Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of aqueous solutions using
... In standard FT-JR instruments, the measured signal has a large dynamic range caused by the broad spectrum of the source and the basic working principle of the instrument (which is the measurement of intensity as a function of pathlength difference in the two arms of a Michelson interferometer) . As ...
... In standard FT-JR instruments, the measured signal has a large dynamic range caused by the broad spectrum of the source and the basic working principle of the instrument (which is the measurement of intensity as a function of pathlength difference in the two arms of a Michelson interferometer) . As ...
Interference3
... coefficient of reflection from the surface of a rarer medium but opposite in sign. • Intensity of reflected light is the same for a ray incident from either side of the boundary. • Negative sign in amplitude indicates a phase change of occurring due to reflection at medium I and II. There are two ...
... coefficient of reflection from the surface of a rarer medium but opposite in sign. • Intensity of reflected light is the same for a ray incident from either side of the boundary. • Negative sign in amplitude indicates a phase change of occurring due to reflection at medium I and II. There are two ...
Low-Coherence Fibre-Optic Interferometric Sensors
... fringe in the interference fringe pattern. It is so important because this position refers to the zero value of the OPD and therefore gives information about the measurand. The intensity difference between the central fringe and the first side fringe can be so small that the signal-to-noise ratio re ...
... fringe in the interference fringe pattern. It is so important because this position refers to the zero value of the OPD and therefore gives information about the measurand. The intensity difference between the central fringe and the first side fringe can be so small that the signal-to-noise ratio re ...
Optical communication systems
... transmit information from one place to another. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation like radio waves. Today, infrared light is being used increasingly as the carrier for information in communication systems. The transmission medium is either free space or a light-carrying cable called a fib ...
... transmit information from one place to another. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation like radio waves. Today, infrared light is being used increasingly as the carrier for information in communication systems. The transmission medium is either free space or a light-carrying cable called a fib ...
Fiber Optics Communications
... communicate with their fleets • Lightwave communication started with the invention of photophone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1880, which used Sun light as carrier and air as transmission media. Sound information is transmitted this way up to 200 meters. • The biggest obstacle for using optic fibers ...
... communicate with their fleets • Lightwave communication started with the invention of photophone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1880, which used Sun light as carrier and air as transmission media. Sound information is transmitted this way up to 200 meters. • The biggest obstacle for using optic fibers ...
The Time-Shift Technique for Measurement of Size and Velocity of
... where the subscript (01) refers to the distance between reflection and first mode of second-order refraction and (02) the distance between the reflection and the second mode of second-order refraction (Fig. 3). Signal validation for spray characterization In general a spray is comprised of particles ...
... where the subscript (01) refers to the distance between reflection and first mode of second-order refraction and (02) the distance between the reflection and the second mode of second-order refraction (Fig. 3). Signal validation for spray characterization In general a spray is comprised of particles ...
The Fundamentals of Infrared Spectroscopy
... Using these units, visible light is from 0.36 to 0.75 μm, or 27,778 to 13,333 cm-1. There is a discussion of these units below. In the case of infrared spectroscopy, infrared light passes through a sample and certain frequencies of the light are absorbed by the chemical bonds of the substance, leadi ...
... Using these units, visible light is from 0.36 to 0.75 μm, or 27,778 to 13,333 cm-1. There is a discussion of these units below. In the case of infrared spectroscopy, infrared light passes through a sample and certain frequencies of the light are absorbed by the chemical bonds of the substance, leadi ...
Brightfield Contrasting Techniques
... Use two beams and interferometry to measure the path length difference between adjacent points in the sample ...
... Use two beams and interferometry to measure the path length difference between adjacent points in the sample ...
called optics.·
... with the gas was found to improve the light. An even brighter light was produced by heating a block of lime to incandescence in an oxy hydrogen flame. producing the limelight. which was used for "magic lanterns." and soon after mid-century for the theatrical appli cations that preserve its name to ...
... with the gas was found to improve the light. An even brighter light was produced by heating a block of lime to incandescence in an oxy hydrogen flame. producing the limelight. which was used for "magic lanterns." and soon after mid-century for the theatrical appli cations that preserve its name to ...
Rayleigh Noise Mitigated 70-km-Reach Bi-directional WDM-PON with 10-Gb/s Directly Modulated Manchester-
... ever-increasing bandwidth demand from enterprises and households. One practical and cost-effective approach is to employ centralized light sources (CLS) at the optical line terminal (OLT) and directly re-use the downstream light as the upstream carrier at the optical network units (ONUs) [1]. Recent ...
... ever-increasing bandwidth demand from enterprises and households. One practical and cost-effective approach is to employ centralized light sources (CLS) at the optical line terminal (OLT) and directly re-use the downstream light as the upstream carrier at the optical network units (ONUs) [1]. Recent ...
PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY
... He later realised that the same technique can be applied to optical microscopy. The necessary phase shift is introduced by rings etched accurately onto glass plates so that they introduce the required phase shift when inserted into the optical path of the microscope. When in use, this technique allo ...
... He later realised that the same technique can be applied to optical microscopy. The necessary phase shift is introduced by rings etched accurately onto glass plates so that they introduce the required phase shift when inserted into the optical path of the microscope. When in use, this technique allo ...
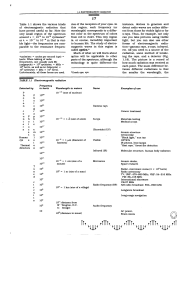
... the longitudinal components of electromagnetic fields, such a distinct PSHE can only be observed in the anomalously refracted beam. As a control experiment, the spin-orbit coupling vanishes for the regularly transmitted beam, which exits the metasurface in the direction of the surface normal. The ph ...
Faraday Rotation - Northeastern University
... Here are notes for calibrating the Faraday rotation setup. They are used to determine the coefficient β=dφ/dρ, which relates the FR angle φ to the measured polarization ρ. First, note that the angle of the linear polarizer POL-1 is rotated by the micrometer. The angle of the polarizer φ is a functio ...
... Here are notes for calibrating the Faraday rotation setup. They are used to determine the coefficient β=dφ/dρ, which relates the FR angle φ to the measured polarization ρ. First, note that the angle of the linear polarizer POL-1 is rotated by the micrometer. The angle of the polarizer φ is a functio ...
Third-harmonic Rayleigh scattering: theory and experiment
... scattering from spherical particles of micrometer size was extensively studied during the past century, both experimentally and theoretically. In 1940 Debye developed light scattering as a method for studying molecular weights, sizes, shapes, and interactions of biological molecules in solutions. Ex ...
... scattering from spherical particles of micrometer size was extensively studied during the past century, both experimentally and theoretically. In 1940 Debye developed light scattering as a method for studying molecular weights, sizes, shapes, and interactions of biological molecules in solutions. Ex ...
CHAPTER 3
... which the light signal travels. In this case, it is the changes in the refractive index of the core and the cladding of the fiber optic cable. This loss is caused by the miniscule variation in the composition and density of the optical glass material itself, which is related to the fiber manufac ...
... which the light signal travels. In this case, it is the changes in the refractive index of the core and the cladding of the fiber optic cable. This loss is caused by the miniscule variation in the composition and density of the optical glass material itself, which is related to the fiber manufac ...
Homework Set #6 Due: 3-28-14
... upon the waveplate. The ordinary and extradinary polarization directions and the extraordinary wave index of refraction depend on input angle. If normal incidence is not used, a half-wave plate will produce elliptically polarized light: the larger the deviation, the worse the effect. If the beam is ...
... upon the waveplate. The ordinary and extradinary polarization directions and the extraordinary wave index of refraction depend on input angle. If normal incidence is not used, a half-wave plate will produce elliptically polarized light: the larger the deviation, the worse the effect. If the beam is ...
FT-IR Glossary - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... Condenser In a microscope, the optical element that focuses light onto the sample. Corrected Peak Area The area that is below a peak, above the baseline and between two vertical lines that define the left and right limits of the area. Corrected Peak Height The difference in the Y axis unit value bet ...
... Condenser In a microscope, the optical element that focuses light onto the sample. Corrected Peak Area The area that is below a peak, above the baseline and between two vertical lines that define the left and right limits of the area. Corrected Peak Height The difference in the Y axis unit value bet ...
plane-polarized
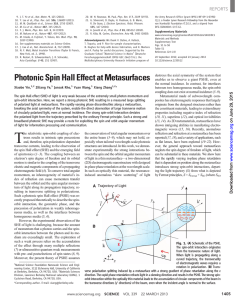
... Superposition of two waves: 1) same amplitude and wavelength, 2) polarized in two perpendicular planes, 3) oscillate with 90o phase difference. A phase difference of 90° means that when one wave is at its peak then the other one is just crossing the zero line. Special electromagnetic wave. At any f ...
... Superposition of two waves: 1) same amplitude and wavelength, 2) polarized in two perpendicular planes, 3) oscillate with 90o phase difference. A phase difference of 90° means that when one wave is at its peak then the other one is just crossing the zero line. Special electromagnetic wave. At any f ...
6.1 Polarization Light is a transverse wave: the electric and magnetic
... birefringent material, not to any particular lines in space, so they might better be called fast and slow directions. They are determined by the crystal structure of the birefringent material. Problem 5: Linearly polarized light enters two sequential quarter-wave plates. The two plates have their fa ...
... birefringent material, not to any particular lines in space, so they might better be called fast and slow directions. They are determined by the crystal structure of the birefringent material. Problem 5: Linearly polarized light enters two sequential quarter-wave plates. The two plates have their fa ...
Chapter 12: Light
... Section 2: Light and Color Color and Wavelength • The colors of the visible spectrum differ from one another in terms of wavelength • Each combination of wavelengths has its own special sense of color • When white light strikes most objects certain colors are absorbed and certain colors are reflect ...
... Section 2: Light and Color Color and Wavelength • The colors of the visible spectrum differ from one another in terms of wavelength • Each combination of wavelengths has its own special sense of color • When white light strikes most objects certain colors are absorbed and certain colors are reflect ...
Optimizing Fluorescence Signal Quality
... When dealing with fluorescence in general and throughout this optimizing fluorescence signal quality procedure, several terms may arise that might seem esoteric. Please familiarize yourself with the following nomenclature: Fluorescence: the emission of a photon from a molecule (or atom) that had bee ...
... When dealing with fluorescence in general and throughout this optimizing fluorescence signal quality procedure, several terms may arise that might seem esoteric. Please familiarize yourself with the following nomenclature: Fluorescence: the emission of a photon from a molecule (or atom) that had bee ...
PPT
... Silicone diode Charge transfer detector Photoconductor Thermocouple (voltage) or barometer (resistance) ...
... Silicone diode Charge transfer detector Photoconductor Thermocouple (voltage) or barometer (resistance) ...
PowerPoint - ECSE - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... Microbends are used to intentionally kill some modes and reduce modal dispersion Modal dispersion and chromatic dispersion share the characteristic that they cause intersymbol interference (and hence a strong upper bound on bit rate) Diffraction with polychromatic light will lead to the ...
... Microbends are used to intentionally kill some modes and reduce modal dispersion Modal dispersion and chromatic dispersion share the characteristic that they cause intersymbol interference (and hence a strong upper bound on bit rate) Diffraction with polychromatic light will lead to the ...
Use of Broadband, Continuous-Wave Diode Lasers in Cavity Ring
... F IG . 4. Molecules of methylene blue are diffusing into the probe beam over several minutes. The t is to a simple diffusion model. The oscillations, therefore, are not related to the diffusion process but are believed to be the result of photothermal beam steering caused by an ...
... F IG . 4. Molecules of methylene blue are diffusing into the probe beam over several minutes. The t is to a simple diffusion model. The oscillations, therefore, are not related to the diffusion process but are believed to be the result of photothermal beam steering caused by an ...
Prediction of photothermal phase signatures from arbitrary
... chemical, thermal or material property changes.1 In biomedical applications, plasmonic nanoparticles can be used as labels in cells and tissues and are imaged via various effects, including photothermal (PT) imaging, photoacoustic shock-wave imaging, and polarization imaging. 25 Electromagnetic ene ...
... chemical, thermal or material property changes.1 In biomedical applications, plasmonic nanoparticles can be used as labels in cells and tissues and are imaged via various effects, including photothermal (PT) imaging, photoacoustic shock-wave imaging, and polarization imaging. 25 Electromagnetic ene ...