Beginning Research on the Quantification of Spatial Order
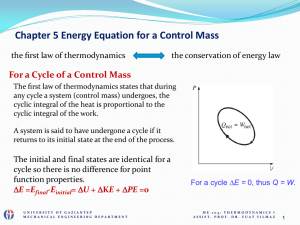
... Whereas the First Law of thermodynamics states that total energy is conserved, albeit in altered form, the Second Law pertains to the way in which energy might change form, as regards the potential to do useful work, in the manner that a heat engine does useful mechanical work. In 1867 Clausius expr ...
... Whereas the First Law of thermodynamics states that total energy is conserved, albeit in altered form, the Second Law pertains to the way in which energy might change form, as regards the potential to do useful work, in the manner that a heat engine does useful mechanical work. In 1867 Clausius expr ...
Review of Chemical Thermodynamics 7.51 September 1999 ∆G
... ∆H — Change in enthalpy between reactants and products; this is the heat given off or absorbed by a reaction at constant pressure. Reactions that absorb heat have positive ∆H’s and those that produce heat have negative ∆H’s. ∆S — Change in entropy between reactants and products; entropy is a statist ...
... ∆H — Change in enthalpy between reactants and products; this is the heat given off or absorbed by a reaction at constant pressure. Reactions that absorb heat have positive ∆H’s and those that produce heat have negative ∆H’s. ∆S — Change in entropy between reactants and products; entropy is a statist ...
q 2 - q 1
... Lewis and Randall considered the following three process : 1. the heat reservoir in the weight –heat reservoir system is at temperature T2 . The weight is then allowed to fall , performing work w, and the heat produced ,q , enters the heat reservoir . 2. the heat reservoir at the temperature T2 is ...
... Lewis and Randall considered the following three process : 1. the heat reservoir in the weight –heat reservoir system is at temperature T2 . The weight is then allowed to fall , performing work w, and the heat produced ,q , enters the heat reservoir . 2. the heat reservoir at the temperature T2 is ...
Notation for states and processes, significance of the word
... 1 bar. The standard-state pressure in general is symbolized as p°. Hitherto p° has customarily been taken as 1 atm. For the future it is recommended that p° should customarily be taken as 10 Pa (1 bar). It should be understood that the present recommended change in the standard-state pressure carrie ...
... 1 bar. The standard-state pressure in general is symbolized as p°. Hitherto p° has customarily been taken as 1 atm. For the future it is recommended that p° should customarily be taken as 10 Pa (1 bar). It should be understood that the present recommended change in the standard-state pressure carrie ...
pdf 728k
... which cannot change no matter what processes occur” The total energy of the universe cannot change for any process. During a process, energy of system changes and this change is accounted for in terms of internal energy. The change in internal energy of a system can only be done by transferrin ...
... which cannot change no matter what processes occur” The total energy of the universe cannot change for any process. During a process, energy of system changes and this change is accounted for in terms of internal energy. The change in internal energy of a system can only be done by transferrin ...
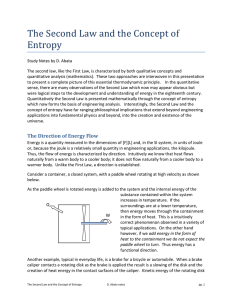
The Second Law and the Concept of Entropy
... separated and are allowed to mix due to molecular motion (e.g. Brownian motion) then the expectation that they will eventually separate is unrealistic and outside of the realm of statistical behavior. Consider two gasses separated by a diaphragm and then the diaphragm suddenly removed. The two gases ...
... separated and are allowed to mix due to molecular motion (e.g. Brownian motion) then the expectation that they will eventually separate is unrealistic and outside of the realm of statistical behavior. Consider two gasses separated by a diaphragm and then the diaphragm suddenly removed. The two gases ...
4. Classical Thermodynamics
... a wall which means that it neither moves, nor allows particles to transfer from one system to the other. However, it is not in any other way special and it will allow heat (to be defined shortly) to be transmitted between systems. If in doubt, think of a thin sheet of metal. • An isolated system, wh ...
... a wall which means that it neither moves, nor allows particles to transfer from one system to the other. However, it is not in any other way special and it will allow heat (to be defined shortly) to be transmitted between systems. If in doubt, think of a thin sheet of metal. • An isolated system, wh ...
unit ii chemical thermodynamics
... Second law Entropy - entropy change for an ideal gas, reversible and irreversible processes ,entropy of phase transitions. Clausius inequality. Free energy and work function: Helmholtz and Gibbs free energy functions Criteria of spontaneity Gibbs-Helmholtz equation Clausius-Clapeyron ...
... Second law Entropy - entropy change for an ideal gas, reversible and irreversible processes ,entropy of phase transitions. Clausius inequality. Free energy and work function: Helmholtz and Gibbs free energy functions Criteria of spontaneity Gibbs-Helmholtz equation Clausius-Clapeyron ...
ME 204 Thermodynamics I
... control surfaces for various work modes or use the first law or conservation of mass)? (determination of properties from the relation between them) vii) what we have done so far in previous steps, how do we proceed to find whatever it is that is desired? Is a trial-anderror solution necessary? (anot ...
... control surfaces for various work modes or use the first law or conservation of mass)? (determination of properties from the relation between them) vii) what we have done so far in previous steps, how do we proceed to find whatever it is that is desired? Is a trial-anderror solution necessary? (anot ...
Chapter 2 Classical Thermodynamics: The Second Law 2.1 Heat
... This is a substantial chapter, containing many important results and many techniques. There are two common technical difficulties for many students at the beginning: proof of theorems and partial derivatives. We will emphasize the understanding and applications of the theorems and we will do many pr ...
... This is a substantial chapter, containing many important results and many techniques. There are two common technical difficulties for many students at the beginning: proof of theorems and partial derivatives. We will emphasize the understanding and applications of the theorems and we will do many pr ...
Class notes
... The concept of free energy comes from the need to simultaneously deal with the enthalpy energy and entropy of a system G = H -TS G = U+PV - TS dG= dU + PdV + VdP -TdS -SdT dH = dU +pdV at const temp and pressure G= H -TS ...
... The concept of free energy comes from the need to simultaneously deal with the enthalpy energy and entropy of a system G = H -TS G = U+PV - TS dG= dU + PdV + VdP -TdS -SdT dH = dU +pdV at const temp and pressure G= H -TS ...
PDF File - Tulane University
... In general, both the entropy, S, and the Volume, V of any phase varies with temperature and pressure. As temperature increases, both S and V tend to increase (things become more disorganized at high temperature, increasing the entropy and molecules vibrate more at high temperature, increasing the vo ...
... In general, both the entropy, S, and the Volume, V of any phase varies with temperature and pressure. As temperature increases, both S and V tend to increase (things become more disorganized at high temperature, increasing the entropy and molecules vibrate more at high temperature, increasing the vo ...
Entropy. Temperature. Chemical Potential
... we view the closed system as composed of coupled subsystems (all macroscopic), then by definition these equilibria are obtained via an exchange of energy (U ), volume (V ) and particles (N ) among the subsystems. Equilibrium corresponds to the maximum value of the total entropy as a function of thes ...
... we view the closed system as composed of coupled subsystems (all macroscopic), then by definition these equilibria are obtained via an exchange of energy (U ), volume (V ) and particles (N ) among the subsystems. Equilibrium corresponds to the maximum value of the total entropy as a function of thes ...
Chapter Two The Thermodynamic Laws
... "Heat cannot of itself pass from a colder to a hotter body." This statement implies an inequality of the heat transfer between a hot body and a cold body. Heat transfer from a hot body to a cold body can spontaneously occur. However, heat transfer in the reversed direction can not happen without the ...
... "Heat cannot of itself pass from a colder to a hotter body." This statement implies an inequality of the heat transfer between a hot body and a cold body. Heat transfer from a hot body to a cold body can spontaneously occur. However, heat transfer in the reversed direction can not happen without the ...
ENGINEERING_THERMODYNAMICS
... The science, which deals the analysis of various machines by quantity, which involves the transfer of energy into useful work, is called thermodynamics. Many energy conversion devices require the transfer of energy into work. Thermodynamics is applied in various thermal equipments like steam turbine ...
... The science, which deals the analysis of various machines by quantity, which involves the transfer of energy into useful work, is called thermodynamics. Many energy conversion devices require the transfer of energy into work. Thermodynamics is applied in various thermal equipments like steam turbine ...
Estimatin of Social Entropy - Research India Publications
... Entropy has been widely applied in sociology, but this was primarily a late twentiethcentury development. Nineteenth- and early twentieth- century social-systems models generally utilized the companion concept of social equilibrium, rather than the concept of social entropy. In thermodynamics, equil ...
... Entropy has been widely applied in sociology, but this was primarily a late twentiethcentury development. Nineteenth- and early twentieth- century social-systems models generally utilized the companion concept of social equilibrium, rather than the concept of social entropy. In thermodynamics, equil ...
Free Energy. Thermodynamic Identities. Phase
... internal energy is of principal importance because it is conserved; more precisely its change is controlled by the first law. A second energy type of quantity is the enthalpy H = U +P V which is the energy needed/yielded upon creation/destruction of the system with volume V in an environment at a fi ...
... internal energy is of principal importance because it is conserved; more precisely its change is controlled by the first law. A second energy type of quantity is the enthalpy H = U +P V which is the energy needed/yielded upon creation/destruction of the system with volume V in an environment at a fi ...
File
... 6. It is impossible by a cyclic process to transfer heat from a low temperature region to a high temperature region without at the same time converting same work into heat. 7. It is impossible to obtain work by cooling a body below the lowest temperature of the system. 8. There exists a function ‘S’ ...
... 6. It is impossible by a cyclic process to transfer heat from a low temperature region to a high temperature region without at the same time converting same work into heat. 7. It is impossible to obtain work by cooling a body below the lowest temperature of the system. 8. There exists a function ‘S’ ...
4.1 Classical Thermodynamics: The First Law
... steady state. Full thermodynamic equilibrium of a system requires thermal equilibrium with any surroundings and also mechanical equilibrium5. Much of the theory developed here requires that the system be in a certain state with certain properties. If a property such as temperature is varying through ...
... steady state. Full thermodynamic equilibrium of a system requires thermal equilibrium with any surroundings and also mechanical equilibrium5. Much of the theory developed here requires that the system be in a certain state with certain properties. If a property such as temperature is varying through ...
Some general information about thermodynamics
... Internal energy (U) is a measure of the total energy (kinetic, chemical, and potential energies) of the particles of the system. Internal energy is related to the temperature of the system. When a system gains internal energy from a process, this change of internal energy is a positive quantity (+ΔU ...
... Internal energy (U) is a measure of the total energy (kinetic, chemical, and potential energies) of the particles of the system. Internal energy is related to the temperature of the system. When a system gains internal energy from a process, this change of internal energy is a positive quantity (+ΔU ...
Review of Chemical Thermodynamics 7
... H — Change in enthalpy between reactants and products; this is the heat given off or absorbed by a reaction at constant pressure. Reactions that absorb heat have positive H’s and those that produce heat have negative H’s. S — Change in entropy between reactants and products; entropy is a statis ...
... H — Change in enthalpy between reactants and products; this is the heat given off or absorbed by a reaction at constant pressure. Reactions that absorb heat have positive H’s and those that produce heat have negative H’s. S — Change in entropy between reactants and products; entropy is a statis ...
Chapter 1 - All Made Easy
... Equilibrium: In thermodynamics, the concept of equilibrium includes not only a balance of forces but also a balance of other influencing factors, such as thermal equilibrium, pressure equilibrium, phase equilibrium, etc. Zeroth law of thermodynamics is law of thermal equilibrium, which states that if ...
... Equilibrium: In thermodynamics, the concept of equilibrium includes not only a balance of forces but also a balance of other influencing factors, such as thermal equilibrium, pressure equilibrium, phase equilibrium, etc. Zeroth law of thermodynamics is law of thermal equilibrium, which states that if ...