaging4–6 . However, the widespread use of negative refraction at optical frequencies is challenged by high losses and strong dispersion effects, which typically limit operation t ...
... refraction1–3 . The last of these has attracted particular interest, mainly because of its promise for super-resolution imaging4–6 . However, the widespread use of negative refraction at optical frequencies is challenged by high losses and strong dispersion effects, which typically limit operation t ...
Nonlinear Optical Methods to Study Condensed Phase
... and induce changes of electronic state, chemical constitution etc. (Figure 1). The dynamical information is often hidden behind a mask of spectral broadening resulting from these influences, and this makes linear spectroscopy (i.e. absorption spectra) of limited value for the study of condensed phas ...
... and induce changes of electronic state, chemical constitution etc. (Figure 1). The dynamical information is often hidden behind a mask of spectral broadening resulting from these influences, and this makes linear spectroscopy (i.e. absorption spectra) of limited value for the study of condensed phas ...
Optical spectroscopy techniques
... Improvement in SNR of H2O absorption line due to phase-‐modulation spectroscopy ...
... Improvement in SNR of H2O absorption line due to phase-‐modulation spectroscopy ...
Two-dimensional control of light with light on metasurfaces
... opposite sides of the nanostructure. Intensity masks are placed in both paths and imaged onto the metasurface to control the spatial intensity distribution on the metasurface (Figure 2a). In order to introduce temporal control, a liquid–crystal phase modulator is used to control the relative phase o ...
... opposite sides of the nanostructure. Intensity masks are placed in both paths and imaged onto the metasurface to control the spatial intensity distribution on the metasurface (Figure 2a). In order to introduce temporal control, a liquid–crystal phase modulator is used to control the relative phase o ...
Microsoft Word Format - University of Toronto Physics
... Light scattering allows one to learn about certain properties of matter. Elastic light scattering involves no change in wavelength (or photon energy) from the incident beam while inelastic scattering involves a change. An example of elastic light scattering is Rayleigh scattering, which occurs from ...
... Light scattering allows one to learn about certain properties of matter. Elastic light scattering involves no change in wavelength (or photon energy) from the incident beam while inelastic scattering involves a change. An example of elastic light scattering is Rayleigh scattering, which occurs from ...
CH915: Elemental Analysis
... • Also integrated-circuit chip • Contains an array of capacitors that store charge when light creates electron-hole pairs • Accumulated charge is read out at given time interval • Each wavelength is detected at a different spot • Much more sensitive than photodiode array detectors ...
... • Also integrated-circuit chip • Contains an array of capacitors that store charge when light creates electron-hole pairs • Accumulated charge is read out at given time interval • Each wavelength is detected at a different spot • Much more sensitive than photodiode array detectors ...
Photorefractive cyclometalated complexes
... non-uniform illumination [2,3]. PR media are photoconductors, in which light absorption induces the formation of mobile charge carriers that diffuse or drift through macroscopic distances establishing a charge distribution and the related internal electric field, called space-charge field Esc. If th ...
... non-uniform illumination [2,3]. PR media are photoconductors, in which light absorption induces the formation of mobile charge carriers that diffuse or drift through macroscopic distances establishing a charge distribution and the related internal electric field, called space-charge field Esc. If th ...
Opto acoustic
... using Mie theory the scattering may be determined knowing; the size parameter (perimeter compared to wavelength), refractive index ratio between particle and media. ...
... using Mie theory the scattering may be determined knowing; the size parameter (perimeter compared to wavelength), refractive index ratio between particle and media. ...
UV Spectroscopy
... Principle: Colorimetry analysis method is useful in determining the concentration of coloured solutions using the visible region (400nm–750nm) of electromagnetic spectrum and Beer Lambert’s law. If the test solution is colourless then a suitable complexing agent can be added to test solution to get ...
... Principle: Colorimetry analysis method is useful in determining the concentration of coloured solutions using the visible region (400nm–750nm) of electromagnetic spectrum and Beer Lambert’s law. If the test solution is colourless then a suitable complexing agent can be added to test solution to get ...
Polarized light and polarizers
... Right vs. Left Circular (or Helical) Polarization E-field variation over time (at z = 0) … or, more generally, ...
... Right vs. Left Circular (or Helical) Polarization E-field variation over time (at z = 0) … or, more generally, ...
Chapter 35
... gation are shifted with respected to each other, as shown above, they are said to have a phase difference. Clearly, the phase difference becomes zero again if two plane waves are shifted with respect to each other by an integer number of wavelengths. Thus we care about shifts of lengths less than a ...
... gation are shifted with respected to each other, as shown above, they are said to have a phase difference. Clearly, the phase difference becomes zero again if two plane waves are shifted with respect to each other by an integer number of wavelengths. Thus we care about shifts of lengths less than a ...
Phase Contrast
... Cells have higher n than water. Light moves slower in higher n, consequently resulting in a phase retardation Phase shift depends on n and on thickness of specimen detail ...
... Cells have higher n than water. Light moves slower in higher n, consequently resulting in a phase retardation Phase shift depends on n and on thickness of specimen detail ...
Photoacoustic imaging velocimetry for flow
... velocimetry, the position of the tracer in each reconstructed image should be scaled. In the paper, the centre of the tracer has been used to describe the position simply. And the centre and the size were assessed by the midpoint and the length of the tracer in the moving direction approximately. Fo ...
... velocimetry, the position of the tracer in each reconstructed image should be scaled. In the paper, the centre of the tracer has been used to describe the position simply. And the centre and the size were assessed by the midpoint and the length of the tracer in the moving direction approximately. Fo ...
Light Kit Student Concepts/Objectives per Lesson
... 2. Kit Objectives for this lesson: Observe and discuss the reflections of light from a white screen, a silvered (mirrored) surface and a half-silvered surface Compare an object with its image in a plane mirror Determine, through observations and measurements, that the image seen in a mirror appears ...
... 2. Kit Objectives for this lesson: Observe and discuss the reflections of light from a white screen, a silvered (mirrored) surface and a half-silvered surface Compare an object with its image in a plane mirror Determine, through observations and measurements, that the image seen in a mirror appears ...
FTIR Instrumentation
... The beamsplitter is the heart of the interferometer. Essentially a half-silvered mirror, the beamsplitter reflects about half of an incident light beam while simultaneously transmitting the remaining half. One half of this split light beam travels to the interferometer's moving mirror while the othe ...
... The beamsplitter is the heart of the interferometer. Essentially a half-silvered mirror, the beamsplitter reflects about half of an incident light beam while simultaneously transmitting the remaining half. One half of this split light beam travels to the interferometer's moving mirror while the othe ...
Determination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids
... index of a sample at a fixed but arbitrary temperature and, with an independent differential measurement, to determine the temperature dependence of refractive index afterwards. This way no active temperature control was needed. However, the real situation is more complicated. In our measurements th ...
... index of a sample at a fixed but arbitrary temperature and, with an independent differential measurement, to determine the temperature dependence of refractive index afterwards. This way no active temperature control was needed. However, the real situation is more complicated. In our measurements th ...
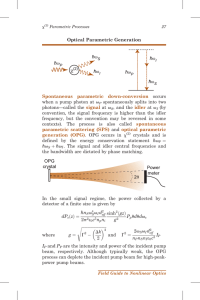
Optical Parametric Generation Spontaneous parametric down
... where k1 , k2 , and k3 are the k vectors corresponding to the frequencies v1, v2, and v3, respectively. The magnitude of a k vector is nv=c ¼ 2pn=l, and its direction is parallel to the propagation direction. For linearly polarized fields, the index is either o or e polarized. Phase matching occurs ...
... where k1 , k2 , and k3 are the k vectors corresponding to the frequencies v1, v2, and v3, respectively. The magnitude of a k vector is nv=c ¼ 2pn=l, and its direction is parallel to the propagation direction. For linearly polarized fields, the index is either o or e polarized. Phase matching occurs ...
Near-field amplitude and phase recovery using phase
... evanescent fields[10], or a combination of both[11]. There is interest in measuring the amplitude and phase changes separately, since these signals contain different but complimentary information about the sample. In sSNOM, the tip is raster-scanned over the sample surface in close proximity and for ...
... evanescent fields[10], or a combination of both[11]. There is interest in measuring the amplitude and phase changes separately, since these signals contain different but complimentary information about the sample. In sSNOM, the tip is raster-scanned over the sample surface in close proximity and for ...
Slide 1
... Abstract: Acousto-optic (AO) imaging is a new dual-wave modality that combines ultrasound with diffuse light to achieve deep-tissue imaging of optical properties with the spatial resolution of ultrasound. In this technique, the sample is simultaneously insonified by an ultrasound beam and illuminate ...
... Abstract: Acousto-optic (AO) imaging is a new dual-wave modality that combines ultrasound with diffuse light to achieve deep-tissue imaging of optical properties with the spatial resolution of ultrasound. In this technique, the sample is simultaneously insonified by an ultrasound beam and illuminate ...
2. Spectral Stray Light
... originating channel. These are characterised by a different method described in sec. 2.2. 2.2 Using a monochromator The measurements to quantify the stray light in the neighbourhood of the originating channel were performed using a monochromator providing a spectral bandwidth of 1.3 nm. While this i ...
... originating channel. These are characterised by a different method described in sec. 2.2. 2.2 Using a monochromator The measurements to quantify the stray light in the neighbourhood of the originating channel were performed using a monochromator providing a spectral bandwidth of 1.3 nm. While this i ...
Lecture 21: Polarisation of light and other waves
... If 45◦ plane polarised light is incident on a plate which is birefringent, then the H and V phases, which were initially equal, are out of step when they emerge from the plate. The extent to which they are out of step depends on the difference in refractive indices and on the thickness of the plate ...
... If 45◦ plane polarised light is incident on a plate which is birefringent, then the H and V phases, which were initially equal, are out of step when they emerge from the plate. The extent to which they are out of step depends on the difference in refractive indices and on the thickness of the plate ...