P and S waves activity - Teacher instructions
... Finally ensure learners know that seismic waves go from crust to core, but not core to crust and that S waves do not reach other side of Earth from where earthquake originated because they cannot pass through the sea. This will be important information to complete Tasks 1 and 2. Some of this subjec ...
... Finally ensure learners know that seismic waves go from crust to core, but not core to crust and that S waves do not reach other side of Earth from where earthquake originated because they cannot pass through the sea. This will be important information to complete Tasks 1 and 2. Some of this subjec ...
Geosphere - Written - Geological Society of India
... More warm climate comparing to the Late Pleistocene climate Colder climate comparing to the recent climate Tectonic uplifting Remnants to high tide event ...
... More warm climate comparing to the Late Pleistocene climate Colder climate comparing to the recent climate Tectonic uplifting Remnants to high tide event ...
Slide 1
... • A simple pendulum approximates SHM if its amplitude is not large. Its period in that case is: ...
... • A simple pendulum approximates SHM if its amplitude is not large. Its period in that case is: ...
PHYS 342: Modern Physics
... • For now, we will concentrate on mechanical waves traveling through a material medium – For example: water, sound, seismic waves – The wave is the propagation of the disturbance: they do not carry the medium with it ...
... • For now, we will concentrate on mechanical waves traveling through a material medium – For example: water, sound, seismic waves – The wave is the propagation of the disturbance: they do not carry the medium with it ...
Government takes continued action on earthquake preparedness
... levers to help communities and families prepare for and recover from a disaster. “The work to improve our emergency preparedness continues through infrastructure funding, improvements to alerting systems, hiring new staff, and creating awareness materials to reach British Columbians where they live. ...
... levers to help communities and families prepare for and recover from a disaster. “The work to improve our emergency preparedness continues through infrastructure funding, improvements to alerting systems, hiring new staff, and creating awareness materials to reach British Columbians where they live. ...
Thursday, 15 April - Southern California Earthquake Center
... Earthquakes and Triggered Slip Events on the Lenwood Fault at Fry Mountain Playa: Is the Northern Lenwood Due for a Shake-Up? (04-136) Khatib, F., Lebeon, M., Rockwell, T., Lindvall, S., Cadena, A., Verdugo, D., Rubin, C., Horner, J., Seitz, G., and Bowman-Weaver, C. ...
... Earthquakes and Triggered Slip Events on the Lenwood Fault at Fry Mountain Playa: Is the Northern Lenwood Due for a Shake-Up? (04-136) Khatib, F., Lebeon, M., Rockwell, T., Lindvall, S., Cadena, A., Verdugo, D., Rubin, C., Horner, J., Seitz, G., and Bowman-Weaver, C. ...
What is a wave
... A standing wave is produced when two waves with the same amplitude, wavelength and frequency travel in opposite directions and interfere (fig. 4.7, pg. 389). Node – point on a standing wave that always undergoes complete destructive interference and therefore is stationary. Antinode – a point in ...
... A standing wave is produced when two waves with the same amplitude, wavelength and frequency travel in opposite directions and interfere (fig. 4.7, pg. 389). Node – point on a standing wave that always undergoes complete destructive interference and therefore is stationary. Antinode – a point in ...
Slide 1 - Mr Lundy`s Room
... • A simple pendulum approximates SHM if its amplitude is not large. Its period in that case is: ...
... • A simple pendulum approximates SHM if its amplitude is not large. Its period in that case is: ...
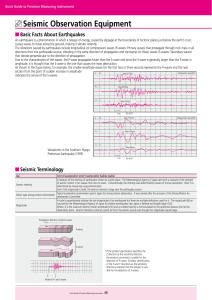
Seismic Observation Equipment
... A measure of the intensity of earthquake motion at a given place. The Meteorological Agency of Japan sets forth a measure of the strength of seismic motion in ten classes from zero to seven. Conventionally, the intensity was determined by means of human perception. Now, it is Seismic intensity det ...
... A measure of the intensity of earthquake motion at a given place. The Meteorological Agency of Japan sets forth a measure of the strength of seismic motion in ten classes from zero to seven. Conventionally, the intensity was determined by means of human perception. Now, it is Seismic intensity det ...
earthquakes
... 2. The point of first break or movement along a fault is called the earthquake’s focus (or hypocenter). The point on the earth’s surface directly above the focus is called the epicenter. 3. There are several types of earthquake, or seismic, waves: (a) P (primary) waves are compressional waves that c ...
... 2. The point of first break or movement along a fault is called the earthquake’s focus (or hypocenter). The point on the earth’s surface directly above the focus is called the epicenter. 3. There are several types of earthquake, or seismic, waves: (a) P (primary) waves are compressional waves that c ...
Term Project Exercise 1
... these are stated in the reading “Shaky Preparation” (available from ANGEL). For example, it is common belief that most earthquake activity occurs along the boundaries between the tectonic plates. To see evidences, we can perform an attribute query of earthquake magnitude to show that large earthquak ...
... these are stated in the reading “Shaky Preparation” (available from ANGEL). For example, it is common belief that most earthquake activity occurs along the boundaries between the tectonic plates. To see evidences, we can perform an attribute query of earthquake magnitude to show that large earthquak ...
Chapter 9
... Precursor Studies – Strain Accumulation • Scientists measure how much strain accumulates along a fault segment each year, how much time has passed since the last earthquake there, and how much strain was released in the last earthquake. • This information is then used to calculate the time requ ...
... Precursor Studies – Strain Accumulation • Scientists measure how much strain accumulates along a fault segment each year, how much time has passed since the last earthquake there, and how much strain was released in the last earthquake. • This information is then used to calculate the time requ ...
SHM and Waves
... • A simple pendulum approximates SHM if its amplitude is not large. Its period in that case is: ...
... • A simple pendulum approximates SHM if its amplitude is not large. Its period in that case is: ...
Chapter 5 Earthquakes - Sandpoint Middle
... • Drop, cover, and hold to protect yourself indoors during an earthquake. If possible, crouch under a desk or table, or against an interior wall or bathroom plumbing that extends floor to ceiling. • Avoid windows, mirrors, wall hangings, and furniture that might topple. • After a major earthquake, g ...
... • Drop, cover, and hold to protect yourself indoors during an earthquake. If possible, crouch under a desk or table, or against an interior wall or bathroom plumbing that extends floor to ceiling. • Avoid windows, mirrors, wall hangings, and furniture that might topple. • After a major earthquake, g ...
Chapter 5 Assignment GEarthOL
... Your assignment is to fill out the evaluation rubric provided here by identifying factors that would influence the risk of damage from a future earthquake. The location that scores the highest on your scoring rubric will receive additional county funds to protect key structures from earthquake damag ...
... Your assignment is to fill out the evaluation rubric provided here by identifying factors that would influence the risk of damage from a future earthquake. The location that scores the highest on your scoring rubric will receive additional county funds to protect key structures from earthquake damag ...
An____________is a movement of Earth’s lithosphere shift, releasing stored energy.
... that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere suddenly shift, releasing stored energy. The energy released during an earthquake is carried by vibrations called ________________ waves. Many people are killed or injured when coastal areas are hit by a tsunami. • A ___________ is a large sea wave generated ...
... that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere suddenly shift, releasing stored energy. The energy released during an earthquake is carried by vibrations called ________________ waves. Many people are killed or injured when coastal areas are hit by a tsunami. • A ___________ is a large sea wave generated ...
Presentation
... on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cause the shaking that we feel. ...
... on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cause the shaking that we feel. ...
Word format
... B. doesn’t change for an earthquake, no matter how far away it was C. is measured using the moment magnitude scale D. will be the same for all earthquakes having an identical magnitude E. none of the above ...
... B. doesn’t change for an earthquake, no matter how far away it was C. is measured using the moment magnitude scale D. will be the same for all earthquakes having an identical magnitude E. none of the above ...
Geography Revision - Geography at InterHigh
... what is happening, and why it has its name. The 4 examples we talked about were the Mid-Atlantic ridge, the Himalayas, the San Andreas Fault and the Andes. Which of these places go with each types of plate margins? What can happen along any of these faults? (not pleasant!) ...
... what is happening, and why it has its name. The 4 examples we talked about were the Mid-Atlantic ridge, the Himalayas, the San Andreas Fault and the Andes. Which of these places go with each types of plate margins? What can happen along any of these faults? (not pleasant!) ...
Unit 4 Lesson 8
... • The movement of tectonic plates breaks Earth’s crust into a series of faults, which are breaks in Earth’s crust along which blocks of rocks move. • The release of energy that accompanies the movement of rock along a fault is what causes an earthquake. ...
... • The movement of tectonic plates breaks Earth’s crust into a series of faults, which are breaks in Earth’s crust along which blocks of rocks move. • The release of energy that accompanies the movement of rock along a fault is what causes an earthquake. ...
Locating the Epicenter
... Explain that scientists consider three important factors when determining the likelihood of an earthquake to generate a tsunami. First, they determine whether the earthquake had a magnitude greater than 7.0. Magnitude describes the amount of shaking and energy released during a quake. On average, on ...
... Explain that scientists consider three important factors when determining the likelihood of an earthquake to generate a tsunami. First, they determine whether the earthquake had a magnitude greater than 7.0. Magnitude describes the amount of shaking and energy released during a quake. On average, on ...
News
... and the Surfrider Foundation, a non-profit organization with over 50,000 members worldwide dedicated to the protection and enjoyment of our world’s oceans, waves and beaches. He spoke on January 12, 2012, at the Winter Conference of the Association of Pacific Ports, a trade and information associati ...
... and the Surfrider Foundation, a non-profit organization with over 50,000 members worldwide dedicated to the protection and enjoyment of our world’s oceans, waves and beaches. He spoke on January 12, 2012, at the Winter Conference of the Association of Pacific Ports, a trade and information associati ...
P and S waves
... We’d like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you. Whether you already offer OCR quali ...
... We’d like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you. Whether you already offer OCR quali ...
Magnitude 6.2, CENTRAL ITALY Wednesday, 24 th August, 2016 at
... region. As many of the earthquakes are in the crust, and the area is highly populated many of these earthquakes have a human impact. Notably the L'Aquila earthquake in April 2009 which killed at leastInterferogra ...
... region. As many of the earthquakes are in the crust, and the area is highly populated many of these earthquakes have a human impact. Notably the L'Aquila earthquake in April 2009 which killed at leastInterferogra ...
About Earthquake Early Warning
... There are two main types of seismic waves: P-waves, or initial tremors, and Swave, or main tremors. P-waves are the first to travel outward. They are followed by S-waves, which cause stronger tremors. Most earthquake-induced damage results from these Swaves. --- Traveling speed of seismic waves --P- ...
... There are two main types of seismic waves: P-waves, or initial tremors, and Swave, or main tremors. P-waves are the first to travel outward. They are followed by S-waves, which cause stronger tremors. Most earthquake-induced damage results from these Swaves. --- Traveling speed of seismic waves --P- ...
Tsunami

A tsunami (plural: tsunamis or tsunami; from Japanese: 津波, lit. ""harbor wave"";English pronunciation: /tsuːˈnɑːmi/), also known as a seismic sea wave, is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations of underwater nuclear devices), landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. In being generated by the displacement of water, a tsunami contrasts both with a normal ocean wave generated by wind and with tides, which are generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on bodies of water.Tsunami waves do not resemble normal sea waves, because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide, and for this reason they are often referred to as tidal waves, although this usage is not favored by the scientific community because tsunamis are not tidal in nature. Tsunamis generally consist of a series of waves with periods ranging from minutes to hours, arriving in a so-called ""wave train"". Wave heights of tens of meters can be generated by large events. Although the impact of tsunamis is limited to coastal areas, their destructive power can be enormous and they can affect entire ocean basins; the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was among the deadliest natural disasters in human history with at least 230,000 people killed or missing in 14 countries bordering the Indian Ocean.The Greek historian Thucydides suggested in his late-5th century BC History of the Peloponnesian War, that tsunamis were related to submarine earthquakes, but the understanding of a tsunami's nature remained slim until the 20th century and much remains unknown. Major areas of current research include trying to determine why some large earthquakes do not generate tsunamis while other smaller ones do; trying to accurately forecast the passage of tsunamis across the oceans; and also to forecast how tsunami waves would interact with specific shorelines.