CONNECTIVE TISSUE
... epithelium and the muscle has a scattering of elongate nuclei between pink collagen fibers. c. Duodenum (CT 5). The connective tissue under the epithelium will demonstrate namy of the connective cell types. 3. Dense irregular connective tissue Large collagen fibers arranged in an irregular meshwork. ...
... epithelium and the muscle has a scattering of elongate nuclei between pink collagen fibers. c. Duodenum (CT 5). The connective tissue under the epithelium will demonstrate namy of the connective cell types. 3. Dense irregular connective tissue Large collagen fibers arranged in an irregular meshwork. ...
how exercise builds muscle
... provide the energy the muscle needs. Basically, glycolysis releases energy for making ATP by breaking down sugars only partially but without need for oxygen. The type II fibers differ mainly in their oxidative properties. Type IIa fibers have more mitochondria and are thus more similar to type I. Be ...
... provide the energy the muscle needs. Basically, glycolysis releases energy for making ATP by breaking down sugars only partially but without need for oxygen. The type II fibers differ mainly in their oxidative properties. Type IIa fibers have more mitochondria and are thus more similar to type I. Be ...
Desmin (Muscle Cell Marker) Ab-1
... Catalog # MS-376-S0, -S1, or -S (0.1ml, 0.5ml, or 1.0ml) Catalog # MS-376-R7 (7.0ml) Catalog # MS-376-PCS INTENDED USE: ...
... Catalog # MS-376-S0, -S1, or -S (0.1ml, 0.5ml, or 1.0ml) Catalog # MS-376-R7 (7.0ml) Catalog # MS-376-PCS INTENDED USE: ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Architectural Patterns Ch 9 final
... tissue - is a group of similar cells specialized for the performance of a common function histology = the study of tissues Types of Tissues: 1. Epithelial Tissue epithelium = a sheet of cells that covers an external or internal surface on many surfaces, epithelial cells are often modified into g ...
... tissue - is a group of similar cells specialized for the performance of a common function histology = the study of tissues Types of Tissues: 1. Epithelial Tissue epithelium = a sheet of cells that covers an external or internal surface on many surfaces, epithelial cells are often modified into g ...
Physiology
... unit is actually (usually) triphasic • Duration is between 3 and 15 msec • Magnitude is between 20-2000 microvolts, depending on the size of the motor unit • Frequency of http://www.holycross.edu/departments/biology/kprestwi/phys'02/labs/emg_lab/Phys'02_L1_Intro_E-myo&FFT.pdf ...
... unit is actually (usually) triphasic • Duration is between 3 and 15 msec • Magnitude is between 20-2000 microvolts, depending on the size of the motor unit • Frequency of http://www.holycross.edu/departments/biology/kprestwi/phys'02/labs/emg_lab/Phys'02_L1_Intro_E-myo&FFT.pdf ...
Cytoskeleton
... • Motor molecules also carry vesicles or organelles to various destinations along “monorails’ provided by the cytoskeleton. • Interactions of motor proteins and the cytoskeleton circulates materials within a cell via streaming. • Recently, evidence is accumulating that the ...
... • Motor molecules also carry vesicles or organelles to various destinations along “monorails’ provided by the cytoskeleton. • Interactions of motor proteins and the cytoskeleton circulates materials within a cell via streaming. • Recently, evidence is accumulating that the ...
Chapter 9 Muscle
... located in one muscle 肌肉, but they are scattered 分散 throughout the muscle and are not adjacent 不相鄰 to each other ...
... located in one muscle 肌肉, but they are scattered 分散 throughout the muscle and are not adjacent 不相鄰 to each other ...
continue
... • 2 categories of NE receptors – alpha adrenergic receptors • NE binding is excitatory ...
... • 2 categories of NE receptors – alpha adrenergic receptors • NE binding is excitatory ...
Nerve supply of the human vastus medialis muscle
... branch, supplies the upper lateral portion of the muscle. The other part, a medial branch, supplies the middle and lower portion of the muscle. There is a distalward increase in the numbers of nerve fibres supplying the muscle, with the lowermost muscle fibres receiving the richest nerve supply. The ...
... branch, supplies the upper lateral portion of the muscle. The other part, a medial branch, supplies the middle and lower portion of the muscle. There is a distalward increase in the numbers of nerve fibres supplying the muscle, with the lowermost muscle fibres receiving the richest nerve supply. The ...
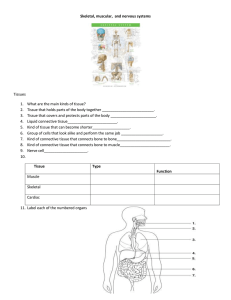
Skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems
... Why do you think that there is more than one muscle? ________________ ...
... Why do you think that there is more than one muscle? ________________ ...
POMPE DISEASE OR TYPE II GLYCOGENOSIS
... Pompe disease has changed its clinical course. ΑlphaAlglucosidase infusions were performed with the recombinant form of human acid α-glucosidase. Such treatment can stop or slow the progression of the disease. It has been effective even in children with the classic phenotype with rapid progress, red ...
... Pompe disease has changed its clinical course. ΑlphaAlglucosidase infusions were performed with the recombinant form of human acid α-glucosidase. Such treatment can stop or slow the progression of the disease. It has been effective even in children with the classic phenotype with rapid progress, red ...
BIOMORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF THE HIP JOINT OF SOME
... fundamental provisions in this area included in the textbooks and reference books. A study of literary study shows that sufficiently studied now only the structure of musculoskeletal system at all levels of structural organization [2, 3]. The powerful development of pelvic limbs and tail reduction w ...
... fundamental provisions in this area included in the textbooks and reference books. A study of literary study shows that sufficiently studied now only the structure of musculoskeletal system at all levels of structural organization [2, 3]. The powerful development of pelvic limbs and tail reduction w ...
11-6_UpLowMotorneurons_NemethO
... Motor cortex: region of cortex in the frontal lobe that is involved with voluntary movement. Upper motor neurons: cells that carry motor commands from primary motor cortex (pyramidal cells of precentral gyrus) to the spinal cord, through descending motor pathways to lower motor neurons. The fibers u ...
... Motor cortex: region of cortex in the frontal lobe that is involved with voluntary movement. Upper motor neurons: cells that carry motor commands from primary motor cortex (pyramidal cells of precentral gyrus) to the spinal cord, through descending motor pathways to lower motor neurons. The fibers u ...
EMG - AState.edu
... So far, all of these activities have involved the normal equipment that is used to study electricity: manufactured circuit elements. We have studied capacitors, resistors, and power supplies. For this capstone activity, though, we are going to investigate a much different electrical system: the huma ...
... So far, all of these activities have involved the normal equipment that is used to study electricity: manufactured circuit elements. We have studied capacitors, resistors, and power supplies. For this capstone activity, though, we are going to investigate a much different electrical system: the huma ...
暨 南 大 学 考 试 试 卷
... B. They can release Ca2+ into the sarcoplasma. C. They branch among themselves that they form the entire planes of T tubules interlacing among all the separate myofibrils. D. They can transmit action potential to the deep interior of the muscle fiber as well to excite each myofibril. 15) The incorre ...
... B. They can release Ca2+ into the sarcoplasma. C. They branch among themselves that they form the entire planes of T tubules interlacing among all the separate myofibrils. D. They can transmit action potential to the deep interior of the muscle fiber as well to excite each myofibril. 15) The incorre ...
CNS And Anesthesia
... A neuron consists of a cell body or soma, dendrites, and a nerve fiber or axon. The axon of one neuron terminates (synapses) near the cell body or dendrites of another neuron. Neurons are cells that transfer stimuli to other cells. The larger nerve fibers are surrounded by a coat of fatty material-t ...
... A neuron consists of a cell body or soma, dendrites, and a nerve fiber or axon. The axon of one neuron terminates (synapses) near the cell body or dendrites of another neuron. Neurons are cells that transfer stimuli to other cells. The larger nerve fibers are surrounded by a coat of fatty material-t ...
If Looks Could Kill: Botox and the Neuromuscular Junction
... from a Hollywood doomsday movie, such a deadly substance is, in fact, the most modern weapon available in the pharmaceutical industry’s persistent fight against “signs of aging.” Botox—injected into the faces of hundreds of thousands of Americans each year, it is one of the deadliest toxins on earth ...
... from a Hollywood doomsday movie, such a deadly substance is, in fact, the most modern weapon available in the pharmaceutical industry’s persistent fight against “signs of aging.” Botox—injected into the faces of hundreds of thousands of Americans each year, it is one of the deadliest toxins on earth ...
Motor Unit and All or None principle
... The interplay between muscles that generate movement through contraction (agonists) and muscles responsible for opposing movement (antagonists) is called inter-muscle ...
... The interplay between muscles that generate movement through contraction (agonists) and muscles responsible for opposing movement (antagonists) is called inter-muscle ...
Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate
... group (Fig.1). Masson trichrome staining at 7 days demonstrated the fibrotic area was significantly smaller in MSC-exosome group than in control group. At vascular staining of CD31 in TA muscles at 7 days, capillary density in MSC-exosome group was significantly increased than in control group. To ...
... group (Fig.1). Masson trichrome staining at 7 days demonstrated the fibrotic area was significantly smaller in MSC-exosome group than in control group. At vascular staining of CD31 in TA muscles at 7 days, capillary density in MSC-exosome group was significantly increased than in control group. To ...
Midterm 2 - Creighton Biology
... a small number of slow oxidative fibers are each fully activated. a small number of fast glycolytic fibers are each fully activated. a large number of slow oxidative fibers are each partially activated. a large number of fast glycolytic fibers are each partially activated. all the fibers in the musc ...
... a small number of slow oxidative fibers are each fully activated. a small number of fast glycolytic fibers are each fully activated. a large number of slow oxidative fibers are each partially activated. a large number of fast glycolytic fibers are each partially activated. all the fibers in the musc ...
Chapter 40 - Cloudfront.net
... 3-Nervous: senses stimuli and transmits signals from 1 part of the animal to another Neuron: functional unit that transmits impulses Dendrites: transmit impulses from tips to rest of neuron Axons: transmit impulses toward another neuron or effector ...
... 3-Nervous: senses stimuli and transmits signals from 1 part of the animal to another Neuron: functional unit that transmits impulses Dendrites: transmit impulses from tips to rest of neuron Axons: transmit impulses toward another neuron or effector ...
Effect of Nm blockers on Frog Rectus Abdomens Muscle
... Depolarization 1- Resting potential: • In order to maintain the cell membrane potential, cells keep a low concentration of sodium ions and high levels of potassium ions within the cell (intracellular). • The sodium-potassium pump moves 3 sodium ions out and moves 2 potassium ions in, thus in total ...
... Depolarization 1- Resting potential: • In order to maintain the cell membrane potential, cells keep a low concentration of sodium ions and high levels of potassium ions within the cell (intracellular). • The sodium-potassium pump moves 3 sodium ions out and moves 2 potassium ions in, thus in total ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.