Taiga/Central Finland - Protection of Taiga and Freshwater
... compensation for reducing use because if it remained landowner and agreed to a forest management plan, it could profit from this in its forest certification. In some of this public land, forestry ended altogether after acquisition and the ecosystems were left to develop naturally. In other parts, a ...
... compensation for reducing use because if it remained landowner and agreed to a forest management plan, it could profit from this in its forest certification. In some of this public land, forestry ended altogether after acquisition and the ecosystems were left to develop naturally. In other parts, a ...
Chapter_3_2008
... ponds will lead to water accumulation in soil due to ground water table rise and following soil Carbon sequestration The same effect will have a restoration of beaver population on small forest water streams as it was on East European Plain at all post-glacial time before growth of human population ...
... ponds will lead to water accumulation in soil due to ground water table rise and following soil Carbon sequestration The same effect will have a restoration of beaver population on small forest water streams as it was on East European Plain at all post-glacial time before growth of human population ...
Document
... Due to fire suppression and fuels buildups, atypical catastrophic fires now occur on the east-side…. Timber harvesting is one way to reduce fuel loads in east-side stands to less damaging levels. ...
... Due to fire suppression and fuels buildups, atypical catastrophic fires now occur on the east-side…. Timber harvesting is one way to reduce fuel loads in east-side stands to less damaging levels. ...
Amazon Environmental Research Institute
... We support a robust REDD+1 mechanism for climate change mitigation that also protects and enhances the ecological co-benefits essential for the integrity and sustainability of forest ecosystems and for human well-being. Tropical forests are a critical component of international climate change mitiga ...
... We support a robust REDD+1 mechanism for climate change mitigation that also protects and enhances the ecological co-benefits essential for the integrity and sustainability of forest ecosystems and for human well-being. Tropical forests are a critical component of international climate change mitiga ...
The Tropical Rainforest - Fitz
... Unlike worms, fungi are decomposers that can be found both on the forest floor as well as on the trunks of trees. Tropical fungi feed on decaying plant matter and are typically clustered into groups connected by an extensive root system. Saprophytic bacteria are typically found ubiquitously in nutri ...
... Unlike worms, fungi are decomposers that can be found both on the forest floor as well as on the trunks of trees. Tropical fungi feed on decaying plant matter and are typically clustered into groups connected by an extensive root system. Saprophytic bacteria are typically found ubiquitously in nutri ...
The Natural State of the Forest By
... In addition to these problems, overcrowding in the forest can result in devastating droughts. The densely populated ecosystem requires a greater amount of water than previously needed in order to sustain the growth of the nearly 300-1000 stems per acre. The increased demand for water has become one ...
... In addition to these problems, overcrowding in the forest can result in devastating droughts. The densely populated ecosystem requires a greater amount of water than previously needed in order to sustain the growth of the nearly 300-1000 stems per acre. The increased demand for water has become one ...
Terrestrial biomes
... • Migration – seasonal travel to find food • No reptiles or amphibians • Many migratory birds (few predators there) ...
... • Migration – seasonal travel to find food • No reptiles or amphibians • Many migratory birds (few predators there) ...
Tundra - sabresocials.com
... cold. Trees have adapted to the winter by going into a period of dormancy or sleep. They also have thick bark to protect them from the cold weather. Trees flower and grow during the spring and summer growing season. Many different kinds of trees, shrubs, and herbs grow in deciduous forests. Most of ...
... cold. Trees have adapted to the winter by going into a period of dormancy or sleep. They also have thick bark to protect them from the cold weather. Trees flower and grow during the spring and summer growing season. Many different kinds of trees, shrubs, and herbs grow in deciduous forests. Most of ...
My trip to the La Hesperia nature conservation reserve in Ecuador`s
... result, the huge number of niches in Ecuador supports 18% of global bird species, 10% of the world’s plant species and 8% of animal species; 4,500 species of butterfly call Ecuador their home. The Cloud Forest Cloud forest is a unique ecosystem which is formed by the interaction of several special c ...
... result, the huge number of niches in Ecuador supports 18% of global bird species, 10% of the world’s plant species and 8% of animal species; 4,500 species of butterfly call Ecuador their home. The Cloud Forest Cloud forest is a unique ecosystem which is formed by the interaction of several special c ...
Chapter 7 - Kennedy APES
... and long, warm summers. Most of the trees in these forests survive winter by dropping their leaves, which decay and produce nutrient-rich soil. 1. Broadleaf, deciduous trees dominate this biome. Leaves drop in fall, trees become dormant (storing water and nutrients in their roots), and new leaves gr ...
... and long, warm summers. Most of the trees in these forests survive winter by dropping their leaves, which decay and produce nutrient-rich soil. 1. Broadleaf, deciduous trees dominate this biome. Leaves drop in fall, trees become dormant (storing water and nutrients in their roots), and new leaves gr ...
Effects of plant diversity on nutrient cycling in a
... A. Biomes B. Climate diagrams C. Microclimate D. Ecotones II. Organism adaptations and tolerance ...
... A. Biomes B. Climate diagrams C. Microclimate D. Ecotones II. Organism adaptations and tolerance ...
Chapter 6 - School City of Hobart
... Soil varies from place to place, and it plays an important role in what kinds of plants can survive in an ecosystem. Although similar biomes in different part of earth will share similar climate and organisms, there are differences. ...
... Soil varies from place to place, and it plays an important role in what kinds of plants can survive in an ecosystem. Although similar biomes in different part of earth will share similar climate and organisms, there are differences. ...
matura
... The Aripo Savannas have an international reputation for their unusual flora in striking vegetation communities. It is one of the more intensively studied areas of natural ecosystems in Trinidad. Of the 457 species of flora and fauna identified so far, 31 are endemic to the Aripo Savannas with 16 to ...
... The Aripo Savannas have an international reputation for their unusual flora in striking vegetation communities. It is one of the more intensively studied areas of natural ecosystems in Trinidad. Of the 457 species of flora and fauna identified so far, 31 are endemic to the Aripo Savannas with 16 to ...
maintaining biological diversity - Ministry of Forests, Lands and
... Maintaining a network of representative ecosystems and special habitats Networks consist of areas under protection or restricted management and corridors connecting these areas. Their purpose is to maintain special habitats such as wetlands and a component of older forests within a landscape unit. ...
... Maintaining a network of representative ecosystems and special habitats Networks consist of areas under protection or restricted management and corridors connecting these areas. Their purpose is to maintain special habitats such as wetlands and a component of older forests within a landscape unit. ...
Animal types/Plant types Parrots Monkeys Jaguars Snakes
... Olympic Rain Forest - N. America Amazon Rain Forest - S. America Malaysian Rain Forest - Asia Congo River Basin - Africa Tasmanian Rain Forest - Australia Bialowieza Forest – Europe So I guess this is one from everywhere ...
... Olympic Rain Forest - N. America Amazon Rain Forest - S. America Malaysian Rain Forest - Asia Congo River Basin - Africa Tasmanian Rain Forest - Australia Bialowieza Forest – Europe So I guess this is one from everywhere ...
Biome Photostory Topic Quiz
... • a. dense, thick soil that supports a dense layer of plants on the forest floor • b. species of animals with specialized ways of surviving in order to avoid competition • c. very few species of trees, due to poor soil quality • d. plants and animals that are very similar due to year-round warmth an ...
... • a. dense, thick soil that supports a dense layer of plants on the forest floor • b. species of animals with specialized ways of surviving in order to avoid competition • c. very few species of trees, due to poor soil quality • d. plants and animals that are very similar due to year-round warmth an ...
Ecology and The Biosphere
... Latitude, soil and local climates for the most part determine what kinds of plants grow Grasslands are a region where the average annual precipitation is great enough to support grasses, and in some areas a few trees. The precipitation is so erratic that drought and fire prevent large forests from g ...
... Latitude, soil and local climates for the most part determine what kinds of plants grow Grasslands are a region where the average annual precipitation is great enough to support grasses, and in some areas a few trees. The precipitation is so erratic that drought and fire prevent large forests from g ...
Forest Biome
... a layer known as the herb layer. This is where the grasses and wildflowers grow . Other plants, bushes and small trees make up the understory (also known as the shrub layer). ...
... a layer known as the herb layer. This is where the grasses and wildflowers grow . Other plants, bushes and small trees make up the understory (also known as the shrub layer). ...
tropical rain forests and the main causes of their decrease
... forest farmers. It corresponds to 20 milion families. Each family clears a hectar of forest every year. Together it makes 200 000 km2/year. Most farmers exploit secondary forest, but 50 milion cultivators destroy primary forests. Some ethnic groups practise shifting cultivation. It means that they g ...
... forest farmers. It corresponds to 20 milion families. Each family clears a hectar of forest every year. Together it makes 200 000 km2/year. Most farmers exploit secondary forest, but 50 milion cultivators destroy primary forests. Some ethnic groups practise shifting cultivation. It means that they g ...
Management, Silviculture and Harvesting
... A stand is even-aged when all of the trees are approximately the same age, generally because of their simultaneous regeneration. This is the case in most Pennsylvania forests. Evenaged management may include these harvest types: ! Regeneration or clear-cut: harvesting most or all of the trees in a s ...
... A stand is even-aged when all of the trees are approximately the same age, generally because of their simultaneous regeneration. This is the case in most Pennsylvania forests. Evenaged management may include these harvest types: ! Regeneration or clear-cut: harvesting most or all of the trees in a s ...
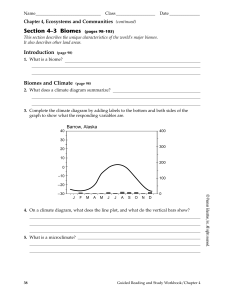
Section 4–3 Biomes
... 22. What is humus? It is a material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter that makes soil fertile. ...
... 22. What is humus? It is a material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter that makes soil fertile. ...
Word - Wallace Resource Library
... Over half of the world’s rainforest lies in the Brazilian Amazon River basin of South America which in turn holds about a third of the remaining tropical rainforest. Another 20% is found in Indonesia and the Congo basin in Central Africa and the balance scattered around the tropical regions of the g ...
... Over half of the world’s rainforest lies in the Brazilian Amazon River basin of South America which in turn holds about a third of the remaining tropical rainforest. Another 20% is found in Indonesia and the Congo basin in Central Africa and the balance scattered around the tropical regions of the g ...
Chapter 9
... Forest Ecosystems? • Concept 9-1 Ecologically valuable forest ecosystems are being cut and burned at unsustainable rates in many parts of the world. ...
... Forest Ecosystems? • Concept 9-1 Ecologically valuable forest ecosystems are being cut and burned at unsustainable rates in many parts of the world. ...
Forest
A forest is a large area of land covered with trees or other woody vegetation. Hundreds of more precise definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing and ecological function. According to the widely-used United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization definition, forests covered an area of four billion hectares (15 million square miles) or approximately 30 percent of the world's land area in 2006.Forests are the dominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are distributed across the globe. Forests account for 75% of the gross primary productivity of the Earth's biosphere, and contain 80% of the Earth's plant biomass.Forests at different latitudes form distinctly different ecozones: boreal forests near the poles tend to consist of evergreens, while tropical forests near the equator tend to be distinct from the temperate forests at mid-latitude. The amount of precipitation and the elevation of the forest also affects forest composition.Human society and forests influence each other in both positive and negative ways. Forests provide ecosystem services to humans and serve as tourist attractions. Forests can also impose costs, affect people's health, and interfere with tourist enjoyment. Human activities, including harvesting forest resources, can negatively affect forest ecosystems.