Handout on Revenge
... If an operator O satisfies the above axioms, so does the operator OO, OOO, etc. This raises two natural questions: 1. What is the intended interpretation of ∆? 2. Can we say something about the conceptual role of ∆ to narrow its possible interpretations down? I address question 1. in other work, in ...
... If an operator O satisfies the above axioms, so does the operator OO, OOO, etc. This raises two natural questions: 1. What is the intended interpretation of ∆? 2. Can we say something about the conceptual role of ∆ to narrow its possible interpretations down? I address question 1. in other work, in ...
PDF
... 1. Continue defining and exploring first-order theory of simple arithmetic, iQ. i Q is a first-order finite axiomatization of a “number-like” domain. Even though i Q is extremely weak as you see from Problem Set 3 from Boolos & Jeffrey, we can, nevertheless, show in constructive type theory, either ...
... 1. Continue defining and exploring first-order theory of simple arithmetic, iQ. i Q is a first-order finite axiomatization of a “number-like” domain. Even though i Q is extremely weak as you see from Problem Set 3 from Boolos & Jeffrey, we can, nevertheless, show in constructive type theory, either ...
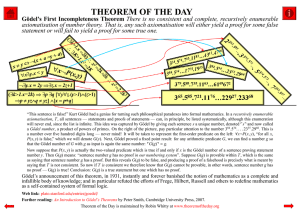
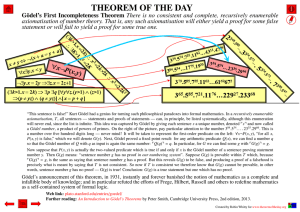
Gödel`s First Incompleteness Theorem
... Gödel’s announcement of this theorem, in 1931, instantly and forever banished the notion of mathematics as a complete and infallible body of knowledge; and in particular refuted the efforts of Frege, Hilbert, Russell and others to redefine mathematics as a self-contained system of formal logic. ...
... Gödel’s announcement of this theorem, in 1931, instantly and forever banished the notion of mathematics as a complete and infallible body of knowledge; and in particular refuted the efforts of Frege, Hilbert, Russell and others to redefine mathematics as a self-contained system of formal logic. ...
Lecture_ai_3 - WordPress.com
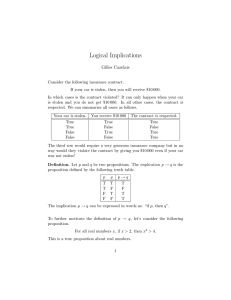
... • Interpretation of implication is T if the previous statement has T value • Interpretation of Biconditionalis T only when symbols on the both sides are either T or F ,otherwise F ...
... • Interpretation of implication is T if the previous statement has T value • Interpretation of Biconditionalis T only when symbols on the both sides are either T or F ,otherwise F ...
Section 5.4: Russell`s Paradox
... are many examples of sentences which can at first seem paradoxical (and hence not statements) but are indeed statements (since they are either true or false), and likewise, there can be other statements which are paradoxes like Russell’s paradox. To illustrate, we consider some examples. Example 2.1 ...
... are many examples of sentences which can at first seem paradoxical (and hence not statements) but are indeed statements (since they are either true or false), and likewise, there can be other statements which are paradoxes like Russell’s paradox. To illustrate, we consider some examples. Example 2.1 ...
Math 2283 - Introduction to Logic
... If two sentences are accepted as true, of which one has the form of an implication while the other is the antecedent of this implication, then that sentence may also be recognized as true, which forms the consequent of the implication. (We detach thus, so to speak, the antecedent from the whole impl ...
... If two sentences are accepted as true, of which one has the form of an implication while the other is the antecedent of this implication, then that sentence may also be recognized as true, which forms the consequent of the implication. (We detach thus, so to speak, the antecedent from the whole impl ...
PHIL012 Class Notes
... • “a=b” means that “a” and “b” are names that refer to the same objects, which can denote numbers or sets. • “a=b” also means that whatever claims are made of a must also be true of b (and vice versa) if “a=b” is true. ...
... • “a=b” means that “a” and “b” are names that refer to the same objects, which can denote numbers or sets. • “a=b” also means that whatever claims are made of a must also be true of b (and vice versa) if “a=b” is true. ...