Physical Process
... Scientists cannot predict when volcanoes will erupt. People live near volcanoes because volcanic ash is extremely fertile and good for farming. ...
... Scientists cannot predict when volcanoes will erupt. People live near volcanoes because volcanic ash is extremely fertile and good for farming. ...
Physical and Ecological Processes
... Scientists cannot predict when volcanoes will erupt. People live near volcanoes because volcanic ash is extremely fertile and good for farming. ...
... Scientists cannot predict when volcanoes will erupt. People live near volcanoes because volcanic ash is extremely fertile and good for farming. ...
When Earth Shakes
... or volcanic eruption. In Alaska's Valdez Inlet, a landslide triggered by the earthquake produced a tsunami 67 meters (220 ft) high— taller than a 20-story building. ...
... or volcanic eruption. In Alaska's Valdez Inlet, a landslide triggered by the earthquake produced a tsunami 67 meters (220 ft) high— taller than a 20-story building. ...
Rapid Changes
... the same thing happens with a large area of rock or soil at once. A landslide is the fast movement of soil and rocks down a slope. Landslides can be very dangerous. Landslides occur in the ocean, along the coast, and on shore. Many factors determine how stable a slope is. Some landslides occur natur ...
... the same thing happens with a large area of rock or soil at once. A landslide is the fast movement of soil and rocks down a slope. Landslides can be very dangerous. Landslides occur in the ocean, along the coast, and on shore. Many factors determine how stable a slope is. Some landslides occur natur ...
Unit 13: Earthquakes A. Earthquakes 1. Earthquake
... a. the greatest damage to structures is from landslides, or the sinking of the ground triggered by the vibrations 3. Fire a. start when gas and electrical lines were cut b. water lines may also break so that fires can’t be stopped ...
... a. the greatest damage to structures is from landslides, or the sinking of the ground triggered by the vibrations 3. Fire a. start when gas and electrical lines were cut b. water lines may also break so that fires can’t be stopped ...
File
... – Large number of scientific centres to be set up – Warning system must be strong – Building structures should be changed – Prevent changes in environmental conditions ...
... – Large number of scientific centres to be set up – Warning system must be strong – Building structures should be changed – Prevent changes in environmental conditions ...
PRESENTATION on the topic of natural disasters
... intensity of warming fire, it is the most important characteristic. The zone, which runs a chemical reaction and heated flammable substance called fire front. Layered heating process, oxidation and combustion takes so long until it will burn the entire volume of combustible material. The space in wh ...
... intensity of warming fire, it is the most important characteristic. The zone, which runs a chemical reaction and heated flammable substance called fire front. Layered heating process, oxidation and combustion takes so long until it will burn the entire volume of combustible material. The space in wh ...
Earthquakes
... What causes Earthquakes? Movement along faults: occurs when the energy exceeds the friction holding the sides of the fault together and is suddenly released. Movement of magma (volcanic) ...
... What causes Earthquakes? Movement along faults: occurs when the energy exceeds the friction holding the sides of the fault together and is suddenly released. Movement of magma (volcanic) ...
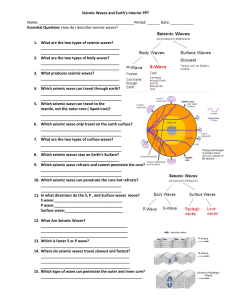
Seismic Waves and Earth`s Interior PPT Name
... The energy of earthquakes moves away from the focus in all directions. While some of the waves occur on the surface, other waves of energy move through the planet at very deep levels. The large earthquake that triggered the tsunami of 2004 sent waves of energy through much of the planet. Many earthq ...
... The energy of earthquakes moves away from the focus in all directions. While some of the waves occur on the surface, other waves of energy move through the planet at very deep levels. The large earthquake that triggered the tsunami of 2004 sent waves of energy through much of the planet. Many earthq ...
exchange of seismic/tsunami information between asean member
... System was identified to be an important means through which seismic/tsunami information could be efficiently exchanged in real-time within ASEAN member states. ...
... System was identified to be an important means through which seismic/tsunami information could be efficiently exchanged in real-time within ASEAN member states. ...
Earthquake Epicenters Plate Tectonics
... vibrate parallel to the direction of movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
... vibrate parallel to the direction of movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
Click here for the "Dynamic Earth Vocabulary"
... particles in the ground to move in a push-pull motion similar to a coiled spring. Secondary Wave: Known as a “s-wave”, is a type of seismic wave that causes particles to move in an up-down motion. Rolling Wave: Known as a “r-wave”, is a type of surface seismic wave that on the surface of the Earth m ...
... particles in the ground to move in a push-pull motion similar to a coiled spring. Secondary Wave: Known as a “s-wave”, is a type of seismic wave that causes particles to move in an up-down motion. Rolling Wave: Known as a “r-wave”, is a type of surface seismic wave that on the surface of the Earth m ...
Stresses, Faults, Folds, and Earthquakes
... and S wave, traveling along the land surface like water waves. There are several types of surface waves; the two most important are Raleigh waves (R) and Love waves (L) , named for the scientists who first identified them. A. Raleigh Waves-The R waves move continuously forward, although the individu ...
... and S wave, traveling along the land surface like water waves. There are several types of surface waves; the two most important are Raleigh waves (R) and Love waves (L) , named for the scientists who first identified them. A. Raleigh Waves-The R waves move continuously forward, although the individu ...
The 2009 Samoa Earthquake and Tsunami
... tension that is build up along geologic faults or by volcanic activity. A tsunami is defined as a very large wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption. In addition both of these terms have a very similar definition in which they share some common causes. Both of these definitions ...
... tension that is build up along geologic faults or by volcanic activity. A tsunami is defined as a very large wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption. In addition both of these terms have a very similar definition in which they share some common causes. Both of these definitions ...
Earthquakes
... § Describe the three types of stress that can cause an earthquake. § Connect the three types of stress to the different types of faults. § Define epicenter and focus. § Describe the three types of waves generated by an earthquake. § Explain how information about earthquakes is collected and used to ...
... § Describe the three types of stress that can cause an earthquake. § Connect the three types of stress to the different types of faults. § Define epicenter and focus. § Describe the three types of waves generated by an earthquake. § Explain how information about earthquakes is collected and used to ...
Study Sheet for ESS 202 Plate tectonics Supercontinents and
... relation to earthquakes: 1) both occur near plate boundaries, most explosive volcanoes and largest earthquakes both associated with convergent boundaries (subduction), 2) volcanic eruptions involve deforming crust and lead to earthquakes, 3) earthquakes could reduce stress in a region and trigger im ...
... relation to earthquakes: 1) both occur near plate boundaries, most explosive volcanoes and largest earthquakes both associated with convergent boundaries (subduction), 2) volcanic eruptions involve deforming crust and lead to earthquakes, 3) earthquakes could reduce stress in a region and trigger im ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary Review
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary Review
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
Document
... Earthquakes: Vibrations (seismic waves) within Earth materials are produced by the rapid release of energy Earth’s crust is in constant motion because of tectonic forces Earth’s crust can store elastic energy When forces exceed the elastic limits and structural strength of the rocks, the rocks ...
... Earthquakes: Vibrations (seismic waves) within Earth materials are produced by the rapid release of energy Earth’s crust is in constant motion because of tectonic forces Earth’s crust can store elastic energy When forces exceed the elastic limits and structural strength of the rocks, the rocks ...
Document
... Earthquakes: Vibrations (seismic waves) within Earth materials are produced by the rapid release of energy Earth’s crust is in constant motion because of tectonic forces Earth’s crust can store elastic energy When forces exceed the elastic limits and structural strength of the rocks, the rocks ...
... Earthquakes: Vibrations (seismic waves) within Earth materials are produced by the rapid release of energy Earth’s crust is in constant motion because of tectonic forces Earth’s crust can store elastic energy When forces exceed the elastic limits and structural strength of the rocks, the rocks ...
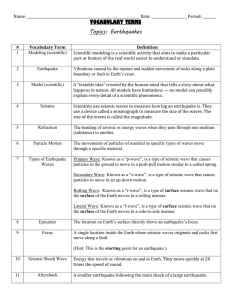
Chapter 8 Vocabulary - Effingham County Schools
... Earthquake Vocabulary 1. fault – a break in the Earth’s crust along which blocks of the crust slide relative to one another. 2. deformation – the change in the shape of rock in response to stress. 3. elastic rebound – the sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its original shape. 4. seismolog ...
... Earthquake Vocabulary 1. fault – a break in the Earth’s crust along which blocks of the crust slide relative to one another. 2. deformation – the change in the shape of rock in response to stress. 3. elastic rebound – the sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its original shape. 4. seismolog ...
Tsunami

A tsunami (plural: tsunamis or tsunami; from Japanese: 津波, lit. ""harbor wave"";English pronunciation: /tsuːˈnɑːmi/), also known as a seismic sea wave, is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations of underwater nuclear devices), landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. In being generated by the displacement of water, a tsunami contrasts both with a normal ocean wave generated by wind and with tides, which are generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on bodies of water.Tsunami waves do not resemble normal sea waves, because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide, and for this reason they are often referred to as tidal waves, although this usage is not favored by the scientific community because tsunamis are not tidal in nature. Tsunamis generally consist of a series of waves with periods ranging from minutes to hours, arriving in a so-called ""wave train"". Wave heights of tens of meters can be generated by large events. Although the impact of tsunamis is limited to coastal areas, their destructive power can be enormous and they can affect entire ocean basins; the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was among the deadliest natural disasters in human history with at least 230,000 people killed or missing in 14 countries bordering the Indian Ocean.The Greek historian Thucydides suggested in his late-5th century BC History of the Peloponnesian War, that tsunamis were related to submarine earthquakes, but the understanding of a tsunami's nature remained slim until the 20th century and much remains unknown. Major areas of current research include trying to determine why some large earthquakes do not generate tsunamis while other smaller ones do; trying to accurately forecast the passage of tsunamis across the oceans; and also to forecast how tsunami waves would interact with specific shorelines.