02.Houtkooper (162)
... isoforms are expressed in trunk and limb muscles from normal adult animals (i.e., the bslow or type I), and the three different fast IIA, IIX, and IIB MyHCs (see Schiaffino & Reggiani 1996). There is a close relationship between V0, the actinactivated ATPase activity of myosin, and the myosin isofor ...
... isoforms are expressed in trunk and limb muscles from normal adult animals (i.e., the bslow or type I), and the three different fast IIA, IIX, and IIB MyHCs (see Schiaffino & Reggiani 1996). There is a close relationship between V0, the actinactivated ATPase activity of myosin, and the myosin isofor ...
T3 Web Sheet (1)
... the front of the chest and extends from the top of the arm to the breastbone as well as the upper ribs (Serratus Anterior). The Pecs aid in the downward and forward motion necessary to perform many athletic ...
... the front of the chest and extends from the top of the arm to the breastbone as well as the upper ribs (Serratus Anterior). The Pecs aid in the downward and forward motion necessary to perform many athletic ...
10. Muscle Tissue - Academic Computer Center
... creatine is called the oxygen debt. This explains why a person can run a 100 meter sprint without using oxygen, but the runner will then spend the next several minutes breathing hard. V. Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types Criteria for classification of muscle fiber types Although all skeletal muscle cells ...
... creatine is called the oxygen debt. This explains why a person can run a 100 meter sprint without using oxygen, but the runner will then spend the next several minutes breathing hard. V. Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types Criteria for classification of muscle fiber types Although all skeletal muscle cells ...
1 General principles of GIT physiology
... located in the cytosol of the smooth muscle cell, which splits the phosphate from the regulatory light chain. Then the cycling stops and contraction ceases. The time required for relaxation of muscle contraction, therefore, is determined to a great extent by the amount of active myosin phosphatase i ...
... located in the cytosol of the smooth muscle cell, which splits the phosphate from the regulatory light chain. Then the cycling stops and contraction ceases. The time required for relaxation of muscle contraction, therefore, is determined to a great extent by the amount of active myosin phosphatase i ...
SESSION 7 - Larynx And Trachea - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... 1. It is the only intrinsic muscle of the larynx that is situated …… …… ……… of the larynx. 2. It is the only muscle that ………….. the cords. 3. It is the only intrinsic muscle that is not supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve but instead by the ……… branch of the ……… laryngeal nerve. ...
... 1. It is the only intrinsic muscle of the larynx that is situated …… …… ……… of the larynx. 2. It is the only muscle that ………….. the cords. 3. It is the only intrinsic muscle that is not supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve but instead by the ……… branch of the ……… laryngeal nerve. ...
Chapter 7. The Cell: Cytoskeleton
... 3-D network inside cell membrane in muscle cells, actin filaments interact with myosin filaments to ...
... 3-D network inside cell membrane in muscle cells, actin filaments interact with myosin filaments to ...
Phonation Extra credit slides2
... Where are the pyriform sinuses located in relationship with the valleculae? A. Inferior (below) B. Superior (above) C. At the same level ...
... Where are the pyriform sinuses located in relationship with the valleculae? A. Inferior (below) B. Superior (above) C. At the same level ...
Muscle Tissue
... •Skeletal muscle •Under voluntary control •Contracts to pull on bones or skin •Produces gross body movements or facial expressions •Characteristics of skeletal muscle cells •Striated •Multinucleate (more than one nucleus) •Long, cylindrical cells © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Skeletal muscle •Under voluntary control •Contracts to pull on bones or skin •Produces gross body movements or facial expressions •Characteristics of skeletal muscle cells •Striated •Multinucleate (more than one nucleus) •Long, cylindrical cells © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Motor components
... Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): progressive degeneration of both upper AND lower motor neurons due to death of anterior horn cells o Clinical Features ...
... Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): progressive degeneration of both upper AND lower motor neurons due to death of anterior horn cells o Clinical Features ...
Canine Iliopsoas Strains
... the inner side of the pelvis respectively. These two muscles join together attach onto the femur (thigh bone). They are responsible for moving the hind limb forward and important stabilisers of the hip joint and the vertebral column. ...
... the inner side of the pelvis respectively. These two muscles join together attach onto the femur (thigh bone). They are responsible for moving the hind limb forward and important stabilisers of the hip joint and the vertebral column. ...
Communication - Mrs Jones A
... An action potential/impulse arrives at the presynaptic knob. The presynaptic membrane depolarises Calcium ion channels in the membrane open. Calcium ions enter the presynaptic knob these cause the Vesicles holding neurotransmitter fuse with the presynaptic membrane. Neurotransmitter/ acetylcholine i ...
... An action potential/impulse arrives at the presynaptic knob. The presynaptic membrane depolarises Calcium ion channels in the membrane open. Calcium ions enter the presynaptic knob these cause the Vesicles holding neurotransmitter fuse with the presynaptic membrane. Neurotransmitter/ acetylcholine i ...
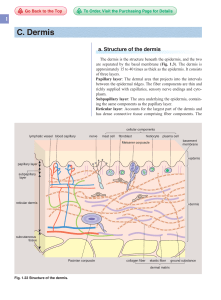
C. Dermis
... The components of ground substance are principally proteoglycans and glycoproteins whose molecular weight is 150,000 to 250,000 and whose sugar content is 2% to 15%. The molecules stabilize the fibers to give flexibility to the skin. Fibronectin, one kind of glycoprotein, contains a domain that conn ...
... The components of ground substance are principally proteoglycans and glycoproteins whose molecular weight is 150,000 to 250,000 and whose sugar content is 2% to 15%. The molecules stabilize the fibers to give flexibility to the skin. Fibronectin, one kind of glycoprotein, contains a domain that conn ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology Abstract: Authors
... Background Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a neurotrophin present in the intestine where it participates in survival and growth of enteric neurons, augmentation of enteric circuits, and stimulation of intestinal peristalsis and propulsion. Previous studies largely focused on the role of ...
... Background Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a neurotrophin present in the intestine where it participates in survival and growth of enteric neurons, augmentation of enteric circuits, and stimulation of intestinal peristalsis and propulsion. Previous studies largely focused on the role of ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
... The ER is an organelle within eukaryote cells. The term Endoplasmic Reticulum means “network within the cell” in Greek. There are 2 types of ER, Rough ER and Smooth ER that are interconnected through their membranes. The organelle is made up of cisturne (in the form of sacs and tubules) and inside t ...
... The ER is an organelle within eukaryote cells. The term Endoplasmic Reticulum means “network within the cell” in Greek. There are 2 types of ER, Rough ER and Smooth ER that are interconnected through their membranes. The organelle is made up of cisturne (in the form of sacs and tubules) and inside t ...
Skeletal muscle morphology in power-lifters with and without
... study on the short term effects (20 weeks) of combined treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist and testosterone on the vastus lateralis muscle (Sinha-Hikim et al. 2002, 2003). However, the magnitude of muscle fiber hypertrophy was higher in trapezius from athletes with long-term A ...
... study on the short term effects (20 weeks) of combined treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist and testosterone on the vastus lateralis muscle (Sinha-Hikim et al. 2002, 2003). However, the magnitude of muscle fiber hypertrophy was higher in trapezius from athletes with long-term A ...
outline5392
... anatomical pathway and territories will be discussed. The information below, and further anatomic details, where applicable, will be utilized: 1. Retinal a) Outer retina b) Inner retina 1) Papillomacular bundle – Ganglion cells arising from the fovea which represent the central 2 degrees of the visu ...
... anatomical pathway and territories will be discussed. The information below, and further anatomic details, where applicable, will be utilized: 1. Retinal a) Outer retina b) Inner retina 1) Papillomacular bundle – Ganglion cells arising from the fovea which represent the central 2 degrees of the visu ...
30. How Animals Move
... • The power stroke slides the actin (thin) filament toward the center of the sarcomere Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • The power stroke slides the actin (thin) filament toward the center of the sarcomere Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.