nupoc study guide - UC Berkeley NROTC
... 1-2 Reversible adiabatic compression of the working fluid until it reaches the temperature TH of the high-temperature reservoir. 2-3 Reversible isothermal expansion during which heat QH is transferred from the high-temperature reservoir TH to the working fluid. 3-4 Reversible adiabatic expansion of ...
... 1-2 Reversible adiabatic compression of the working fluid until it reaches the temperature TH of the high-temperature reservoir. 2-3 Reversible isothermal expansion during which heat QH is transferred from the high-temperature reservoir TH to the working fluid. 3-4 Reversible adiabatic expansion of ...
Thermodynamics - SeyedAhmad.com
... THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating ...
... THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating ...
Thermal Physics
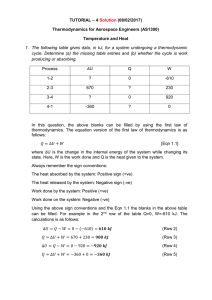
... Temperature and Heat • Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance - a measure of how fast the molecules are moving. Unit: oC or K • Temperature is NOT heat! • Heat is the internal energy that is transferred between bodies in contact. Unit: joules (J) or c ...
... Temperature and Heat • Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance - a measure of how fast the molecules are moving. Unit: oC or K • Temperature is NOT heat! • Heat is the internal energy that is transferred between bodies in contact. Unit: joules (J) or c ...
Physical Chemistry for the Biosciences I (Ch 416 )
... temperature. Since we can only measure temperature we can rewrite: q C.dT C (T2 T1 ) Generally C does not vary much with temperature except near phase transition. T2 and T1 are the final and initial temperatures. So if system cools then the sign of q is negative since it looses heat to surro ...
... temperature. Since we can only measure temperature we can rewrite: q C.dT C (T2 T1 ) Generally C does not vary much with temperature except near phase transition. T2 and T1 are the final and initial temperatures. So if system cools then the sign of q is negative since it looses heat to surro ...
Section 1 – Thermal Energy
... º Think of a snowball melting in your hand. Transfer by Collisions º In your snowball the slower moving particles of your snowball come into contact with the faster moving particles of your hand. º As the particles collide energy is transferred. º One transfers energy to its neighbor and so on. Heat ...
... º Think of a snowball melting in your hand. Transfer by Collisions º In your snowball the slower moving particles of your snowball come into contact with the faster moving particles of your hand. º As the particles collide energy is transferred. º One transfers energy to its neighbor and so on. Heat ...
Energy Transformations
... A calorie is defined as the quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of pure water 1°C. The energy in food is usually expressed in Calories. ...
... A calorie is defined as the quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of pure water 1°C. The energy in food is usually expressed in Calories. ...
heat
... ideal gas at constant volume so that its pressure drops from 2.2 atm to 1.4 atm. Then the gas expands at constant pressure, from a volume of 6.8 L to 9.3 L, where the temperature reaches its original value. Calculate (a) the total work done by the gas in the process, (b) the change in internal energ ...
... ideal gas at constant volume so that its pressure drops from 2.2 atm to 1.4 atm. Then the gas expands at constant pressure, from a volume of 6.8 L to 9.3 L, where the temperature reaches its original value. Calculate (a) the total work done by the gas in the process, (b) the change in internal energ ...
heat
... ideal gas at constant volume so that its pressure drops from 2.2 atm to 1.4 atm. Then the gas expands at constant pressure, from a volume of 6.8 L to 9.3 L, where the temperature reaches its original value. Calculate (a) the total work done by the gas in the process, (b) the change in internal energ ...
... ideal gas at constant volume so that its pressure drops from 2.2 atm to 1.4 atm. Then the gas expands at constant pressure, from a volume of 6.8 L to 9.3 L, where the temperature reaches its original value. Calculate (a) the total work done by the gas in the process, (b) the change in internal energ ...
05Thermal_PhysicsALT
... – Beam wants to expand by ∆L from L0 – Inability to expand causes a compressive strain: ∆L / L0 – and a resulting compressive stress: F/A = Y (∆L / L0 ) (where Y = Elastic or Young’s Modulus; Hooke’s Law) – Since: ∆L = α L0 ∆T, – We have: F/A = Y α ∆T = thermal stress. – Can be compressive or tensil ...
... – Beam wants to expand by ∆L from L0 – Inability to expand causes a compressive strain: ∆L / L0 – and a resulting compressive stress: F/A = Y (∆L / L0 ) (where Y = Elastic or Young’s Modulus; Hooke’s Law) – Since: ∆L = α L0 ∆T, – We have: F/A = Y α ∆T = thermal stress. – Can be compressive or tensil ...
SUMMARY
... evaporated molecules, and (4) reduced atmospheric pressure. Warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air, and the ratio of how much water vapor is in the air to how much could be in the air at that temperature (saturation) is called relative humidity. Thermodynamics is the study of heat and its ...
... evaporated molecules, and (4) reduced atmospheric pressure. Warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air, and the ratio of how much water vapor is in the air to how much could be in the air at that temperature (saturation) is called relative humidity. Thermodynamics is the study of heat and its ...
Q - UCSB Physics
... • Q – W has same value for all processes • Q – W depends only on initial, final state • Q – W is path-independent (these are three equivalent statements) ...
... • Q – W has same value for all processes • Q – W depends only on initial, final state • Q – W is path-independent (these are three equivalent statements) ...
Quiz_MATH.rtf
... D) decreases at high temperature, increases at low E) stays the same 13. (C) Two monatomic ideal gases are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Gas A is composed of molecules with mass m while gas B is composed of molecules with mass 4m. The ratio of the average molecular kinetic energy KA/KB is ...
... D) decreases at high temperature, increases at low E) stays the same 13. (C) Two monatomic ideal gases are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Gas A is composed of molecules with mass m while gas B is composed of molecules with mass 4m. The ratio of the average molecular kinetic energy KA/KB is ...