1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 31 — LIGHT AND OPTICS (3) In lecture 30
... plane and curved mirrors. In this lecture we will use the law of refraction to describe how images are formed by lenses – curved pieces of glass or transparent plastic. The law of refraction allows us to determine how a light ray is bent when it travels from air into glass or clear plastic. We wil ...
... plane and curved mirrors. In this lecture we will use the law of refraction to describe how images are formed by lenses – curved pieces of glass or transparent plastic. The law of refraction allows us to determine how a light ray is bent when it travels from air into glass or clear plastic. We wil ...
lecture 3 Introduction to Laser
... More Electrons in higher energy level Pumping: Process to achieve population inversion usually through external energy source In general if N2 > N1 then MEDIA IS SAID TO BE ACTIVE ...
... More Electrons in higher energy level Pumping: Process to achieve population inversion usually through external energy source In general if N2 > N1 then MEDIA IS SAID TO BE ACTIVE ...
Skowrons Waugh Choose Ohio First poster
... Luminance: luminous intensity per unit projected area, or “brightness” ...
... Luminance: luminous intensity per unit projected area, or “brightness” ...
Acoustooptic interaction of two light beams in a paratellurite crystal
... The dots in Fig. 4 show the experimental values of double-diffraction efficiency I21 as a function of the ultrasonic frequency. It is seen that diffraction into the second order is observed over a narrow frequency range: ∆f = 0.4 MHz. This circumstance indicates the high selectivity of the employed ...
... The dots in Fig. 4 show the experimental values of double-diffraction efficiency I21 as a function of the ultrasonic frequency. It is seen that diffraction into the second order is observed over a narrow frequency range: ∆f = 0.4 MHz. This circumstance indicates the high selectivity of the employed ...
6.1 Characteristics Because VCSELs emit from the top surface of the
... consists of a cladding layer with a lower refractive index than the fiber core it surrounds. This refractive index difference causes a total internal reflection, which guides the propagating light through the fiber core. There are many types of optical fibers with different size cores and cladding. ...
... consists of a cladding layer with a lower refractive index than the fiber core it surrounds. This refractive index difference causes a total internal reflection, which guides the propagating light through the fiber core. There are many types of optical fibers with different size cores and cladding. ...
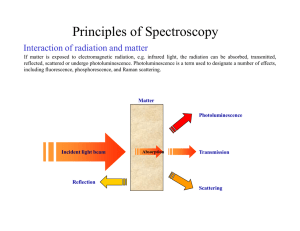
Principles of Spectroscopy
... Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelength. This results in the inte ...
... Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelength. This results in the inte ...
Holography - Princeton University
... of the object beam. Figure 2 illustrates the difference between the two types of holograms. holography, the interference pattern is recorded along the thickness of the emulsion, creating what are known as Bragg diffraction These planes isact similarly to be half-silvered mirrors: some of The unique ...
... of the object beam. Figure 2 illustrates the difference between the two types of holograms. holography, the interference pattern is recorded along the thickness of the emulsion, creating what are known as Bragg diffraction These planes isact similarly to be half-silvered mirrors: some of The unique ...
polarization 3
... For a crossed Nicol position in which the polarizer and analyzer are perpendicular no light comes out of the analyzer. If we place quartz plate cut with faces perpendicular to the optic axis; inbetween polarizer and analyzer, light comes out of the analyzer. Quartz has the property to turn the plane ...
... For a crossed Nicol position in which the polarizer and analyzer are perpendicular no light comes out of the analyzer. If we place quartz plate cut with faces perpendicular to the optic axis; inbetween polarizer and analyzer, light comes out of the analyzer. Quartz has the property to turn the plane ...
L4 INTERFERENCE
... The key to understanding interference is the principle of superposition which says simply that the combined effect of several waves at any place at a particular instant of time is given by the sum (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contri ...
... The key to understanding interference is the principle of superposition which says simply that the combined effect of several waves at any place at a particular instant of time is given by the sum (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contri ...
this PDF file
... extensively studied optical type encoder. In 1990, Ishii et al. [8] proposed laser power back off based on real-time laser intensity variation monitoring and electronic circuit feedback, so as to correct the variation of interference signal resulted from grating process error or environmental fluctu ...
... extensively studied optical type encoder. In 1990, Ishii et al. [8] proposed laser power back off based on real-time laser intensity variation monitoring and electronic circuit feedback, so as to correct the variation of interference signal resulted from grating process error or environmental fluctu ...
LM Ch 8: Bright Field
... 3) Work with the room darkened. The only light you want in your eye is that which comes from the specimen. Everything else is a distraction. 4) If your microscope has a photographic or other reticule it should be in clear focus when the specimen is in focus. The reticule should seem a part of the sp ...
... 3) Work with the room darkened. The only light you want in your eye is that which comes from the specimen. Everything else is a distraction. 4) If your microscope has a photographic or other reticule it should be in clear focus when the specimen is in focus. The reticule should seem a part of the sp ...
TS2
... 560 nm. A PCF was recently reported with close to zero chromatic dispersion over hundreds of nm, making glass almost as free of dispersion as vacuum (26). Hollow-core photonic band gap guidance. Although the first (solid core) photonic band gap fiber was reported in 1998 (27) (Fig. 3, E and F), holl ...
... 560 nm. A PCF was recently reported with close to zero chromatic dispersion over hundreds of nm, making glass almost as free of dispersion as vacuum (26). Hollow-core photonic band gap guidance. Although the first (solid core) photonic band gap fiber was reported in 1998 (27) (Fig. 3, E and F), holl ...
Rotational Raman Spectra of Diatomic Molecules
... A molecule, which lacks a refractive index and a well‐defined size, scatters light elastically according to: y g ...
... A molecule, which lacks a refractive index and a well‐defined size, scatters light elastically according to: y g ...
ZnO/SiO2 microcavity modulator on silicon Abstract - Paul
... Microcavity-based light modulators of the type in Fig. 1(a), fabricated using epitaxiallygrown (Al,Ga)As structures, have intensity ratios R1 between impinging and back-diffracted light beams approaching 50%.3,6 Their fabrication requires piezoelectric layers with a high refractive index contrast to ...
... Microcavity-based light modulators of the type in Fig. 1(a), fabricated using epitaxiallygrown (Al,Ga)As structures, have intensity ratios R1 between impinging and back-diffracted light beams approaching 50%.3,6 Their fabrication requires piezoelectric layers with a high refractive index contrast to ...
Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
... effective wavevector along the interface that can bend transmitted and reflected light into arbitrary directions. In particular, the component dΦ/dy normal to the plane of incidence leads to out-of-plane refraction and reflection. c, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of a metasurface consisti ...
... effective wavevector along the interface that can bend transmitted and reflected light into arbitrary directions. In particular, the component dΦ/dy normal to the plane of incidence leads to out-of-plane refraction and reflection. c, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of a metasurface consisti ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.