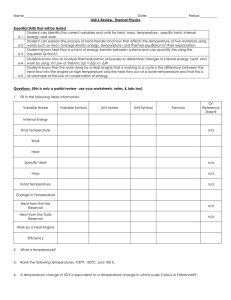
U / ∂V
... height H (where W is the work done on the body); and also when particle with charge q, is moved in a electric field from point at potential Q1, to point a potential Q2, the work done, W, on the charged particle is given as, W=electric energy at point 2(qQ2) - electric energy at point 1(qQ1) It is po ...
... height H (where W is the work done on the body); and also when particle with charge q, is moved in a electric field from point at potential Q1, to point a potential Q2, the work done, W, on the charged particle is given as, W=electric energy at point 2(qQ2) - electric energy at point 1(qQ1) It is po ...
Thermodynamic functions - Phase Transformations Group
... where q is the heat transferred into the system and w is the work done by the system. The historical sign convention is that heat added and work done by the system are positive, whereas heat given off and work done on the system are negative. Equation 1 may be written in differential form as dU = dq ...
... where q is the heat transferred into the system and w is the work done by the system. The historical sign convention is that heat added and work done by the system are positive, whereas heat given off and work done on the system are negative. Equation 1 may be written in differential form as dU = dq ...
Energy - Montana State University Billings
... (pressure goes up; density goes up if T constant) • Inverse relationship between Density and temperature (temperature goes up; density goes down if P constant) • Direct relationship between temperature and pressure (temperature goes up; pressure goes up if density constant) ...
... (pressure goes up; density goes up if T constant) • Inverse relationship between Density and temperature (temperature goes up; density goes down if P constant) • Direct relationship between temperature and pressure (temperature goes up; pressure goes up if density constant) ...
Thermodynamics: Heat and Work
... • If a gas expands rapidly its temperature, pressure, and internal energy decrease. • If this happens in a closed environment, no heat can be transferred to or from the environment, such a process is called an adiabatic process from a Greek word meaning ...
... • If a gas expands rapidly its temperature, pressure, and internal energy decrease. • If this happens in a closed environment, no heat can be transferred to or from the environment, such a process is called an adiabatic process from a Greek word meaning ...
first law of thermodynamics 1.introduction 2.equation form of the first
... is classified as heat energy (Q). Then we can describe the relationship in equation form as follows. ...
... is classified as heat energy (Q). Then we can describe the relationship in equation form as follows. ...
Unit 6 Review
... 15. A gas undergoes an isobaric process where it experiences an increase in temperature while expanding. Is heat being added or removed during this process? Analyze the first law of thermodynamics to help you answer this question. ...
... 15. A gas undergoes an isobaric process where it experiences an increase in temperature while expanding. Is heat being added or removed during this process? Analyze the first law of thermodynamics to help you answer this question. ...
Thermodynamics and the aims of statistical mechanics
... The totality of all possible positions qi for all of the particles i ∈ {1, 2, . . . N } constitutes a 3N -dimensional space called configuration space, Q. Any history of the N particles will be represented by a trajectory γ : R → Q through this space. At any given time t, the trajectory passes throu ...
... The totality of all possible positions qi for all of the particles i ∈ {1, 2, . . . N } constitutes a 3N -dimensional space called configuration space, Q. Any history of the N particles will be represented by a trajectory γ : R → Q through this space. At any given time t, the trajectory passes throu ...
AP Physics – Thermodynamics Wrapup
... a. Identify, given a graph relating the quantity of heat added to a substance and its temperature, the melting point and boiling point and determine the heats of fusion and vaporization and the specific heat of each phase. This requires you to interpret a standard temperature Vs energy graph. Consul ...
... a. Identify, given a graph relating the quantity of heat added to a substance and its temperature, the melting point and boiling point and determine the heats of fusion and vaporization and the specific heat of each phase. This requires you to interpret a standard temperature Vs energy graph. Consul ...
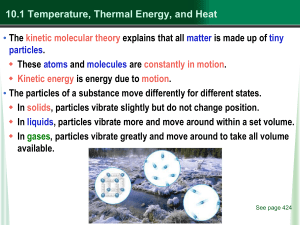
Kinetic Theory
... to a gain or loss of heat to system B, but it’s temperature does not change because it’s so big ...
... to a gain or loss of heat to system B, but it’s temperature does not change because it’s so big ...
Chapter 9: Thermodynamic Processes and Thermochemistry
... because it implies that heat is a substance that is contained in matter. Instead heat (like work) is a way in which energy is exchanged between a system and its surroundings. Ball B gains PE because work was done by ball A on B. Because work is force acting over a distance, work is required to raise ...
... because it implies that heat is a substance that is contained in matter. Instead heat (like work) is a way in which energy is exchanged between a system and its surroundings. Ball B gains PE because work was done by ball A on B. Because work is force acting over a distance, work is required to raise ...
nupoc study guide - UC Berkeley NROTC
... exchange between a surface, Ts, and its surroundings, Tsur, is expressed as qx (Ts4 Ts4ur ) ...
... exchange between a surface, Ts, and its surroundings, Tsur, is expressed as qx (Ts4 Ts4ur ) ...
Lecture 9, February 17, 1997
... • Now if we want the energy lost or gained by either fluid we must let that fluid be the control volume, indicated by the red. ...
... • Now if we want the energy lost or gained by either fluid we must let that fluid be the control volume, indicated by the red. ...
Fluids and Thermo powerpoint
... spontaneously from a colder body to a hotter spontaneously from a colder body to a hotter body. 3: It is not possible to reach a temperature of absolute zero (about -273 C). Since temperature is a measure of molecular ...
... spontaneously from a colder body to a hotter spontaneously from a colder body to a hotter body. 3: It is not possible to reach a temperature of absolute zero (about -273 C). Since temperature is a measure of molecular ...
Lecture - Rutgers Physics
... U, P, T, and V are the state functions, Q and W are not. Specifying an initial and final states of a system does not fix the values of Q and W, we need to know the whole process (the intermediate states). Analogy: in classical mechanics, if a force is not conservative (e.g., friction), the initial a ...
... U, P, T, and V are the state functions, Q and W are not. Specifying an initial and final states of a system does not fix the values of Q and W, we need to know the whole process (the intermediate states). Analogy: in classical mechanics, if a force is not conservative (e.g., friction), the initial a ...